What is the main difference between DNA and RNA?
Deoxyribose vs. Ribose
What element is the backbone of all organic molecules?
Carbon
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides (simple sugars like glucose).
What are the building blocks (monomers) of proteins?
Amino Acids
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
DNA & RNA
What are the 4 nucleotides of DNA?
adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G)
What kind of bond forms when electrons are transferred from one atom to another?
Ionic bond.
An athlete is preparing for a marathon and wants to consume a meal that will provide a sustained, steady release of energy over several hours. Which food would be the best choice?
- A) A sugary sports drink
- B) A candy bar
- C) A large bowl of pasta with whole-wheat noodles
- D) A small piece of fruit
C. A large bowl of pasta with Whole-wheat Noodles
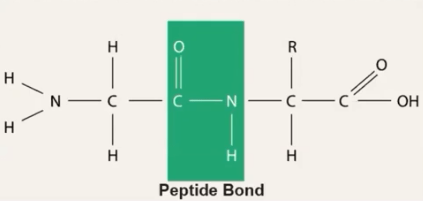
What type of bond forms between amino acids in a protein chain?
Peptide bond.
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What makes water a polar molecule?
Unequal sharing of electrons
Which statement best explains why carbon is central to the structure of all organic molecules?
Carbon can form up to four covalent bonds, allowing a variety of stable, complex molecules such as chains, rings, and branches.
During a 100-meter sprint, a runner needs a quick burst of energy to power their muscles immediately. Which type of carbohydrate is best suited for this situation?
- A) Fiber
- B) Glycogen
- C) Starch
- D) Glucose
D. Glucose
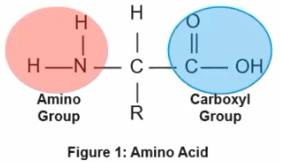
What 2 functional groups make up an Amino Acid?
Amino group and Carboxyl Group
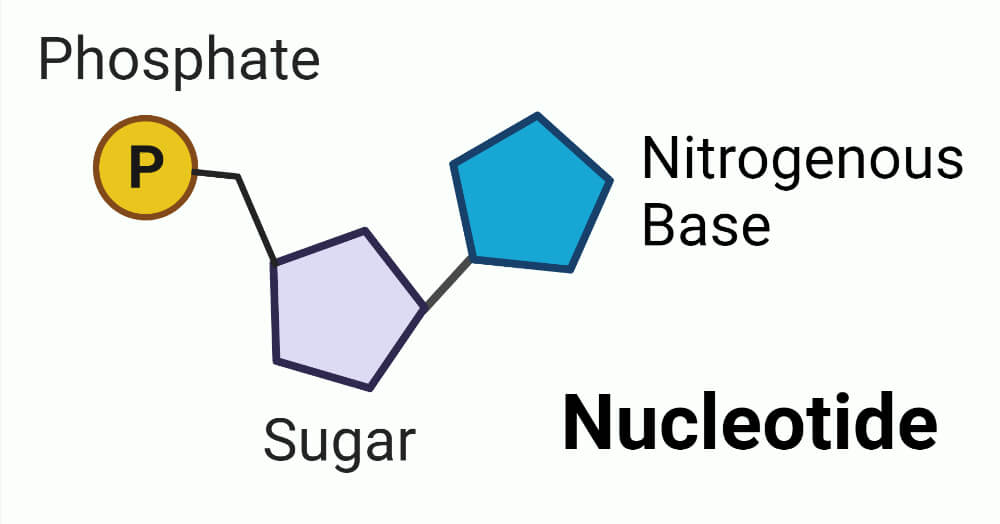
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
What type of attraction allows water molecules to stick to other polar molecules?
Adhesion
Why is nitrogen essential for life?
It’s found in amino acids (proteins) and nucleotides (DNA/RNA).
If the body needs to store energy for a very long period, such as during a time of food scarcity, which macromolecule is the most efficient and densest form of storage?
- A) Glycogen
- B) Complex carbohydrates
- C) Lipids
- D) Protein
C. Lipids
What determines the shape and function of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids (primary structure).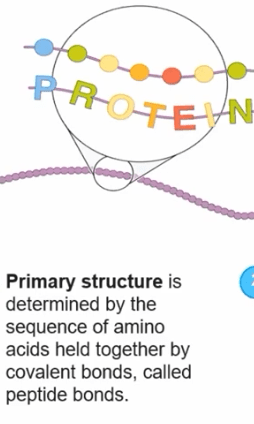
What do Acids and Bases do to H+ concentration?
Acids: Increase H+ concentration
Bases: Decrease H+ concentration by releasing -OH
Fill in the missing blacks:
_____+_____ = Ionic Bond
_____+_____ = Covalent Bond
Ionic = Metal + Nonmetal
Covalent = Nonmetal + Nonmetal
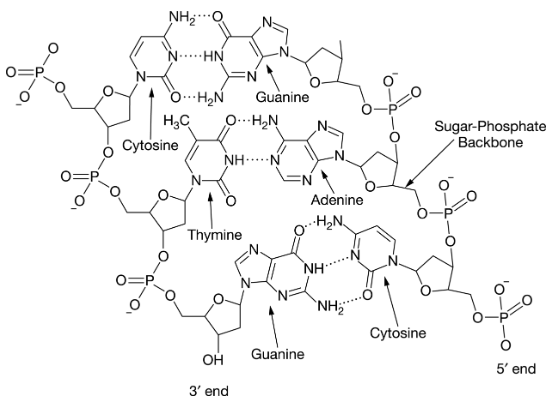 Which of the following statements is true about the molecule above?
Which of the following statements is true about the molecule above?
- A) It is RNA because of the direction of the two strands
- B) It is RNA because of the number of different nucleotides present
- C) It is DNA because of the nature of the hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine
- D) It is DNA because of the nucleotides present
D. It is DNA because of the nucleotides present
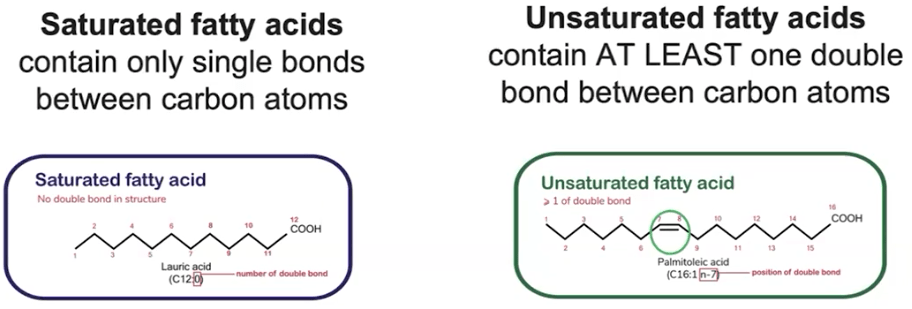
How do saturated and unsaturated fatty acids differ?
Saturated = no double bonds, solid at room temp; Unsaturated = one or more double bonds, liquid at room temp.
Which level of protein structure involves interactions between multiple polypeptide chains?
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
D
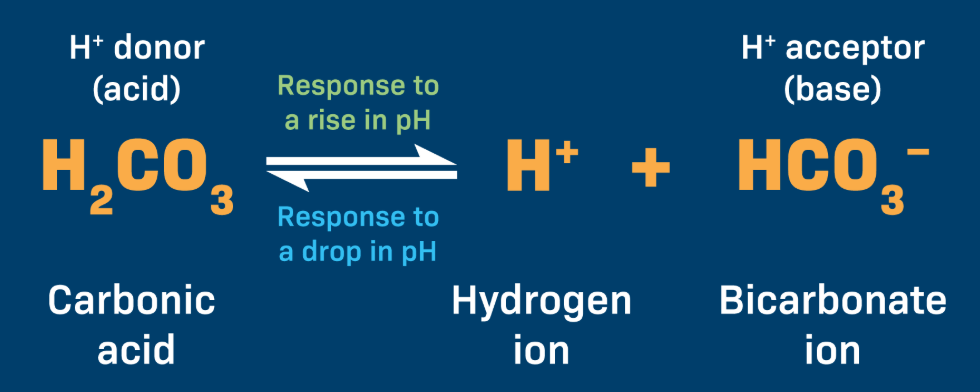
Your blood is usually pH ~7.4. If you drink a soda (acidic), what should your buffer system do?
- Accept Hydrogen Ions
- Donate Hydrogen Ions
Accept Hydrogen Ions
When a solution becomes too acidic—and therefore has a lower pH than is optimal—the buffer system accepts hydrogen ions to reduce this acidity. Inversely, when the solution becomes too basic—and therefore has a higher pH than is optimal—the buffer system donates hydrogen ions to increase the acidity.