This molecule is considered the energy currency of cells.
What is ATP?
This is where glycolysis takes place.
BONUS: explain why this is significant.
What is the cytoplasm?
BONUS: This implies that glycolysis likely evolved first because all cell types can perform glycolysis.
This is the chemical formula for Glucose
What is C6H12O6
This is the monomer of enzymes
What are amino acids?
This relationship is why small cells are more efficient at diffusion
What is high surface area to volume ratio (SA/V) ?
This is the molecule that actually creates ATP through a flow of protons down their concentration gradient.
What is ATP synthase
This is the location of the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle)
What is the mitochondrial matrix
This is the location of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis
What is the Thylakoid
HOW do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
By lowering activation energy.
This molecule is responsible for supplying the carbon needed to make carbohydrates during the calvin cycle
What is carbon dioxide (CO2) ?
Ions like H+ cannot diffuse through the cell membrane because of this chemical property of this structural component.
What are the hydrophobic (or nonpolar) tails?
This molecule is consider the final electron acceptor during the final stage of cellular respiration and generates this byproduct.
What is Oxygen (When Oxygen accepts the electrons, it also binds with some of the H+ ions creating H2O as a biproduct).
This system provides the necessary energy to form a proton gradient during both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
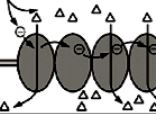
What is the electron transport chain?
Describe what it means for an enzyme to be at optimal temperature or pH
Optimal Temperature or pH refers to the environmental conditions where an enzyme is functioning at its highest rate of reaction.
What is an endotherm and how do they maintain their body temperature?
An animal that is dependent on or capable of the internal generation of heat (AKA warm blooded). And it generates heat as a biproduct of chemical reactions like cellular respiration.
Name the term for respiration NOT requiring oxygen AND the two biproducts that can be formed as a result.
What is Anerobic respiration (or fermentation) and what are alcohol and lactic acid.
Where does the energy come from to move H+ ions against their concentration gradient?
What is the movement of donated electrons from NADH and FADH2 down the ETC.
This is responsible for the energy used to make ATP during the light dependent reactions
What is a proton gradient OR What is a high concentration of H+ Ions moving through ATP synthase
Explain what does it mean for an enzyme to denature (Be as specific as possible and use as many details as you can). What happens to the rate of reaction?
When an enzyme denatures, it loses its shape. This means the substrate can no longer bind to the active site and little to no product will be formed because the rate of reaction slows down or stops entirely.
This molecule provides oxygen as a bi-product when split during the light reaction of photosynthesis
What is water (H2O) ?
This is the role of pigments in plants and HOW do they accomplish this.
What is absorbing light energy by exciting electrons that can be used in the ETC (i.e. moving them out to higher energy level orbitals).
OR - Using light energy to split a molecule of H2O into H+ ions, Oxygen, and free electrons.
Explain the process of cellular respiration including each step, location, and transition molecules starting with Glucose and ending with ATP.
Glucose is broken down in the cytoplasm during glycolysis into pyruvate and generates some ATP and NADH. These molecules then travel to the mitochondrial matrix. Along the way, pyruvate becomes Acetyl CoA. In the mitochondrial matrix, the krebs cycle generates ATP, FADH2, NADH, and the biproduct CO2. The ATP and electron carries go to the Inner Mitochondrial membrane. FADH2 and NADH are oxidized donating their electrons to the ETC and H+ ions. H+ ions are moved across the membrane against their concentration gradient using the energy from the ETC. The H+ ions then move down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase creating ATP. The remaining electrons are accepted by O2 and join with some H+ ions to generate the biproduct water.
Describe why plants gain mass when performing photosynthesis?
Plants are taking in more atoms (H2O and CO2) then they are releasing (O2) and storing them in Glucose molecules
Explain the relationship between substrate concentration and enzyme activity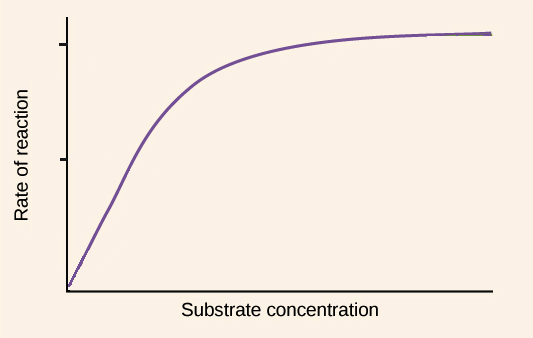
As substrate concentration increases, the rate of enzymatic activity increases until it reaches its saturation point. At this point the reaction remains at a constant rate because all enzymes are actively bound to substrate molecules.
This molecule serves as electron acceptors during reduction reactions of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis
What is NADP+