These are all four of the macromolecules
What are proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids
Condensation of chromatin into chromosomes occur during this stage of the cell cycle.
What is Mitosis (or Prophase)
What is the main function of enzymes?
To decrease the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur and speed up the reaction.
What checkpoint decides whether or not the cell will undergo division or enter to G0 phase?
What is G1 Checkpoint
Green is dominant to yellow in peas.
A true-breeding green pea is crossed to a yellow pea, resulting in green peas in the F1 generation.
If you cross two of the F1 peas, what phenotypic ratio is expected in the offspring?
3:1
The functional group found in ATP.
What is Phosphate group
When a cell is exporting a protein in mass quantities, what 3 organelles are involved?
Rough ER, Golgi Body, Vesicle
What is the formula for photosynthesis? Label reactants and products.
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Reactants then products
What are the 3 steps of interphase and 5 steps of mitosis in order?
What are G1, S, G2, Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
In the pedigree below, person II5 and II6 have another child. What is the chance this child will have the trait?
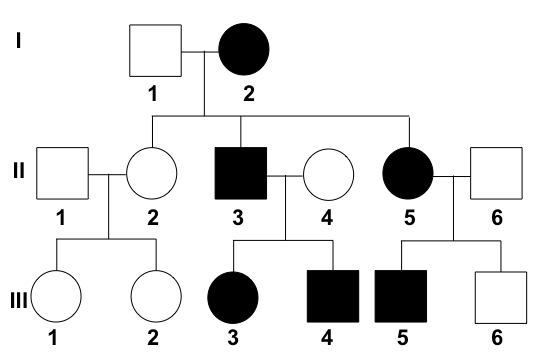
50%
This organelle synthesizes lipids and steroids
Smooth ER
Write the formula for cellular respiration. Label reactants and products.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O
What is a series of chemical reactions during cell signaling mediated by enzymes, in which each kinase in turn phosphorylates and activates another?
What is Phosphorylation Cascade
When a virus penetrates the cell membrane and uses the host cell's enzymes to reproduce the virus.
What is the lytic cycle?
What is the correct order of ALL stages of the M-phase?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis
What is the major difference between C3, C4, and CAM plants?
C3 plants stomata stay open most of the time unless they fully close, C4 plants can partially close their stomata, and CAM plants open their stomata at night.
A diploid organism with a total of 22 chromosomes has an n of
What is 11
Specific enzyme used to cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences.
What is a restriction enzyme?
A cell is placed in an open container. Both the cell and the solution are at 27 C and contain 1.0 M of solute. The cell contains glucose while the solution contains Calcium Chloride. Which way will the water move?
Out of the cell
What is the final electron acceptor? And what does it create when it accepts electrons and hydrogens?
Oxygen
It creates H2O from gaining 2 electrons and 2 hydrogens
A diploid organism with n=5 would have this many chromatids in metaphase
What is 20
The process used to copy DNA fragments millions of times by using DNA polymerase.
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?