Spongy bone contains osteons or trabeculae?
Trabeculae
Which hormone increases osteoclast activity to release more calcium ions into the bloodstream?
Which bone marking indicates a slit-like groove? Fissure or furrow
Fissure
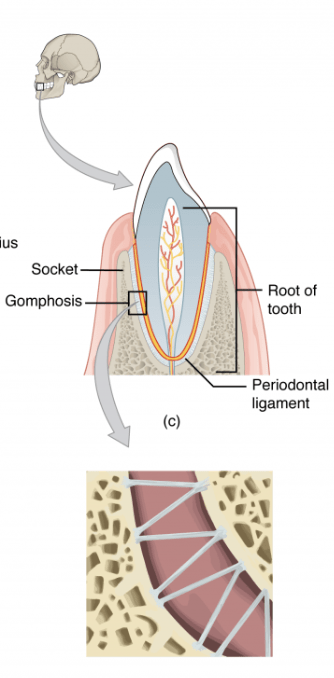
What joint is found in a tooth socket? (symphysis or gomphosis)
Gomphosis (type of fibrous joint)
What is the name of the cartilage that is found at the end of long bones in synovial joints?
Articular cartilage
What is the abnormal lateral curve of the body?
Scoliosis
What structure connects periosteum to bone?
Sharpey's fibers/ fibrous layer of periosteum
What tissue serves as the model for endochondral ossification?
Hyaline cartilage
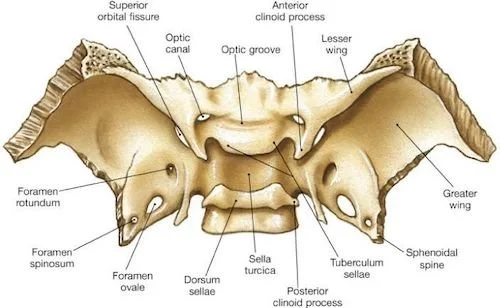
Which bone of the orbit is shaped like a wing and is also known as the keystone bone?
Sphenoid
Name 4 of the 6 distinguishing features of a synovial joint
1. Articular cartilage (usually hyaline)
2. Joint (synovial) cavity
3. Synovial fluid
4. Articular capsule (made of:
a. Fibrous capsule – outer layer
b. Synovial membrane – inner layer)
5. Reinforcing ligaments
6. Nerves and blood vessels
Amphiarthroses example?
Symphysis joints: Pubic symphysis, intervertebral disc
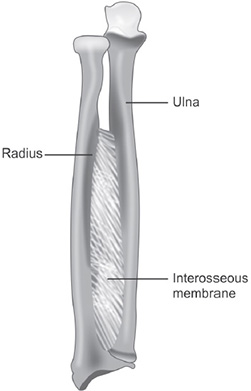
Syndesmosis joints: Interosseus membrane (radius-ulna; tibia-fibula), distal tibiofibular joint
What is a herniated disc?
A spinal disc bulges or ruptures, pressing on nearby nerves.
How do osteocytes in an osteon communicate?
Via canaliculi
What does calcitonin hormone do? How does it affect your osteoblasts?
Decreases blood calcium; increases osteoblast activity
Which bone marking indicates a large rounded (rough) projection? Tuberosity or tubercle
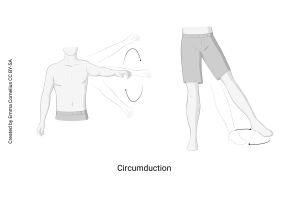
Provide an example of circumduction
Drawing a circle with your arm at the shoulder or with your leg at the hip
Describe what is found in Synovial fluid
Water, nutrients (for articular cartilage), hyaluronic acid
In an autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system targets the synovial membrane. Based on its function, what consequence would most likely result?
Decreased production and regulation of synovial fluid, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and reduced smooth movement between bones.
Bone is constantly being remodeled throughout life.
Name the two main cells responsible for bone resorption and bone deposition, and explain their function.
Osteoclasts break down bone (resorption); osteoblasts build new bone (deposition).
Cranial bones develop within______________; this type of bone development is known as _________ __________
Fibrous membranes; intramembranous ossification
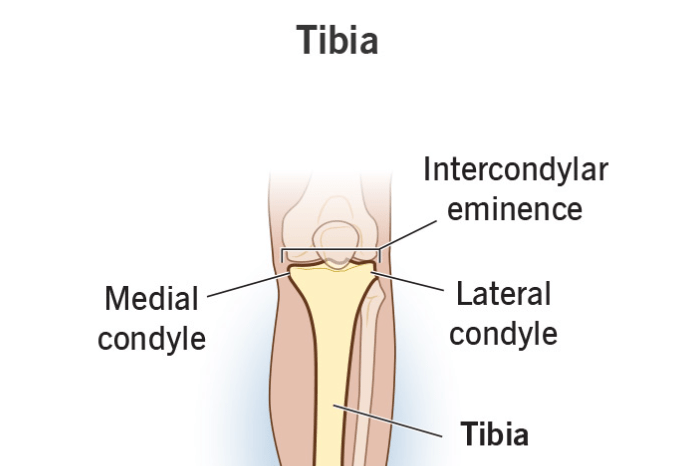
What structures do you look for on the tibia to connect to the femur?
Medial & lateral condyles of tibia (articulating surfaces)
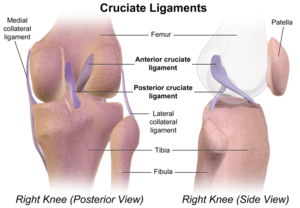
What are the names of the ligaments that protect the alignment of the femoral and tibial condyles?
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
What is the function of the bursae?
Reduces friction between bone and soft tissues
A postmenopausal patient presents with decreased bone mass and frequent fractures. What condition is this likely to be, and what are two ways to help prevent it?
Osteoporosis- bone resorption is greater than bone formation
Prevention-
increased calcium and vitamin D intake;
exercise (weight-bearing);
hormonal support (especially estrogen in postmenopausal women)
avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
Where is yellow marrow found in the long bone? Is it found in infants?
How does cartilage grow at the epiphyseal plate to allow bone lengthening?
Chondrocytes divide and enlarge in the growth zone, pushing the epiphysis away from the diaphysis. The cartilage is then gradually replaced by bone.
What structures do you look for on the humerus to identify anterior and posterior? Right from left?
Anterior/posterior- olecranon fossa (bigger cavity)= posterior view; coronoid fossa (smaller cavity) = anterior view
Right/left- Head points medially toward the shoulder joint
Name one of each of these joints found in the lower limb (for example; cartilaginous- pubic symphysis)
NOTE: not all of these joints are found in the lower limb
fibrous-
plane-
ball and socket-
hinge-
pivot-
condylar-
fibrous- interosseus membrane (tibia-fibula); distal tibiofibular joint
plane- intertarsal joints (between tarsal bone in the foot)
ball and socket- acetabulofemoral joint (hip joint)
hinge- tibiofemoral joint (knee)
pivot- NONE in lower limb
condylar- metatarsophalangeal joints (knuckles)
Note: some joints omitted to avoid confusion; only commonly seen joints listed
Explain the roles of the fibrous capsule and synovial membrane in a synovial joint. Be sure to mention their location and main function.
Fibrous capsule: Outer layer of the joint capsule; DICT; provides strength and structural support.
Synovial membrane: Inner layer of the joint capsule & lines all non-cartilage surfaces inside the capsule; loose areolar CT; produces synovial fluid.
Why is the iliac crest commonly used to obtain red bone marrow in adults?
It is easily accessible, contains abundant red marrow, and is relatively safe to puncture due to its flat structure and distance from vital organs.
