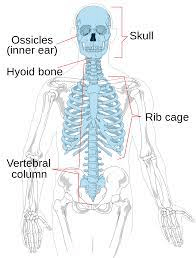
Which skeleton contains the skull, ears, hyoid bone, vertebral column and thoracic cage?
What is the Axial Skeleton?
This bone forms a key part of the cranial floor as well as the floor and side walls of the orbits. Viewed posteriorly it looks like a giant moth.
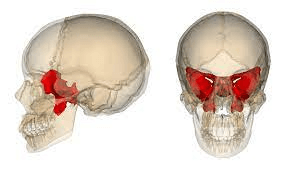
What is the sphenoid bone?
These bones meet to form the upper jaw, part of the floor of the orbits, part of the the roof of the mouth, and part of the floor and walls of the nose.
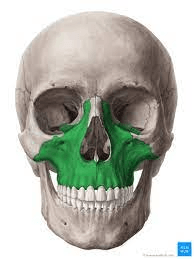
What are the maxillae (singular:maxilla)?
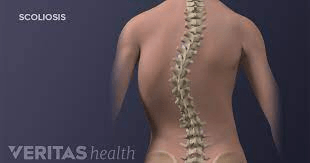
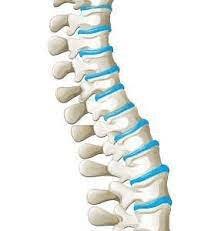
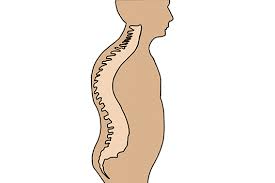
Term for lateral curvature of the spine.
What is scoliosis?
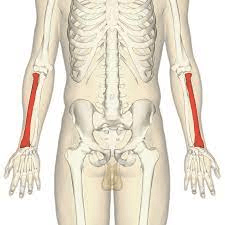 This bone is on the same side as the thumb.
This bone is on the same side as the thumb.
What is the radius?
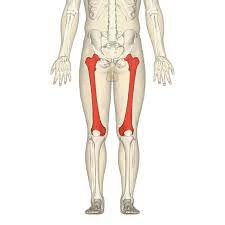 This is the longest and strongest bone in the body.
This is the longest and strongest bone in the body.
What is the femur?
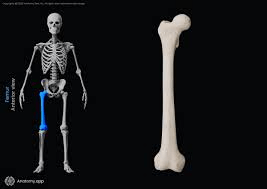
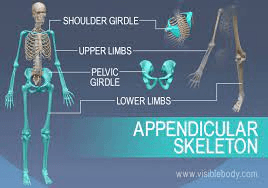
Which skeleton contains the pectoral girdle, upper limbs, pelvic girdle and the lower limbs?
What is the Appendicular Skeleton?
This bone forms the forehead and the roof of the eye sockets (orbits).
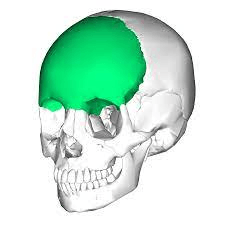
What is the frontal bone?
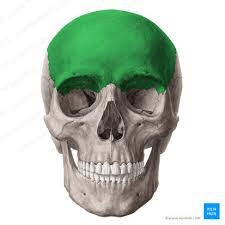
These bones shape the cheeks and form the outer edge of the orbit.
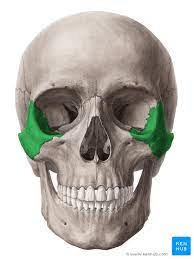
What are the zygomatic bones?
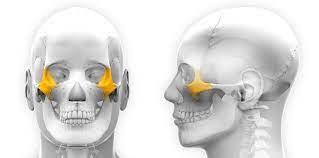
1. This opening allows for passage of the spinal cord.
2. These are the bumps you feel when you run your hand along the spine.
3. These extend from each side of the vertebra.
2&3 serve as attachment points for muscles and ligaments.
1. Vertebral Foramen
2. Spinous process
3. Transverse processes
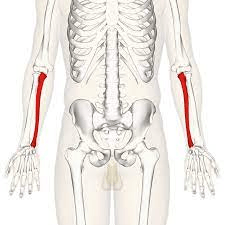 This bone is on the same side as the pinky finger.
This bone is on the same side as the pinky finger.
What is the ulna?
These are the widest point of the femur at the knee.
What are the medial and lateral epicondyle?
How many bones are there in the axial skeleton?
What is 80?
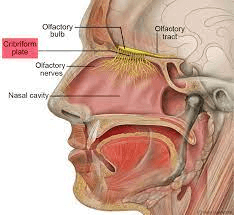
The top of the ethmoid bone is called the _______ ______, it forms part of the roof of the nasal cavity.
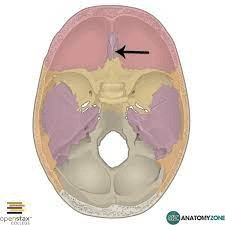
What is the cribriform plate?
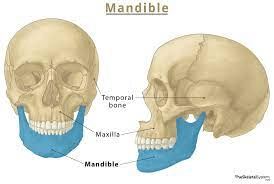
This is the largest and strongest bone of the face. It articulates with the temporal bone at the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), making it the only facial bone that can move.
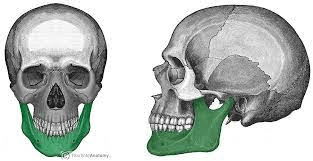
What is the mandible?
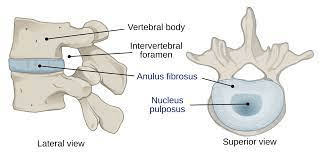
In between each vertebra is a layer of cartilage called an 1. _______ ________.
It consists of two parts. 2.______ _____, a gel-like core and 3.______ ______, a ring of tough fibrocartilage.
1. Intervertebral disc
2. Nucleus pulposus
3. Annulus Fibrosus
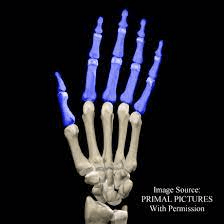
The fingers are formed by bones called ________.
What are phalanges (singular:phalanx)?
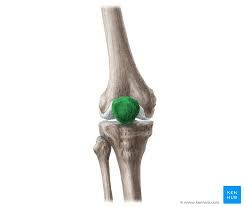 State what bone is highlighted.
State what bone is highlighted.
What is the patella (kneecap)?
How many bones are there in the appendicular skeleton?
What is 126?
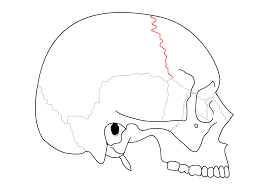
This suture of the skull is the joint between the parietal bones and the frontal bone.
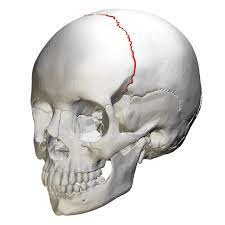
What is the coronal suture?
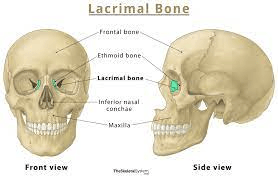
These two, paper-thin bones form part of the sidewall of the orbit.
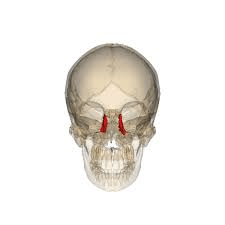
What are the lacrimal bones?
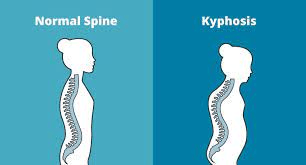
Term for "hunchback", an exaggerated thoracic curvature.
What is kyphosis?
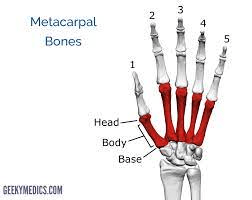
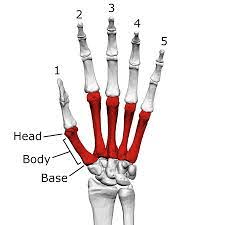 5 bones that form the palm of the hand.
5 bones that form the palm of the hand.
What are metacarpals?
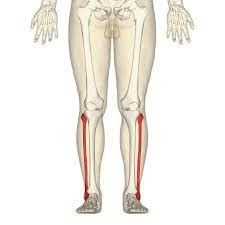 This bone helps stabilize the ankle and it does not bear any weight.
This bone helps stabilize the ankle and it does not bear any weight.
What is the fibula?
The only bone in the body that doesn't articulate with any other bone.
What is the hyoid bone?
This is the suture of the skull that is the line of articulation between the parietal bones and the occipital bone.
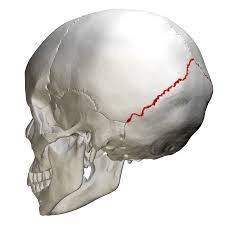
What is the lambdoid suture?
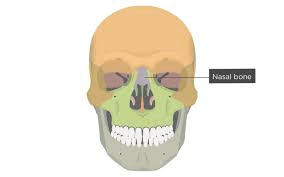
These rectangular bones form the bridge of the nose.
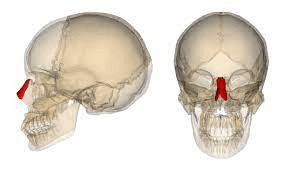
What are the nasal bones?
1. The first cervical vertebrae (C1), helps the head nod 'yes', has no body, consists of a delicate ring and a large vertebral foramen.
2. The second cervical vertebrae (C2), has a projection called the dens, or odontoid process. Allows the head to swivel from side to side (saying 'no').
1. Atlas
2. Axis

A. Scaphoid
B. Lunate
C. Triquetrum
D. Pisiform
E. Trapezium
F. Trapezoid
G. Capitate
H. Hamate
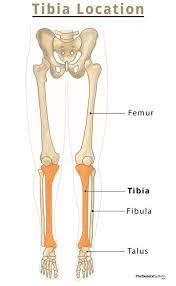
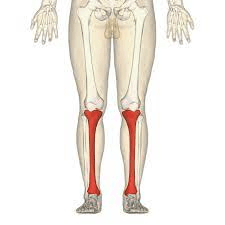 This bone is the only bone in the lower leg that bears weight, it is commonly called the shinbone.
This bone is the only bone in the lower leg that bears weight, it is commonly called the shinbone.
What is the tibia?
The skull is formed by 1. ___ bones that are 2. ________ shaped.
1. 22
2. Irregularly
This suture runs along the top edge of the temporal bone.
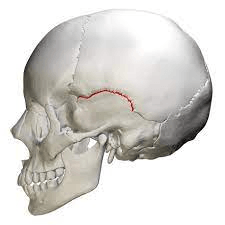
What is the squamous suture?
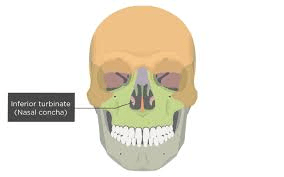
These bones contribute to the nasal cavity.
What are inferior nasal conchae?
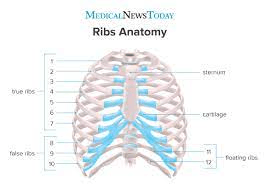
1. Which ribs are considered true ribs?
2. What ribs are considered false ribs?
3. What ribs are considered floating ribs?
1. 1-7
2. 8-10 (attach to cartilage of rib 7), 11&12
3. 11, 12 (do not attach to any part of the anterior thoracic cage)
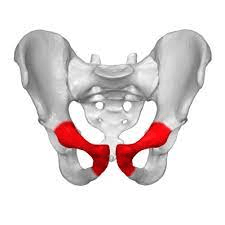
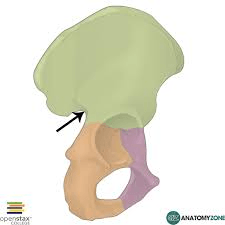
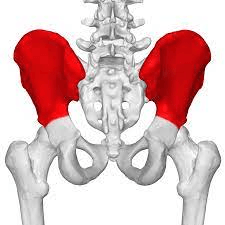 What part of the pelvic girdle is highlighted?
What part of the pelvic girdle is highlighted?
What is the ilium?
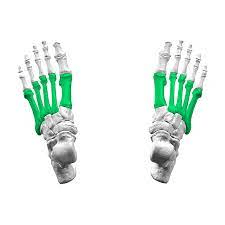 These bones form the middle portion of the foot.
These bones form the middle portion of the foot.
What are metatarsals?
These bones join together at the top of the head to form the top and sides of the cranial cavity.
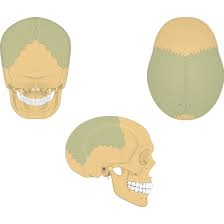
What are the parietal bones?
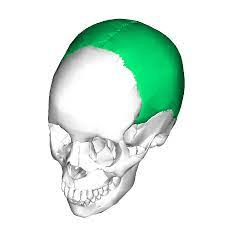
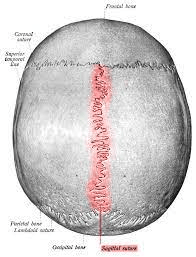
This skull suture is the joint between the right and left parietal bones.
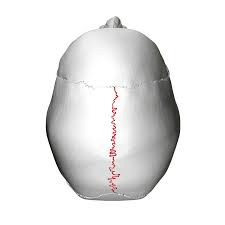
What is the sagittal suture?
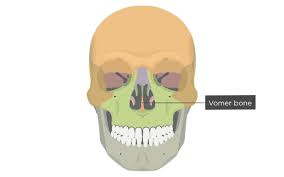
This small bone forms the inferior half of the nasal septum.
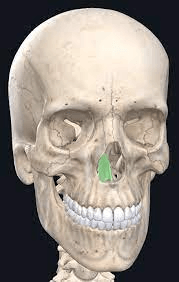
What is the vomer?
The sternum has 3 regions
1. This is an important landmark for CPR, it provides an attachment point for some abdominal muscles.
2. The longest portion, joins the manubrium at the angle of Louis (sternal angle).
3. The broadest portion; the suprasternal notch is easily palpated.
1. Xiphoid Process
2. Body
3. Manubrium
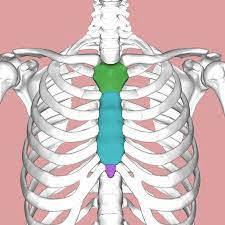
This is the lower posterior portion, what is it called?
What is the ischium?
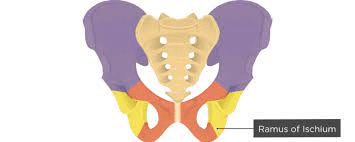
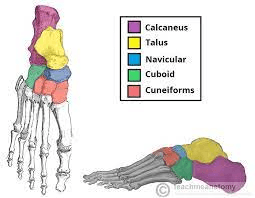
What bones comprise the ankle?
What are tarsal bones?
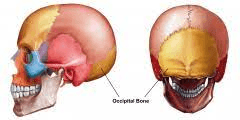
This bone forms the rear of the skull.
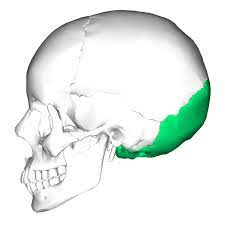
What is the occipital bone?
This is a large opening at the base of the skull that allows the spinal cord to pass through as it connects to the brainstem.
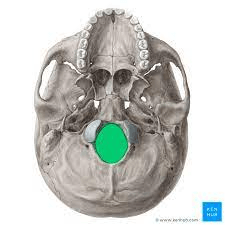
What is the foramen magnum?
These bones form the form the posterior portion of the hard palate, part of the wall of the nasal cavity, and part of the floor of the orbit.
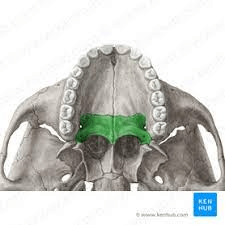
What are the palatine bones?
The two pectoral girdles-one on each side of the body-consist of a 1. ______ and 2.______ ______.
1. Clavicle (collarbone)
2. Scapula (shoulder blade)
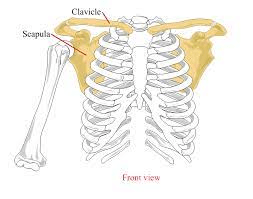
 What bone is highlighted?
What bone is highlighted?
What are the pubic (pubis) bones?
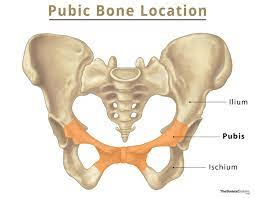
This is the largest tarsal bone, which forms the heel and bears much of the body's weight.
What is the calcaneus?
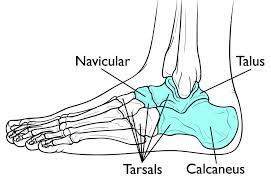
These bones form the sides of the cranium and part of the cranial floor; also contain the structure of the inner and middle ear.
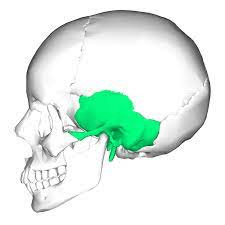
What are the temporal bones?
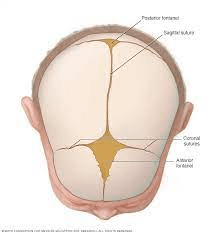
The areas between the unfused bones in an infants skull, which are covered by fibrous membranes, are called 1._______, these should be closed by age 2. ___.
1. Fontanels
2. 2
How many vertebrae does the vertebral column contain?
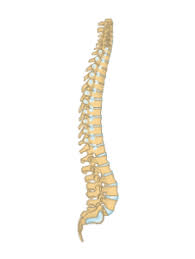
What is 33?
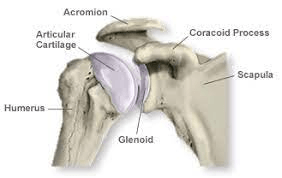
What are the three main features of the scapula?
Acromion process, coracoid process, glenoid cavity.
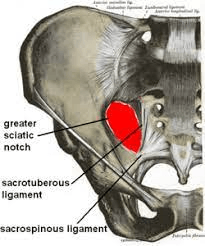
 Point through which the sciatic nerve passes on its path to the back of the thigh.
Point through which the sciatic nerve passes on its path to the back of the thigh.
What is the greater sciatic notch?
Term for great toe.
What is the hallux?
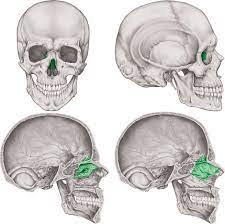
This bone contributes to the walls of the orbits, the roof and walls of the nasal cavity, and the nasal septum.
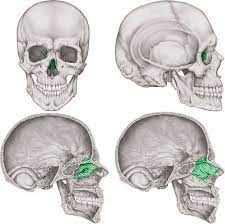
What is the ethmoid bone?
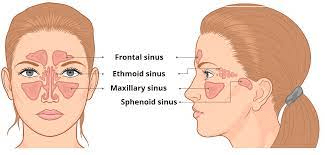
What are the 4 pairs of paranasal sinuses?
1. Sphenoid sinus
2. Frontal Sinus
3. Ethmoid Sinus
4. Maxillary sinus
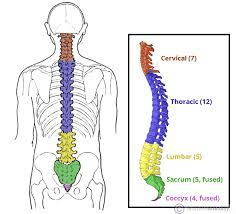
What are the 5 sections of the vertebral column?
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacrum, Coccyx
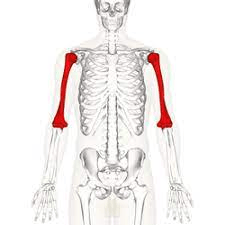 State what bone is highlighted.
State what bone is highlighted.
What is the humerus?
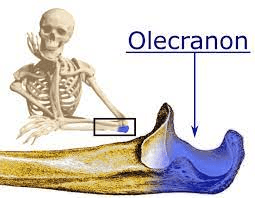
Features include: head, olecranon fossa, olecranon process.
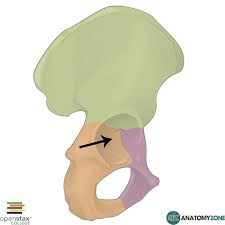 Depression that houses the head of the femur to form the "hip socket"
Depression that houses the head of the femur to form the "hip socket"
What is the acetabulum?
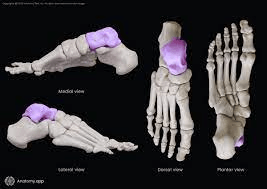 This is the second-largest tarsal bone.
This is the second-largest tarsal bone.
What is the talus?