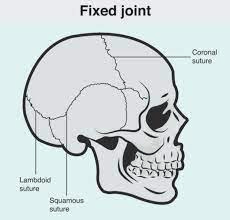
A joint that results when collagen fibers from one bone penetrate the adjacent bone, anchoring the bones in place.
What is a fixed joint?
*Bound by fibers*
*aka fibrous/synarthroses joints*
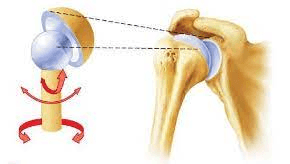
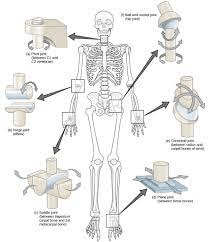
These joints offer the widest ROM of all joints. The ball shaped head of one bone fits into a cup-like socket of another bone to form this joint.
What is a ball-and-socket joint?
1. Bending a joint so as to decrease the angle of the joint.
2. Straightening a joint, increasing the angle between the bones.
What is 1. Flexion, 2. Extension?
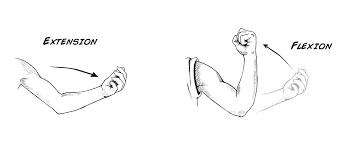
This joint has the most mobility of any joint in the body.
What is the humeroscapular joint?
*shoulder*
In these joints, two bones are joined together by cartilage, they are slightly movable.
What are semi-movable joints?
*aka cartilaginous/amphiarthoroses joints*
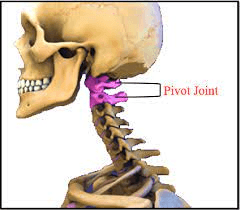
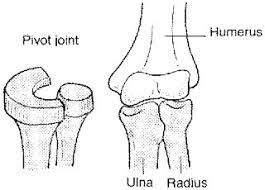
In this joint, a projection from one bone articulates with a ring-shaped socket of another bone, allowing the bones to rotate.
What is a pivot joint?
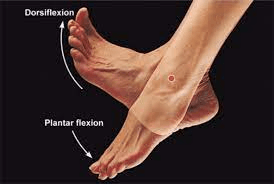
1. Involves moving the toes or foot upward.
2. Involves moving the toes or foot downward.
What is 1. Dorsiflexion, 2. Plantar flexion?
Which joint is the rotator cuff located?
What is the shoulder?
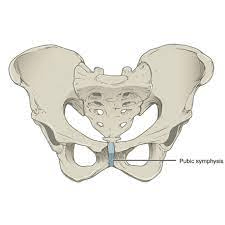
The two pubic portions of the os coxae are joined by a pad of cartilage called a ________. This forms the joint known as the ________ pubis.
What is a symphysis?
These joints allow only back-and-forth movements (flexion and extension).
What are hinge joints?
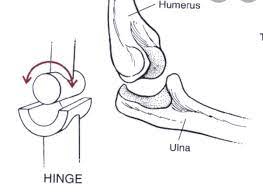
Elbow, knee, interphalangeal joints of the fingers and toes.
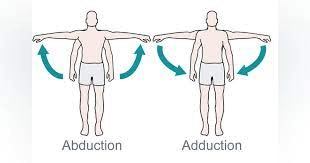
1. Movement of a body part away from the midline of the body.
2. Movement of a body part toward the midline of the body.
What is 1. Abduction, 2. Adduction?
The elbow is a 1._____ joint consisting of 2. ___ articulations.
What is 1. hinge, 2. two?
Intervertebral discs reside between each vertebrae, making the vertebrae of the spine ________ joints.
What are cartilaginous joints?
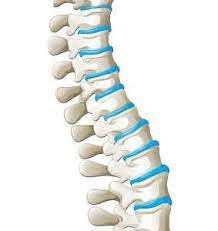
Intervertebral discs aka fibrocartilaginous pads
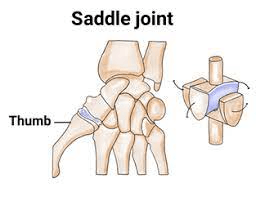
This joint is found only in the thumbs.
What is the saddle joint?
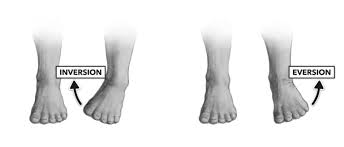
1. Foot movement that turns the sole medially, toward the other foot.
2. Foot movement that turns the sole laterally, away from the other foot.
What is 1. Inversion, 2. Eversion?
This is the largest joint in the body and also the most complex.
*the knee*
These are the most numerous and versatile of all the body's joints, they are freely movable.
What are synovial joints?
*aka diathroses joints*
These joints allow flexion and extension as well as side-to-side movement. An oval convex surface on one bone fits into a similarly shaped depression on another.
What is a condyloid joint?
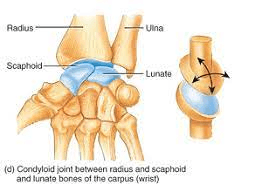 Ex: articulation of the distal end of the radius with the carpal bones of the wrist as well as joints as the base of the fingers.
Ex: articulation of the distal end of the radius with the carpal bones of the wrist as well as joints as the base of the fingers.
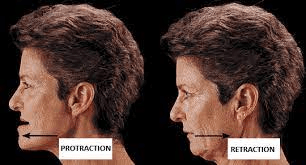
1. Moves a part forward
2. Moves a part backward
What is 1. Protraction, 2. Retraction?
What is the acetabulum?
*The hip socket is much deeper than the socket of the shoulder*
Along with synovial fluid, this structure permits friction-free movement in synovial joints.
What is articular cartilage?
In this joint, two bone surfaces (which are relatively flat) slide over each other.
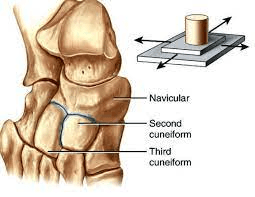
What are gliding joints?
The two most common knee injuries.
What is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the meniscus?
*minimal blood supply*
This ligament keeps the knee from hyperextending.
What is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?