What is a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
A proton (H⁺) donor.
What is the pH of a neutral solution at 25°C?
7.0
What’s a strong acid?
One that completely ionizes in solution.
What is Ka?
Acid dissociation constant.
What is a buffer?
A solution that resists changes in pH.
What is a Brønsted-Lowry base?
A proton (H⁺) acceptor.
How are pH and pOH related?
pH + pOH = 14
Name 3 strong acids.
HCl, HNO₃, H₂SO₄ (others: HBr, HI, HClO₄).
What does a large Ka value mean?
The acid is strong; more dissociation.
What are components of a buffer?
Weak acid and its conjugate base (or vice versa).
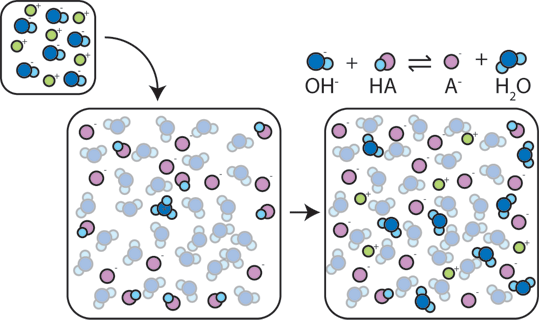
What is the conjugate base of H₂SO₄?
HSO₄⁻
What is the [H⁺] if pH = 3?
1.0 × 10⁻³ M
What’s a weak base?
A base that partially ionizes (like NH₃).
What is the expression for Ka of HA ⇌ H⁺ + A⁻?
Ka = [H⁺][A⁻]/[HA]
What’s the pH at the equivalence point of a strong acid–strong base titration?
7.0
What is the conjugate acid of NH₃?
NH₄⁺
What is the pOH if [OH⁻] = 1 × 10⁻⁵ M?
5
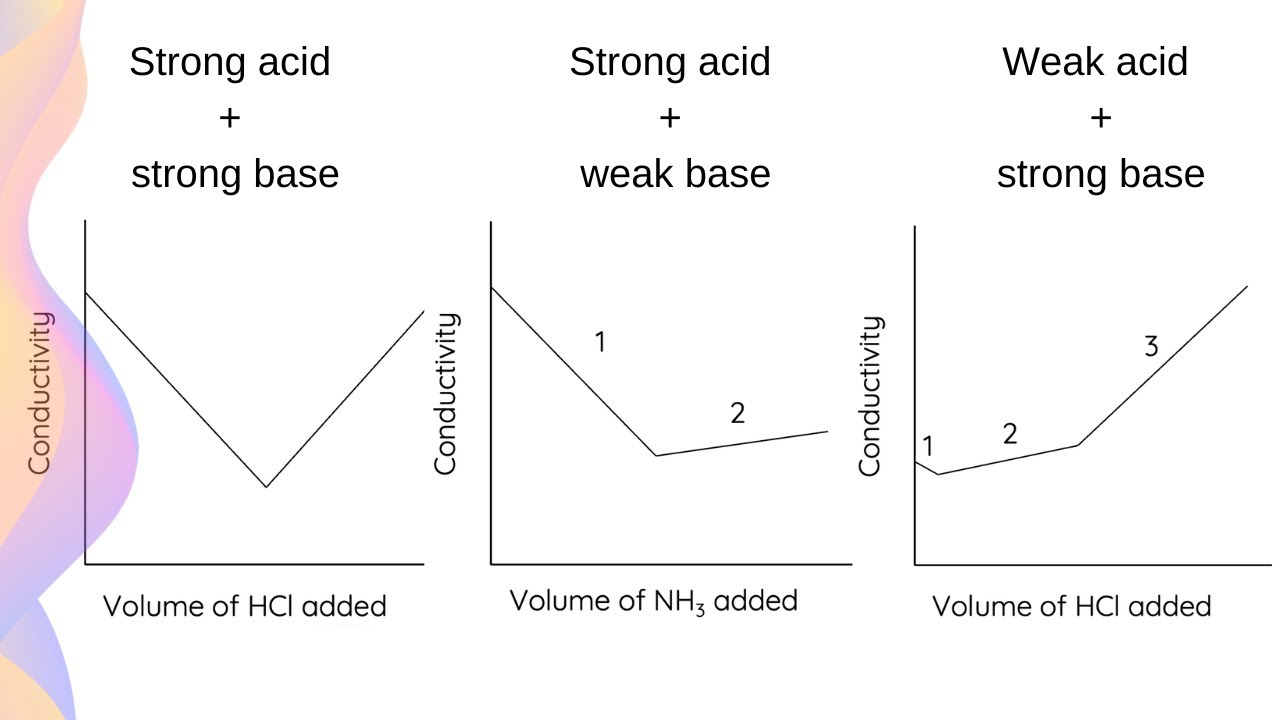
Compare strong and weak acid conductivity.
Strong acids conduct better due to full ionization.
What does it mean if Ka > Kb for a substance?
It behaves more like an acid.
What is the half-equivalence point?
pH = pKa; [acid] = [conj. base].
Identify conjugate acid-base pairs in this reaction: HCl + H₂O → H₃O⁺ + Cl⁻
HCl/Cl⁻ and H₂O/H₃O⁺
How do you calculate pH from [OH⁻]?
First find pOH = -log[OH⁻], then use pH = 14 - pOH
Why is HF a weak acid?
It doesn't fully ionize due to strong H–F bond.
Write the net ionic equation for HCl + NaOH.
H⁺ + OH⁻ → H₂O
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])