This combination of enthalpy and entropy drives a reaction that is thermodynamically favorable at all temperatures.
What is -H, +S (resulting in G < 0)?
By calculating pH, you are describing the concentration of this ion.
What is [H+]?
The equilibrium expression of the formation of ammonia, N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3

The name of this laboratory set up. 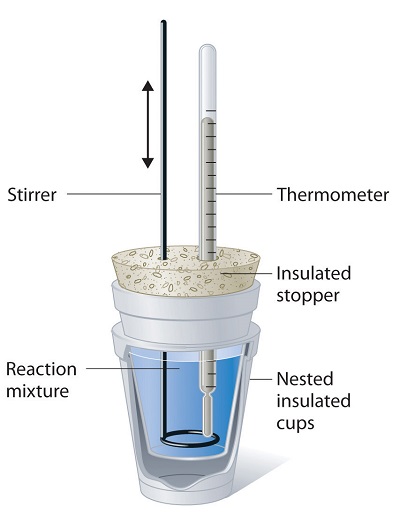
What is a calorimeter?
Three ways to speed up a chemical reaction.
What is 1) add a catalyst, 2) increase surface area, 3) increase reactant concentration, 4) increase temperature, 5) agitation?
The half-cell the anions of the salt bridge flow towards.
What is the anode?
What is the [H+] for a weak acid?
What is solid?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius.
What is specific heat capacity?
The rate law for an elementary step of 2A + B → C + D
What is Rate = k [A]2[B] ?
The cell voltage change when the Q > K.
What is decrease?
The pH of a salt containing conjugates of strong acid/base (ex. NaBr).
What is neutral?
The manipulation of K when a reaction is reversed.
What is 1/K?
The enthalpy of the following reaction: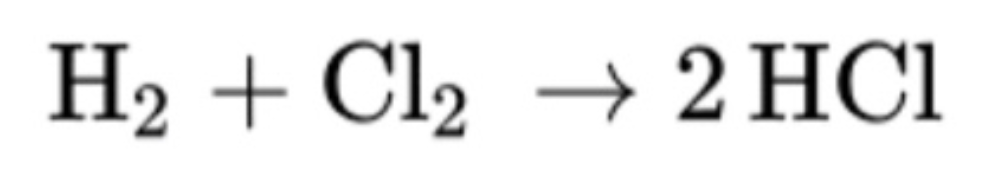
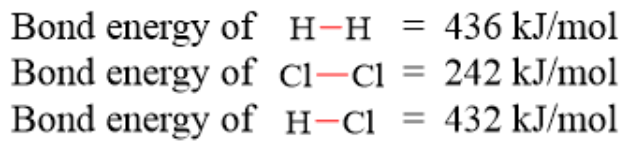
What is -186 kJ/mol?
The order of a reaction when the concentration doubles and the initial rate quadruples.
What is second order?
The half-cell that gains mass in a galvanic electrochemical cell.
What is the cathode?
The pH at the midpoint of a titration of a weak acid with a strong base.
What is pH = pKa?
The two things that do not shift an equilibrium.
What are catalysts and inert gases?
The heat absorbed by 2.76 kg of a substance with a specific heat capacity of 0.562 J/g*C) is heated from 20.5oC to 24.5oC.
What is 6.20 x 103 J?
The step of the reaction mechanism that determines the rate law.
What is the slow step?
What is kinetic control?
The pH when 100 mL of 0.10 M HC2H3O2 is titrated with 50 mL of 0.10 M NaOH. (The Ka of HC2H3O2 = 1.8 x 10-5)
What is 4.75?
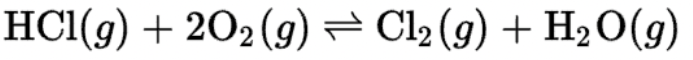 This reaction occurs in a container with a moveable piston. This is the shift in equilibrium when the volume of the container is decreased.
This reaction occurs in a container with a moveable piston. This is the shift in equilibrium when the volume of the container is decreased.
What is toward the products/forward?

What is 155.65 kJ?
The reaction order that has a consistent half-life.
What is 1st order?