_____________=change in activity or turning rate in response to a stimulus _____________=oriented movement +/- from stimulus. Think Mealworms
What is Kinesis and Taxis
what is the source of all energy in a trophic pyramid
sunlight
In a food chain or web do the arrows point from the consumer to the organism being consumed or from the organism being consumed to the organism doing the consumer?
From the organism being consumed to the organism consuming. The arrows show the flow of energy.
Explain the proximate and ultimate causes AND provide an example.
How a behavior occurs and why a behavior occurs in context to natural selection. Red belly stickleback- red is how behavior trigger/why- ensures fertilizations of eggs in his territory
Who is more efficient a lion or an elephant and why?
The lion, they are smaller
If there is a change in the producer level of an energy pyramid what other levels are affected?
All of them.
___________ describes behavior of threats or rituals, sometimes combat that settles dispute over resources or mates ___________ selfless behavior- sacrificing oneself for better of relatives
Agonistic
Altruism
What type of growth curve is represented below
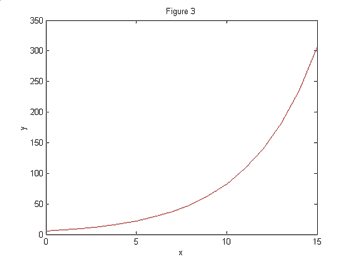
Logarithmic
How much energy is passed up through the trophic levels?
10%
What is the water cycle
Name 1 type of learned behavior providing an example
What is:
habituation: turtle draws its head in after being touched, if touched repeatedly it realizes it is in no danger and does not pull its head back in. Animals no longer fearing humans.
imprinting: ducks
spatial: using landmarks example how birds find nests
associative: learning a response from a stimuli
cognitive: the ability to navigate, example wiggle dance in bees
social: living in families
What type of dispersal is shown
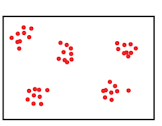
what is clumping
If a lion burns more energy than it consumes daily what will happen to the lion?
The lion will lose weight and eventually starve to death.
This biogeochemical cycle is important for the production of ATP, nucleic acids, and phospholipids.
What is the Phosphorus Cycle
Discuss 4 types of animal communication methods.
What is pheromones, visual, auditory, tactile.
What is density dependent regulation?
●as a population increases, factors can slow or stop growth by decreasing birth rate and increasing death rate
○Competition, predation, toxic wastes, territoriality, disease, intrinsic factors (ie reproduction rates)
What is density independent regulation?
●factors that exert their influence on population size, but the birth/death rate of a population does not change
○Weather, climate, natural disasters
Who are the primary producers in an ecosystem?
Autotrophs
Explain one of the following:
Phototaxis
Chemotaxis
Photo: Movement in response to light
Chemo: Movement in response to chemical signals