 The letter e
The letter e
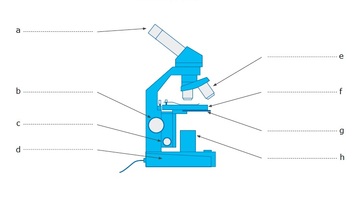
Objectives/objective lens
Organelle which is the site of steroid and lipid synthesis
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum
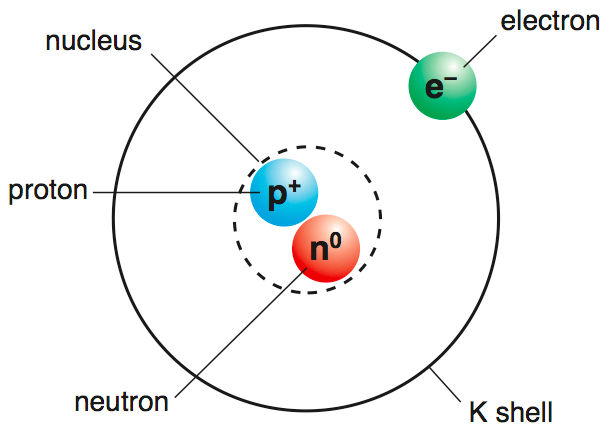
The parts of an atom and their charges.
Proton +
Neutron 0
Electron -
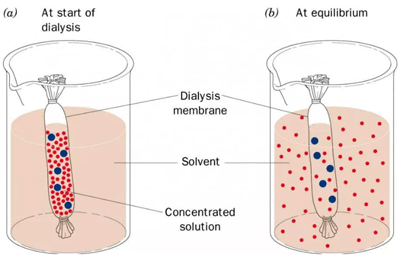
What is this process called?
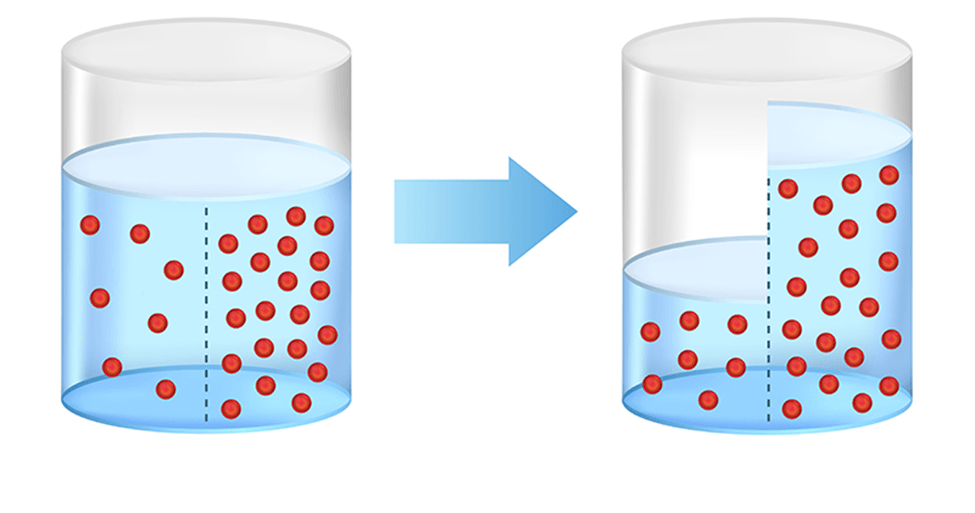
Osmosis.
List the magnification(s) of the objective lens(es).
4x
10x
40x
100x

Convert 250cm to mm.
2500 mm
Define isotope.
Multiple forms of the same element containing equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Differ in atomic mass, same atomic number.

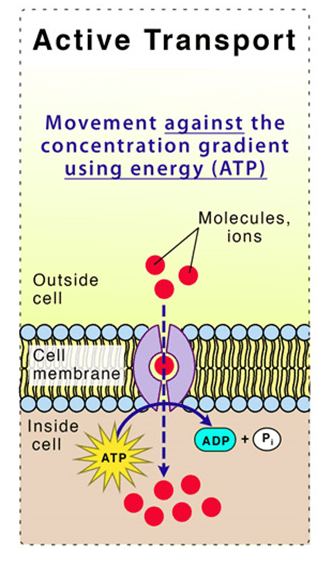
Define active transport.
Movement of ions through proteins against the concentration gradient using ATP.
Calculate the total magnification for the 40x objective.
40x * 10x = 400x
List the two microscopic stains/dye.
Congo Red (Lugo's Iodine)
Methylene Blue
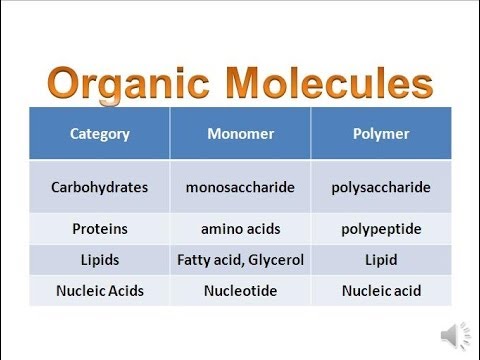
List the four major macromolecules.
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Define and give one example of a hypertonic solution.
Red blood cell in an extremely concentrated solution, water leaves cell and cell goes flat.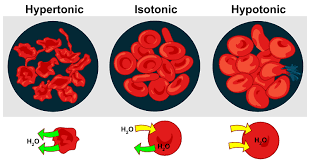
What is depth of field?
Distance between the nearest and farthest elements in a scene that appear to be sharp in an image.

How is a theory different from a hypothesis?
A hypothesis answers a question, its an assumption or prediction that can be tested through scientific experimentation.
A theory is a well tested explanation. Theories have been confirmed through evidence/studies/experimentation.
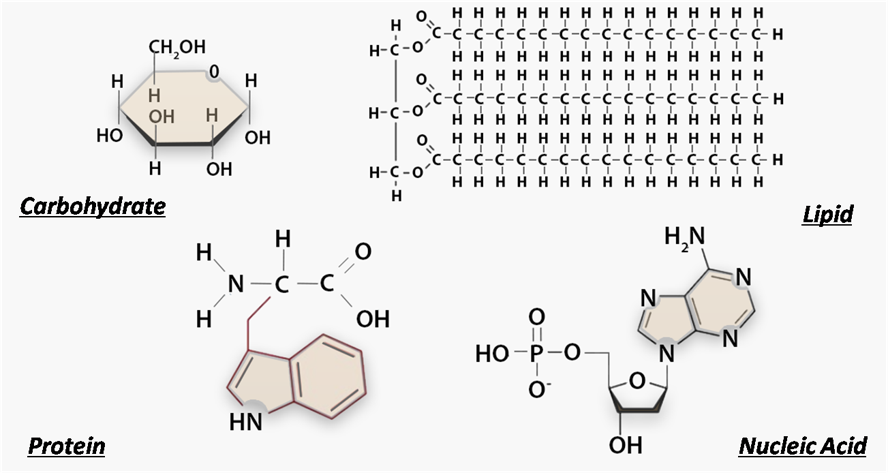
Which macromolecule is this?
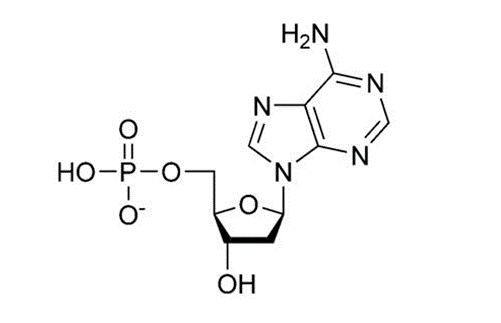
Nucleic Acid
The four factors affecting diffusion rate.
Concentration gradient
Molecular size/permeability
Temperature
Pressure Gradient
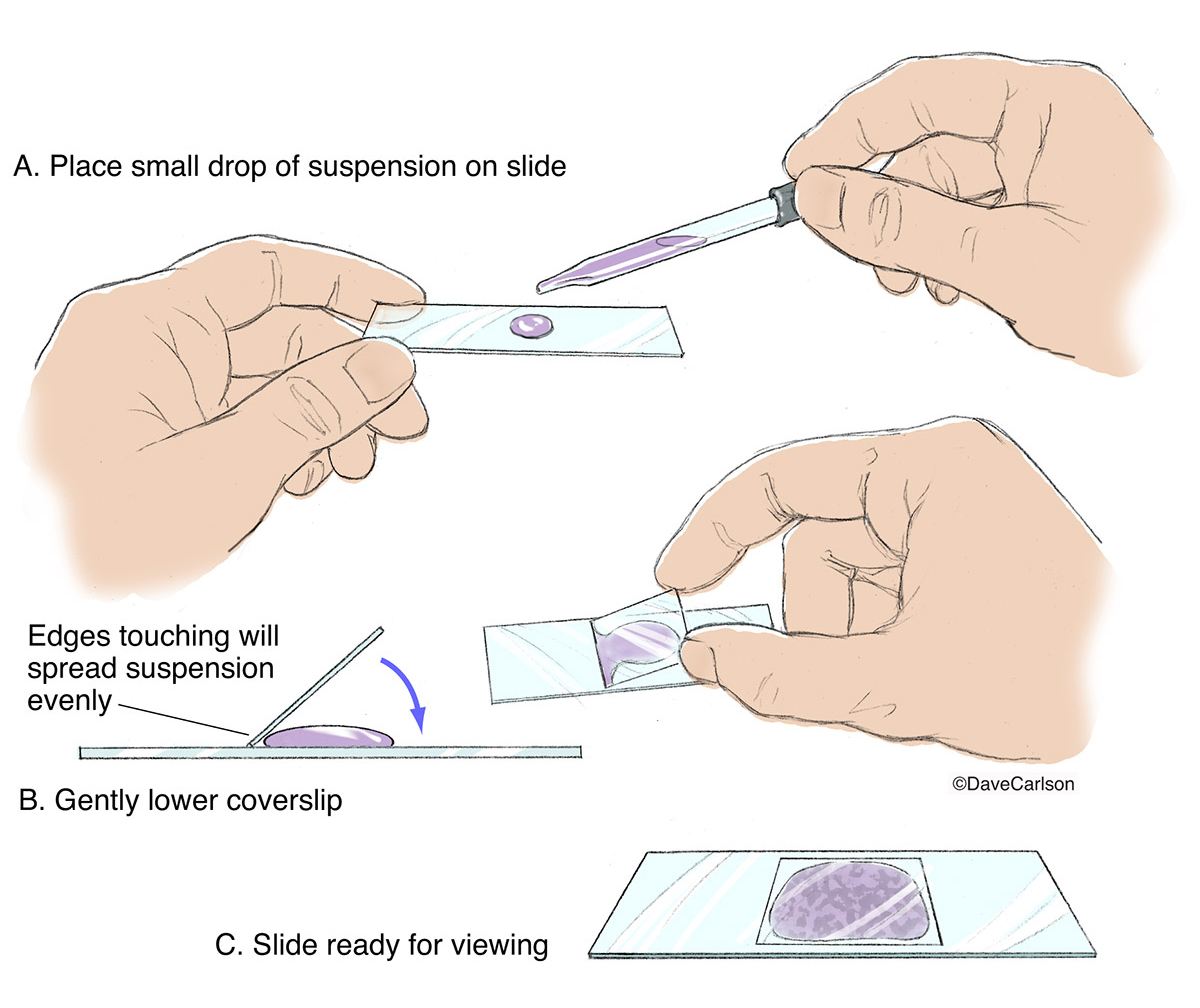
Describe how you would prepare a wet mount.
Place the object in drop of water on clean slide.
Hold a coverslip at 45 degree angle with fingertips.
Lower the coverslip slowly.
List the basic units for temperature, weight, time and length. (5)
meter
liter
gram
second
Celsius
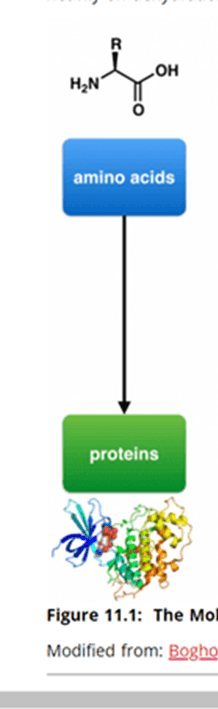
List the four functional groups of an amino acid.
Hydrogen
Carboxyl
Amine
R Group
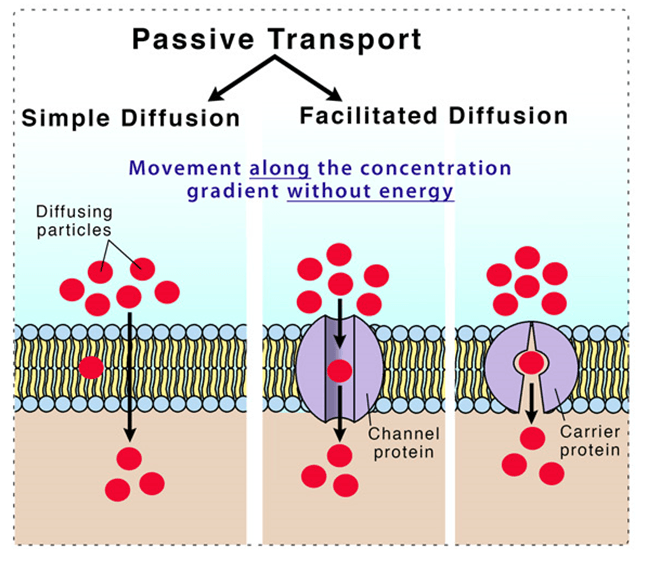
What are the three types of passive transport and how does each work?
Simple diffusion - Diffusion of lipid soluble molecules through the lipid bilayer membrane
Facilitated diffusion - Diffusion of water soluble molecules through a carrier protein
Osmosis - Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, more permeable to water
Two kinds of microscopes we used and what are they used for.
Compound/light microscope
Stereomicroscope

List all 6 differences between plant and animal cells.
Plant: Centrioles absent. Cilia/flagella absent.
Animal: Cell wall absent. Chloroplasts absent. Plastids absent. Central vacuole absent.
/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)
What color does bromothymol blue become in
acidic,
basic,
neutral solutions?
Acidic - yellow
Basic - blue
Neutral - green

Describe the results of the glucose, starch, iodine experiment, the direction of flow of each molecule.
Was the solution hypotonic or hypertonic and how do you know?
The dialysis tubing was permeable to glucose and iodine but not to starch. Starch has a larger molecule size.
Molecules entered the tubing causing swelling in the hypotonic solution.