What are the two different types of maps?
Thematic and Reference Maps
What does GIS stand for?
Geographic Information System
A city’s latitude and longitude describe this type of location.
absolute location
true or false: possibilism and environmental determinism are the same thing.
False
A region defined by government boundaries, like states or countries, is called this.
Formal
The frequency of something within a given unit of area is....
density
What type of thematic map is this? 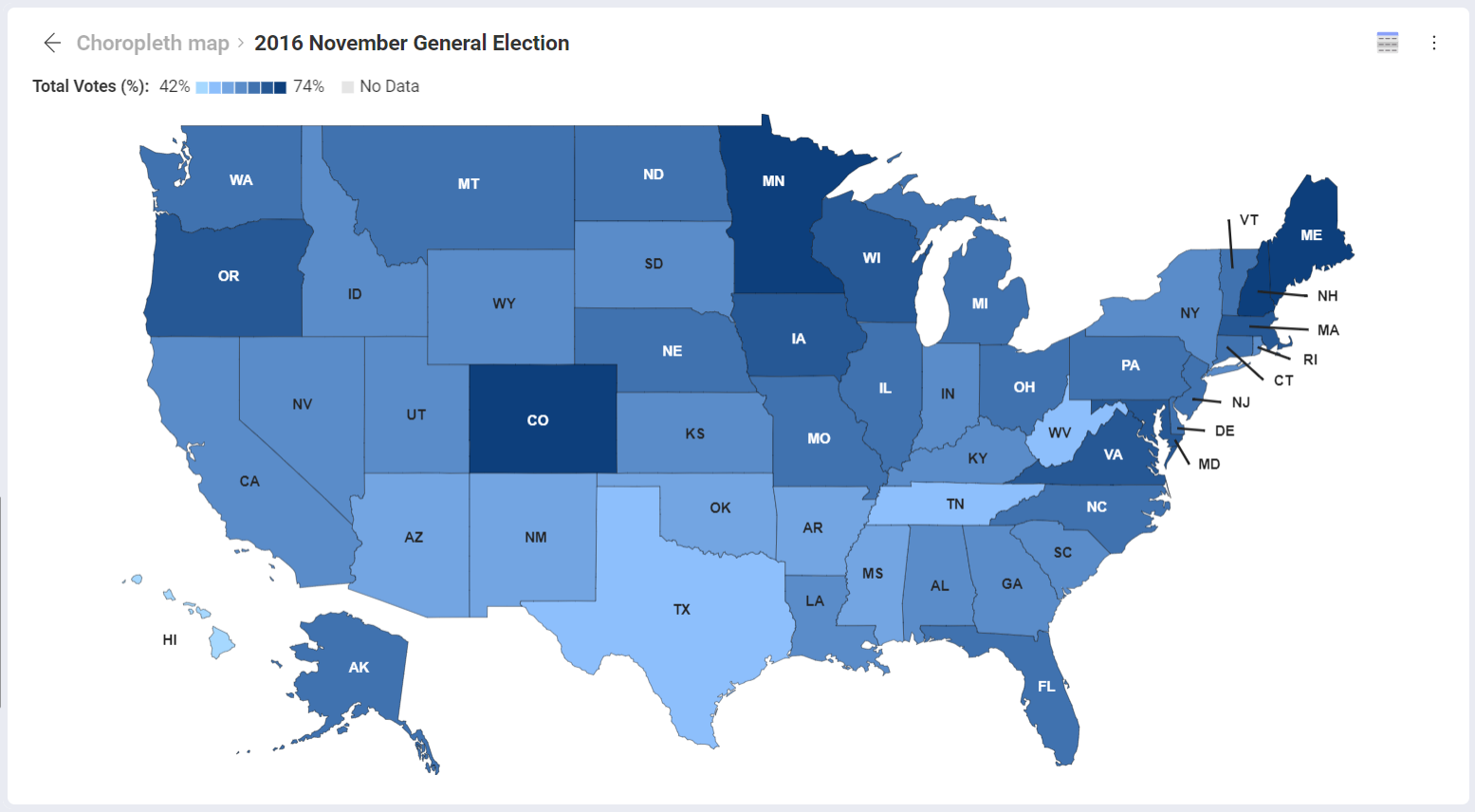
Choropleth
This government survey, taken every 10 years in the United States, provides data that geographers use to study population, demographics, and regional patterns.
Census
Explain the difference between absolute location and relative location.
Absolute = exact spot-on earth (latitude & longitude)
Relative = your location in relation to other places (north, south, east, west)
Give an example of a sustainable practice.
recycling, composting, taking public transportation/walking, etc.
The idea of “the South” or “the Midwest” is an example of this type of region.
Vernacular/perceptual
A specific point on earth distinguished by a particular characteristic. Is the definition for which term?
Place
This type of map projection makes Greenland look much larger than it really is.
Mercator
Provide a real-life example of why/how geographers use the GIS system.
map crime, add in schools/businesses, view deforestation. etc.
True or False: an example of distance decay is the weakening signal of radio waves as you increase the distance from the radio station
True
The theory that climate and landforms strongly shape human culture, and development is known as this.
environmental determinism
A region organized around a central point, like the area served by a television station, is called this.
Functional
What is a node?
A central point or place that connects to surrounding areas
Would a city or county have a larger scale?
city
GIS is powerful because it combines different kinds of data in this way.
layering data sets on the same map?
Saying that Chicago is located on Lake Michigan and is a transportation hub describes this concept. (site or situation)
Situation
The idea that the environment limits some human actions, but people can adjust and adapt, is called this.
Possibilism
What is the scale and scale of analysis of this map?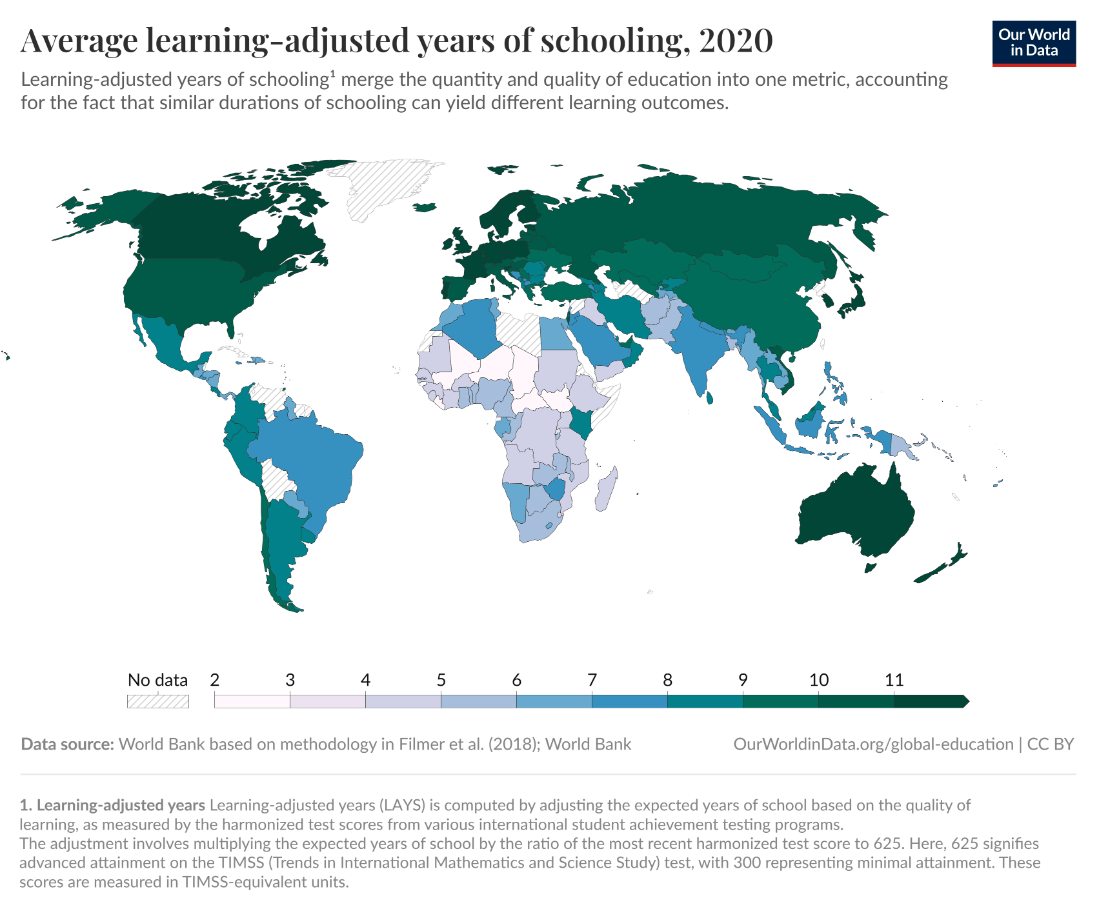
Global scale, national scale of analysis
What is time-space compression?
The shrinking of time, or relative distance because of improved methods of transportation
Explain the difference between a large-scale and small-scale map.
Large-Scale: example a city map, smaller area, but large amount of detail
Smale-Scale: Example map of the Midwest. larger map, smaller amount of detail
Why do geographers use geographic data?
Answers will vary.
Give an example of a "site" factor and a "situation" factor
site = physical natural features (soil, rivers, mountains)
Situation = connections features. A place's location in relation to other places. (roads, nearby cities)
According to the theory of environmental determinism, which of the following areas would have the most productive settlements?
A. Arid
B. Arctic
C. Temperate
D. Tropical
C
Which of the following is an example of scale of analysis?
A. A map comparing rent prices at the state, county, and city level
B. A map showing the physical features of Africa
C. Using latitude and longitude to find Paris, France
D. A thematic map of the climate zones of Earth
A
The spread of something over a given study area is ____________________. Hint: There are two kinds; clustered and dispersed.
Concentration