China instituted this policy in hopes of controlling an out of control population.
This is an examples of a(n) __________ policy.
One child policy
Antinatalist
Identify the region with the largest amout of migrants according to the data here
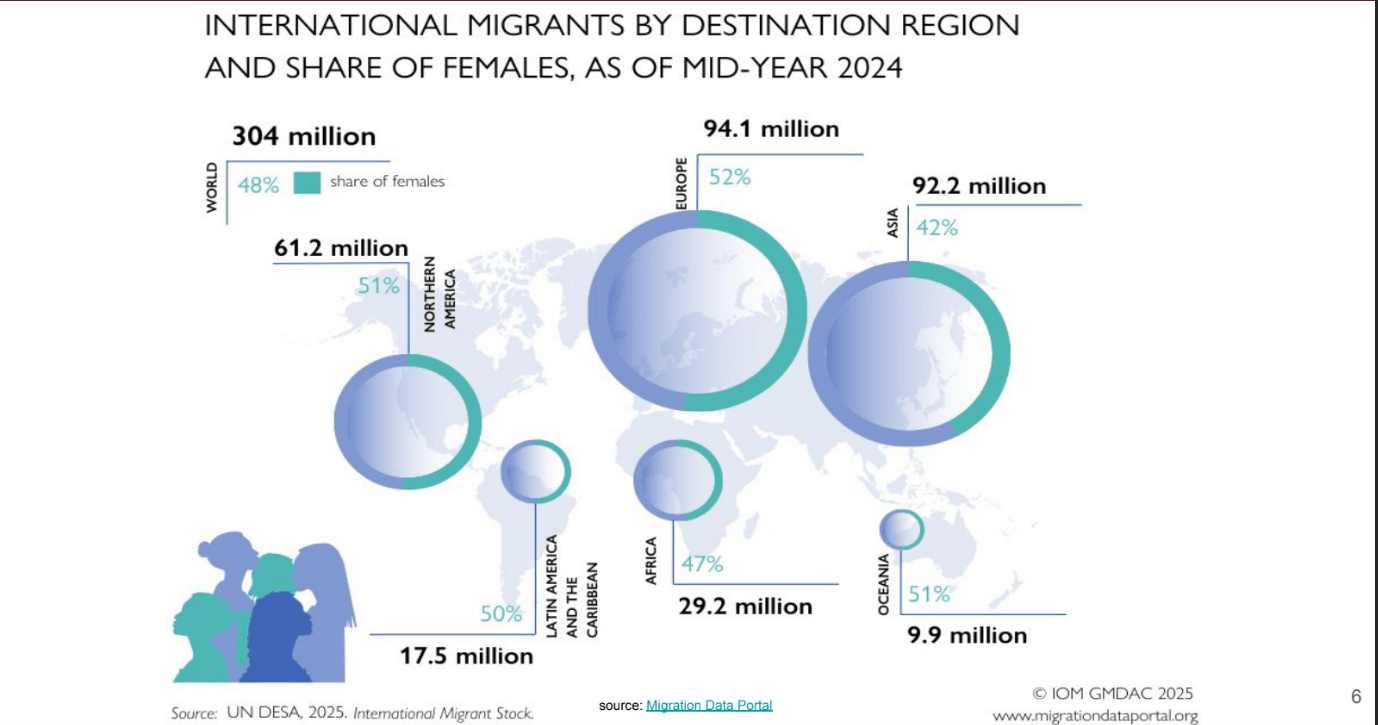
What is Asia
Concave sides on a population pyramid will tell you this about a country….
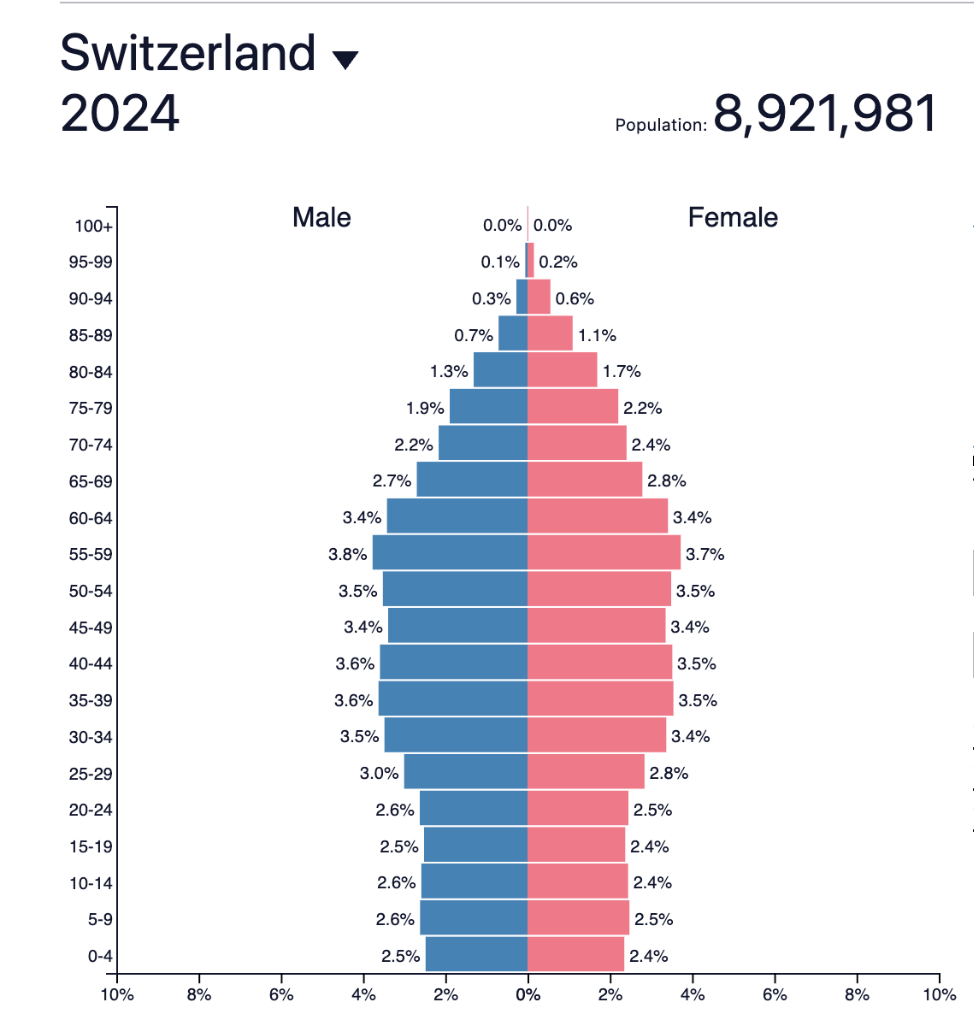
That there is a high death rate
When you are forced out of your home due to economic, social/cultural, poltical, and/or environmental factors
What is a PUSH factor
One of the two revolutions or main reasons that allowed for rapidly declining death rates in the 2nd stage of the DTM.
The Medical Revolution and the Industrial Revolution
Seen here... is a population pyramid of Paraguay, which is in this stage of the demographic transition model.
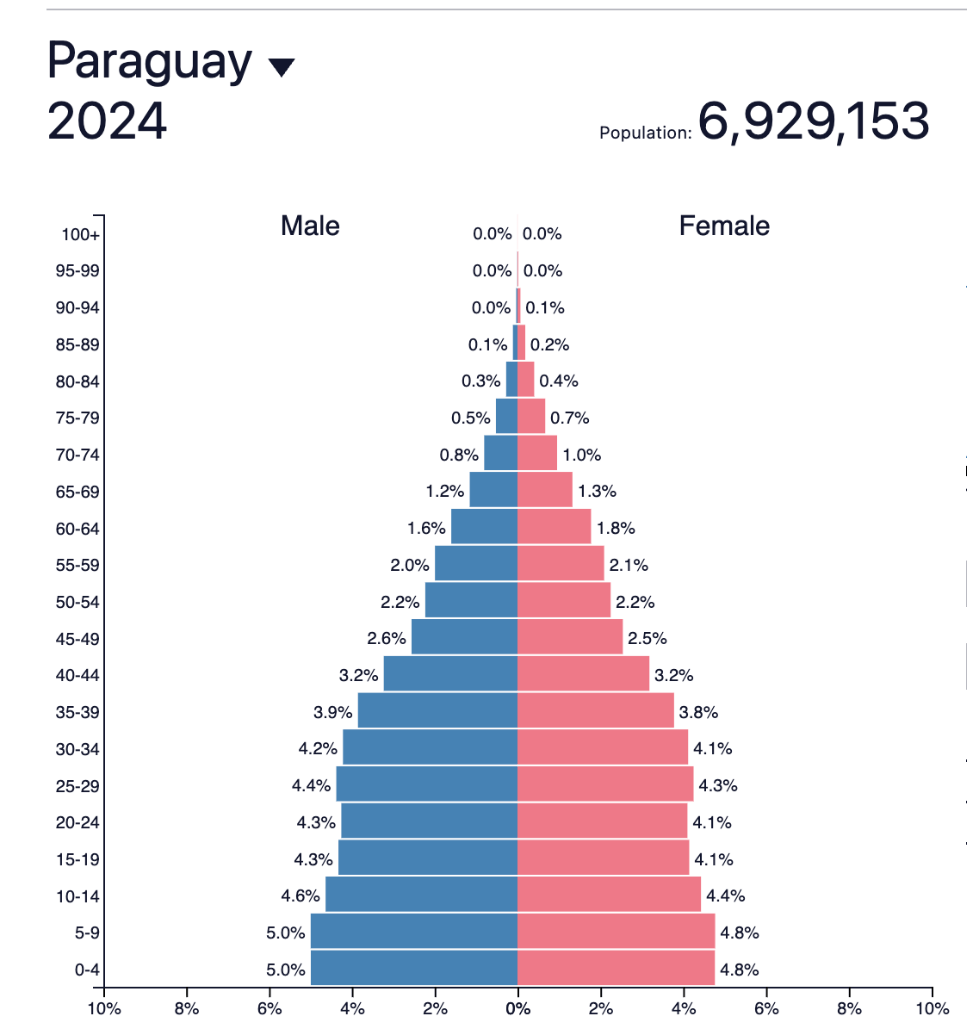
Stage 3, (Low birth rates, low death rates, lower natural increase)
The replacement rate for a population to fully replace itself.
2.1
What is Forced Migration
Identify two social factors that will reduce birth rates in countries that will lead to stage 3 DTM conditions.
Education and Contraception
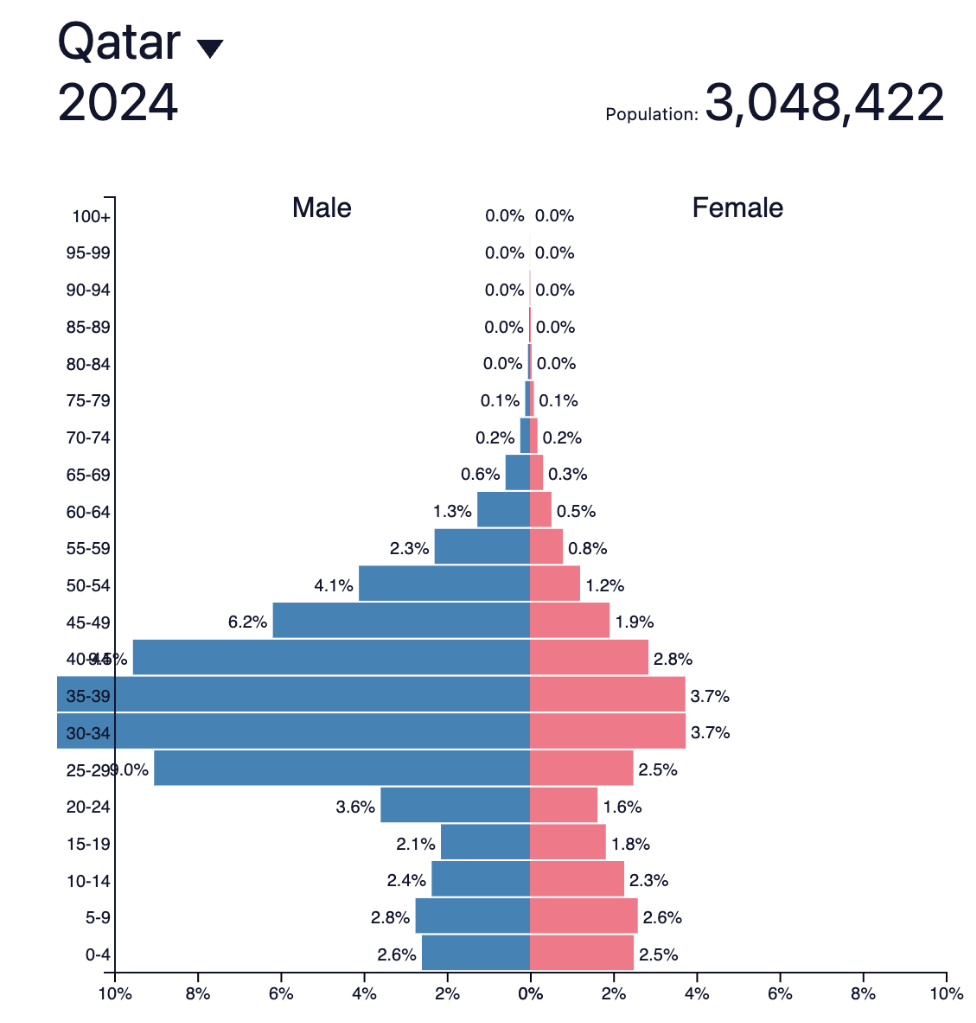
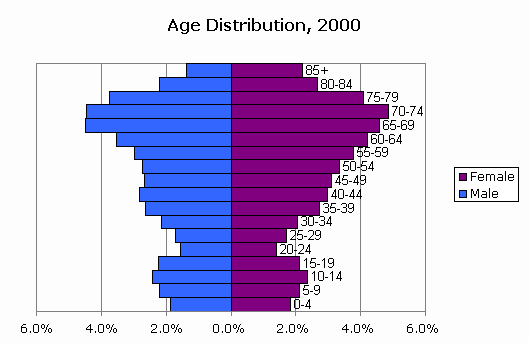 This population pyramid shows an anomaly, the reason for this strange structure is...
This population pyramid shows an anomaly, the reason for this strange structure is...List one PULL factor for each of the following categories:
Economic
Social/Cultural
Political
Environmental
Economic - higher wages
Social/Cultural - religious freedom, educational opportunities (universities), more leisure options
Political - political stability
Environmental - more attractive climate
Two countries that are currently in stage 4 of the DTM (zero growth or declining populations)
China, USA, Brazil, UK, France, Italy, South Korea, Spain, Argentina, Canada, Australia
Explain one potential reason for the skewed pattern you see on the population pyramid.
List all 7 of Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
1. Short distances
2. Urban areas
3. Multiple Steps
4. Rural to urban
5. Counter migration
6. Youth
7. Gender patterns