What are some of the economic concepts that the PPC demonstrate?
The PPC can be used to illustrate the concepts of scarcity, opportunity cost, efficiency, inefficiency, economic growth, and contractions.
Define Comparative Advantage
Comparative advantage is an economy's ability to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partners.
type of unemployment is caused by a recession?
cyclical
The circular flow model illustrates the equality of which of the following?
Total expenditure and total income
The consumer price index measures
The change over time of the weighted prices of a particular group of goods and services
Define Real GDP
an inflation-adjusted measure that reflects the value of all goods and services produced by an economy in a given year.
Draw a PPC with capital goods and consumer goods with increasing opportunity costs.
Bowed out
Define Absolute Advantage
the ability of an individual, company, region, or country to produce a greater quantity of a good or service with the same quantity of inputs per unit of time, or to produce the same quantity of a good or service per unit of time using a lesser quantity of inputs, than its competitors.
Just graduated from college and is now interviewing for jobs. This would best be described as?
Frictional
What is the equation for nominal GDP using the expenditure approach?
GDP = C+I+G+Xn
If an economy is experiencing deflation, who is hurt?
People who took a fixed-rate loan become worse off.
the nominal gross domestic product (GDP) was $50 billion and the GDP deflator was 200. Thus real GDP was
$25 Billion
Draw a PPC with Pizza and Pineapples showing constant opportunity cost
PPC has a straight line

Who has an absolute advantage in Cars
Country B

The unemployment rate in this economy is
10%
What is the equation to find nominal GDP using the income approach?
GDP= R+W+I+P

If year 1 is the base year, the consumer price index for year 2 in this economy is
175
If in a specified year nominal gross domestic product grew by 11 percent and real gross domestic product grew by 4 percent, inflation for this year would be
7%
Draw a PPC for an economy with Capital Goods and Consumer Goods showing the natural rate of unemployment.
Two frontiers. (The outer one represents the 0% unemployment the inner one represents the NRE)
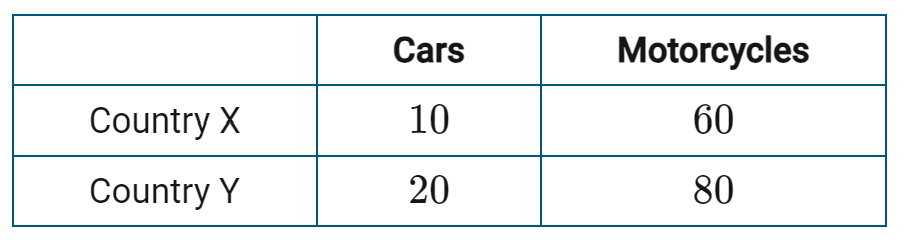
Which country has a comparative advantage in cars? And what is that countries opportunity cost
Y = 1 car = 4 Motorcycles
the elimination of jobs as a result of technological change
structural
The circular-flow model indicates that final goods are produced by
firms and sold in the product markets
In an economy, the price index in 2006 was 100 and the real gross domestic product (GDP) was $1,000. In 2010, the price index was 110 and the nominal GDP was $2,200. Based on that information, which of the following can be inferred about the economy’s nominal GDP in 2006 and real GDP in 2010 ?
Nominal GDP in 2006=$1,000; Real GDP in 2010= $2,000
What is the equation for Real GDP
Real GDP = (Nominal GDP)/(GDP Deflator)
Show what happens in the long run if a country invests in more capital goods than consumer goods on the PPC.
Shifts the Frontier outwards
Is 1 Car for 5 Motorcycle an acceptable trade between Country X and Y? What is the terms of trade range?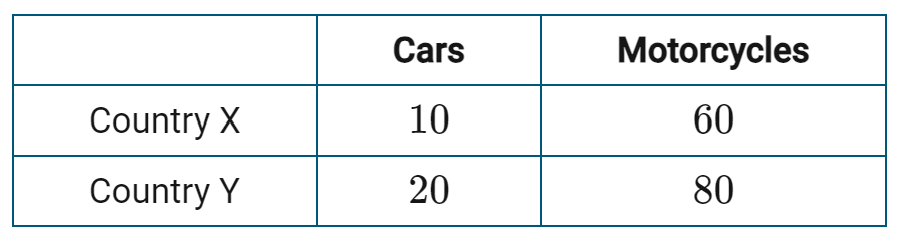
Yes and the range is 1 Car for 4-6 Motorcycles
The natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate when
there is no frictional unemployment

Calculate Nominal GDP
$220 Billion
If the consumer price index increases from 200 to 240 in a one-year period, then the inflation rate is
20%

According to the data above, in which year was real gross domestic product (GDP) the largest?
2010