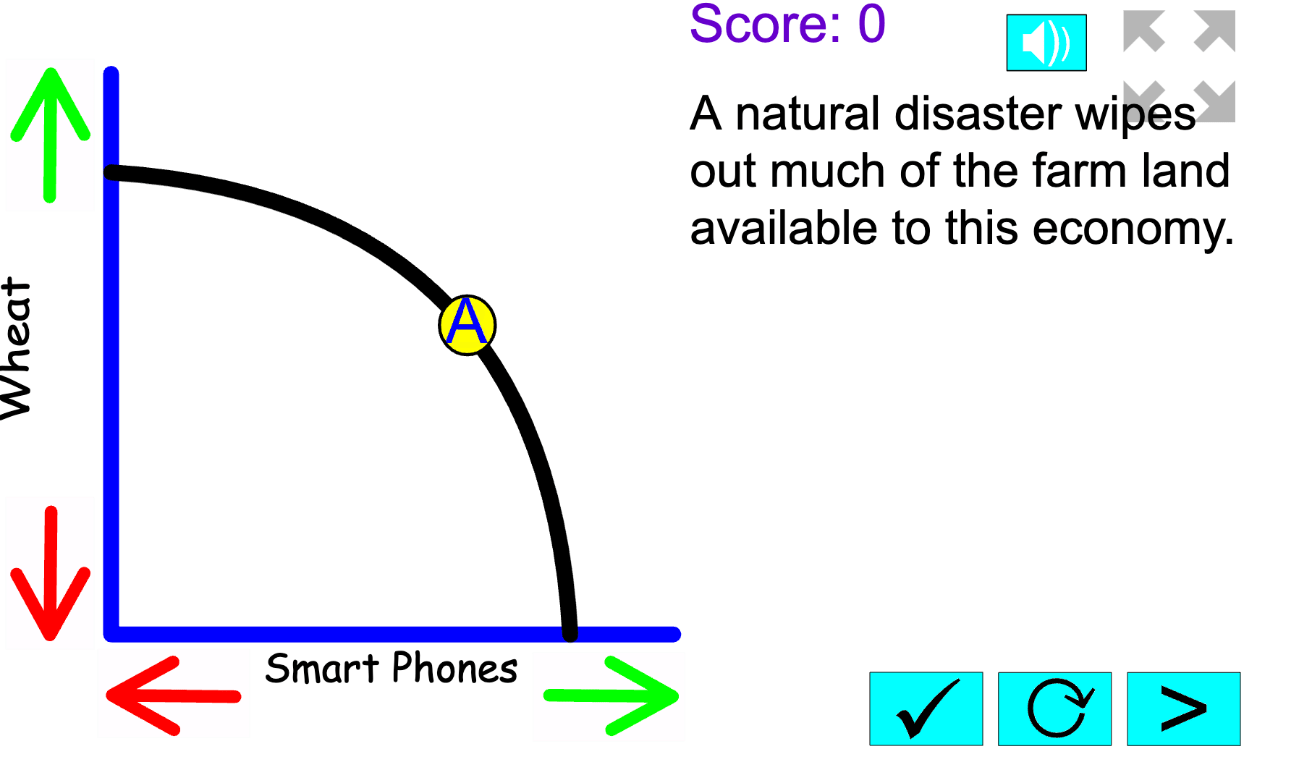
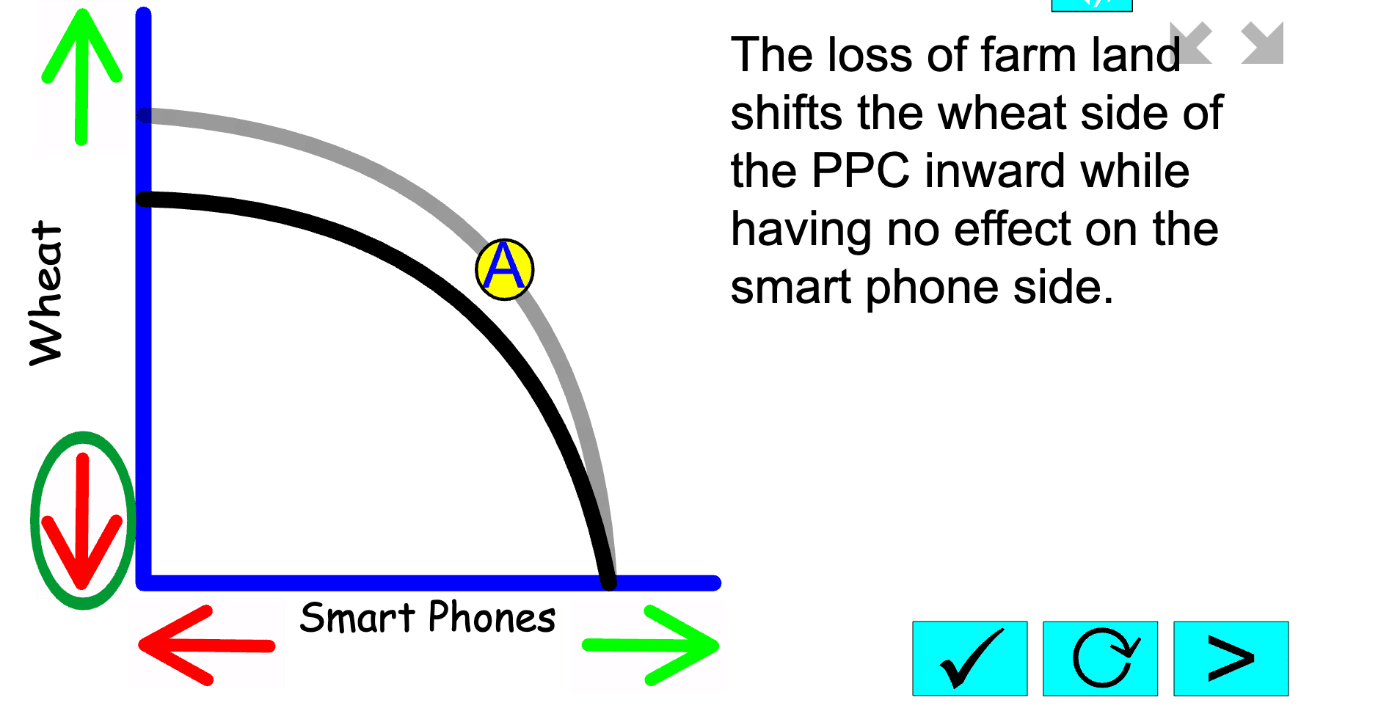
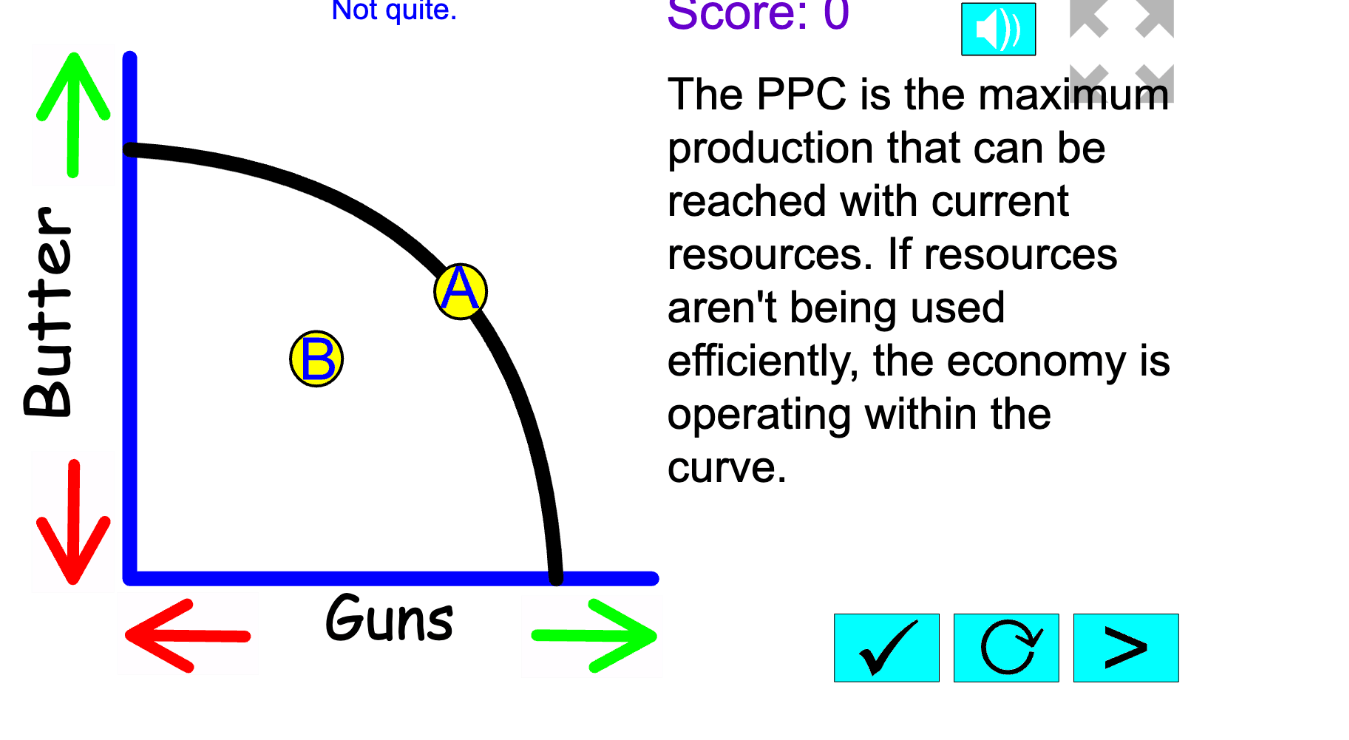
Draw a PPC for an economy that produces Guns (Y) and Butter (X). Draw what happens if the economy starts using its resources inefficiently
When one country make more of a product or can make it using fewer resources.
What is Absolute Advantage.
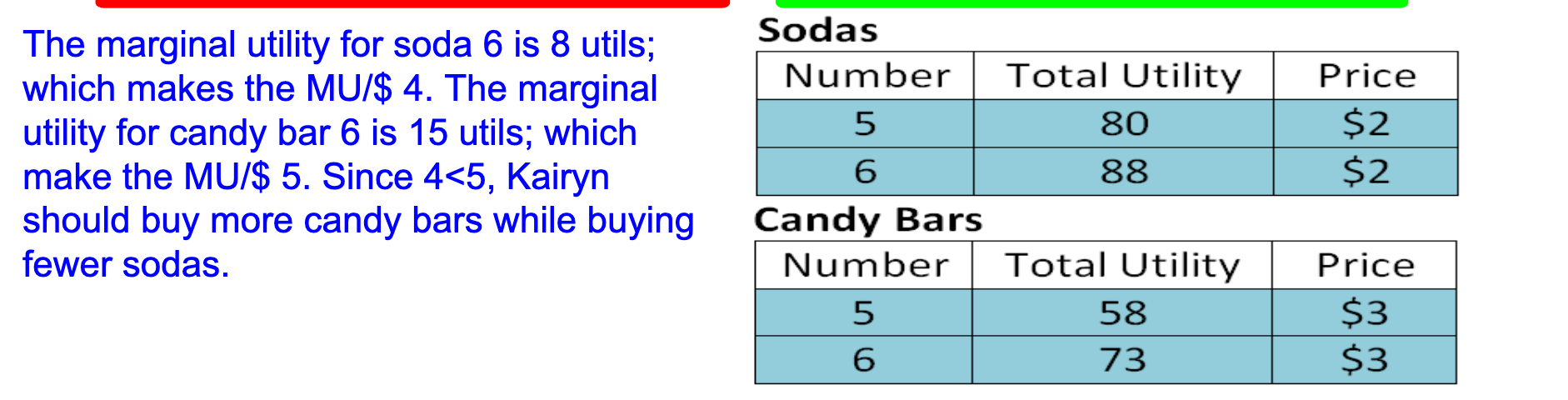
What is the equation for utility maximization?
Utility Maximization occurs when a consumer adjusts their spending to maximize their total utility within their given income limitations. Utility maximization occurs when the marginal utility per dollar for all the goods you purchase are equal (MUx/Px=MUy/Py).
Anna has two hours of free time on Friday night that can be spent studying or watching TV. Anna decides to watch TV. Studying becomes Anna's what?
Opportunity Cost
These are costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered, should not influence future decisions
Sunk Costs
The Chart shows different combinations of cat videos Mia could watch and math problems she could complete in an evening after school. What is her opportunity cost for the first 100 cat videos she watched?
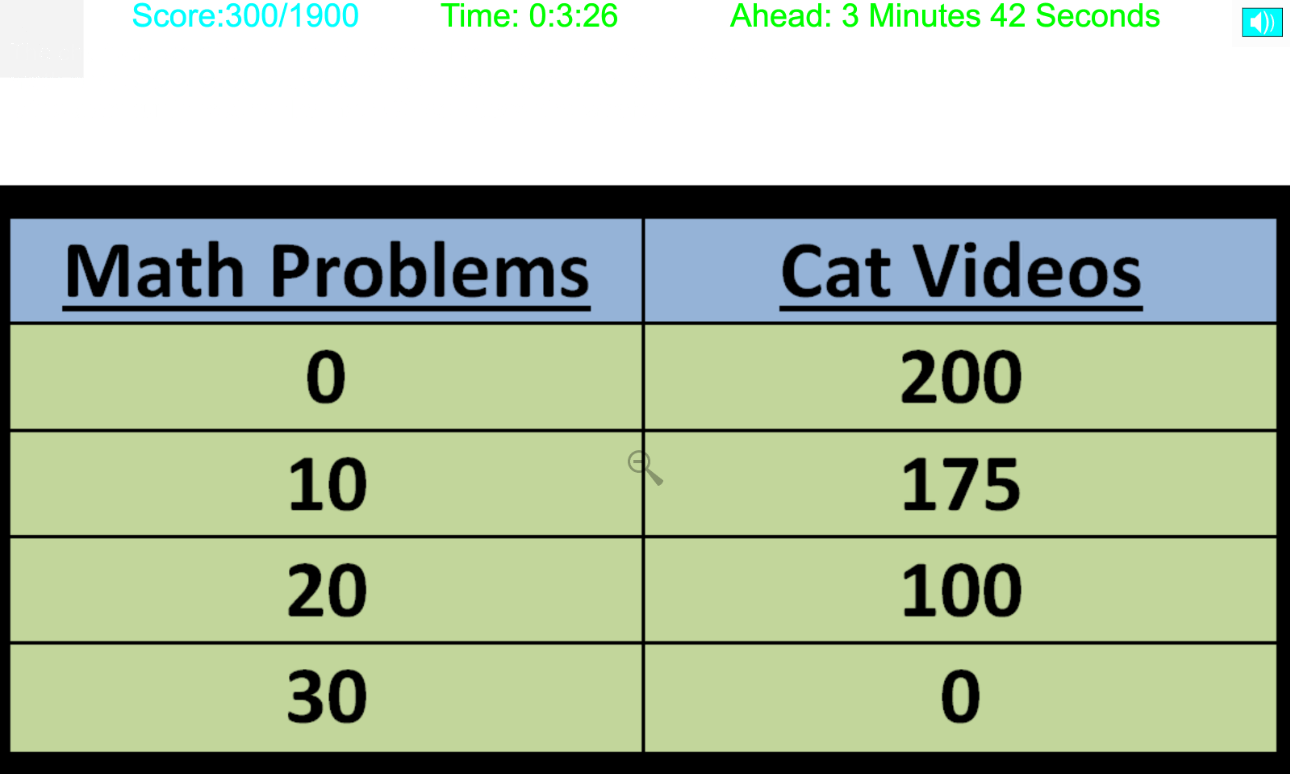
10 Math Problems
When making a rational decision, economists would point out that...
A. marginal cost is of no significance
B. marginal benefit is of no significance
C. marginal benefit should be less than marginal cost
D. marginal benefit should outweigh marginal cost
D. MB>MC
After graduating high school, Billy decided to enroll in a two-year program at the local community college rather than to accept an internship that offered a salary of $15,000 per year. If the annual tuition and fees are $5,000, the annual opportunity cost of attending the community college is:
Opportunity cost includes both explicit and implicit costs. In this question, the $15,000 in salary for the internship you gave up is the implicit cost, and the $5,000 in tuition and fees is the explicit cost of going to the community college.


What type of PPC has a constant opportunity cost? Explain.
When a PPC is a straight line, opportunity costs will be constant. This is caused by the perfect adaptability of resources used to produce both goods. In other words, the resources used to produce one good will be easily converted to the production of the other good.
An example of a straight line PPC might be an economy that produces cakes and cookies. Assuming cakes and cookies use the same ingredients, land, labor, and capital, opportunity costs would be constant. So, increasing the production of cakes by constant amounts does not change the opportunity cost. The ratio remains constant throughout the straight line PPC.
United States: 500 bushels of corn Mexico: 400 bushels of corn Absolute Advantage.
What is the United States?
Which of the following is the Total Utility if consuming one latte yields 20 utils and consuming the second latte increases satisfaction by 17 utils?
Total utility of consuming both lattes is 37
Sylvia works part-time at a local convenience store and earns $12 per hour. She wants to spend next Saturday afternoon attending a sporting event. The full price of the sporting event is $100, but Sylvia was able to get a discounted price of $75 from her cousin who purchased the ticket and is unable to attend. If Sylvia took 5 hours off from her job to attend the sporting event, what was her opportunity cost of attending the concert?
Sylvia would have earned $60 from working for 5 hours (implicit cost). She also spent $75 on the ticket (explicit cost). 60 + 75 = 135.
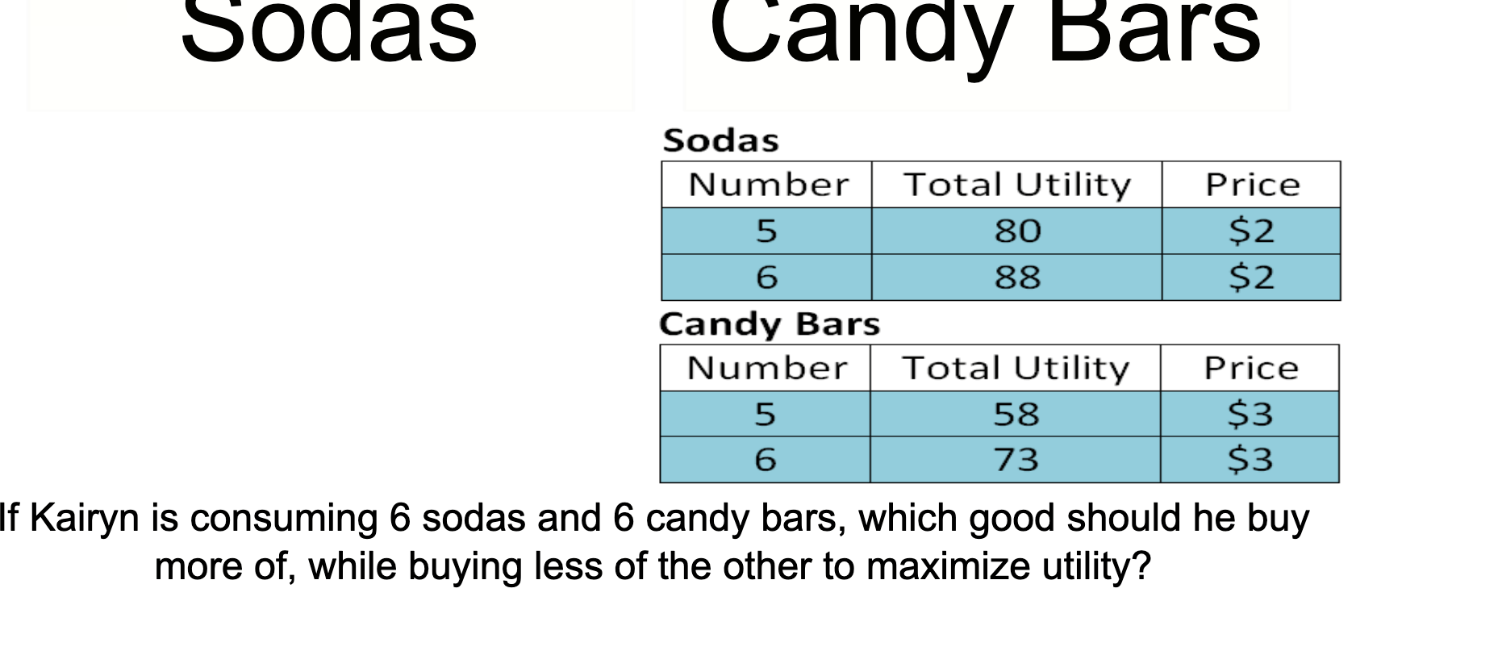
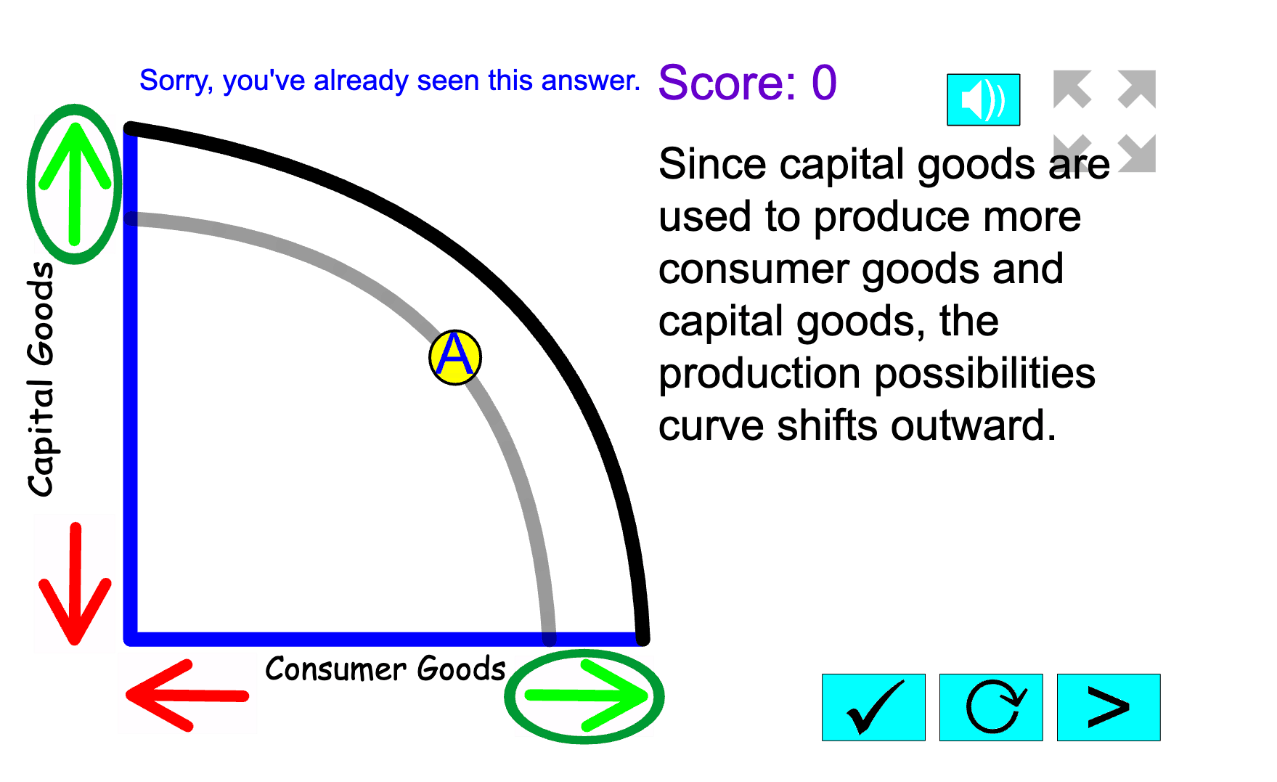
Draw a PPC for an Economy producing Capital and Consumer Goods that shows the impact of more investment in capital goods. Include all labels and arrows

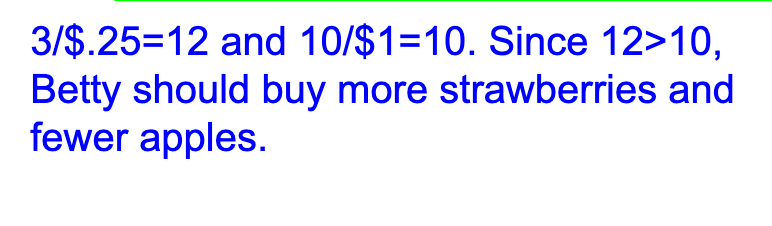
All of the following are included in computing the opportunity cost of attending college EXCEPT:
(A) interest paid on student loans
(B) wages the student gave up to attend college
(C) money spent on books and supplies
(D) money spent on college tuition
(E) money spent on clothing expenses
Answer
Choice E
Explanation
No matter what decision you make, you will always have clothing expenses.
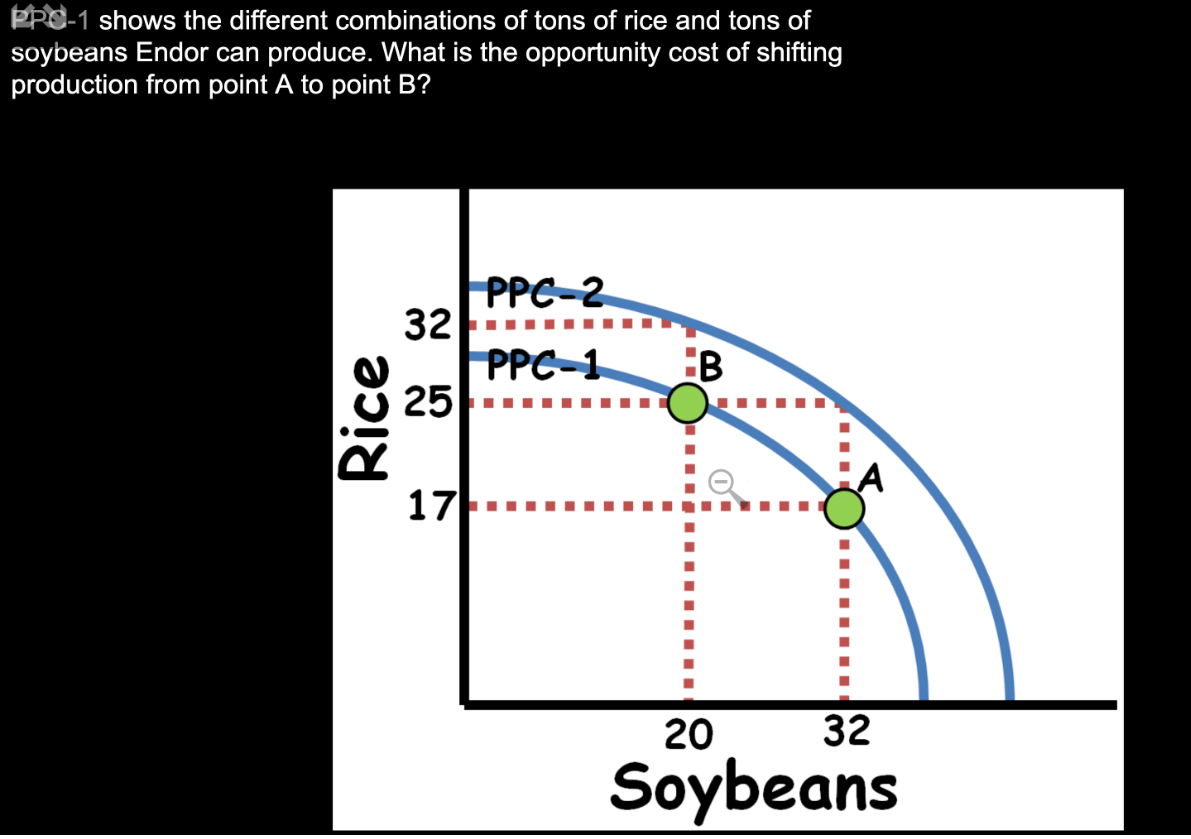
12 Soybeans (32-20)
What are the three shifters of the PPC? Hint. For the third shifter, How can we consume outside the PPC?
Change in the quantity or quality of resources. Change in technology. Trade.
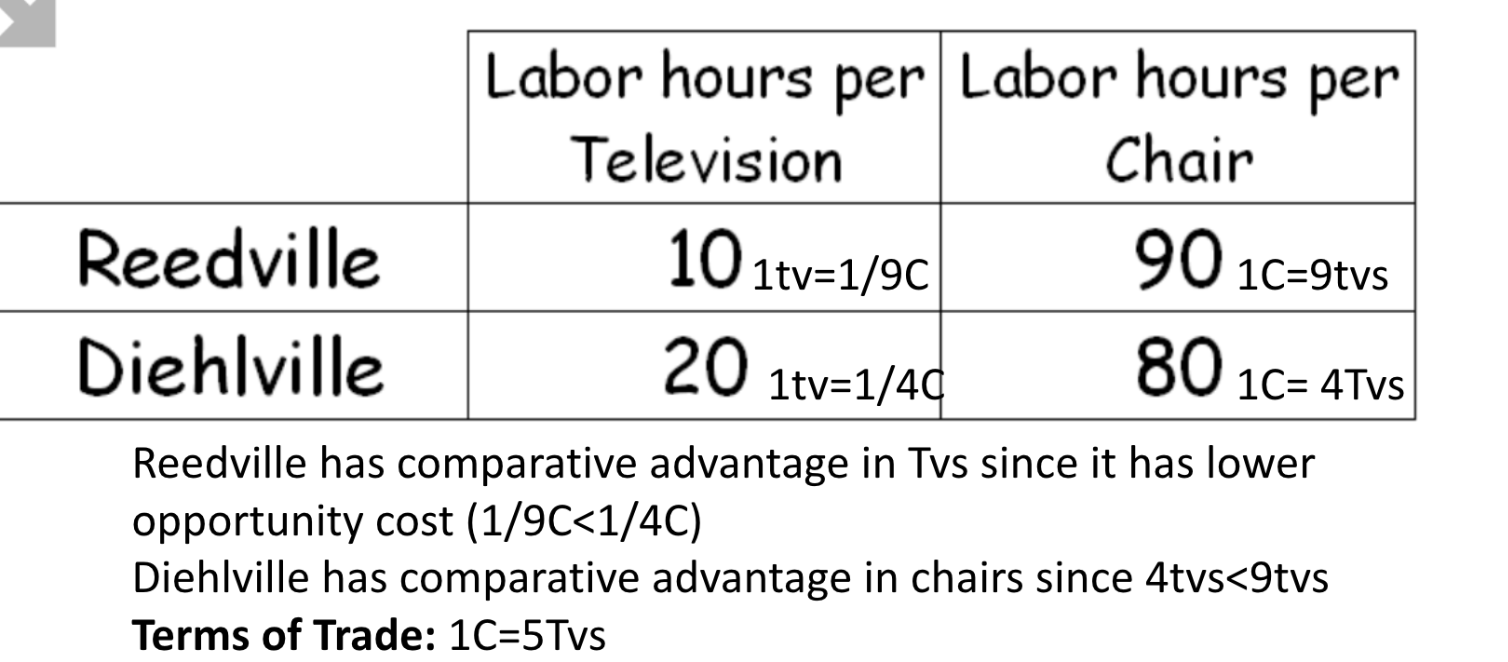
Calculate who has the comparative advantage and absolute advantage in each good. Acceptable Terms of Trade?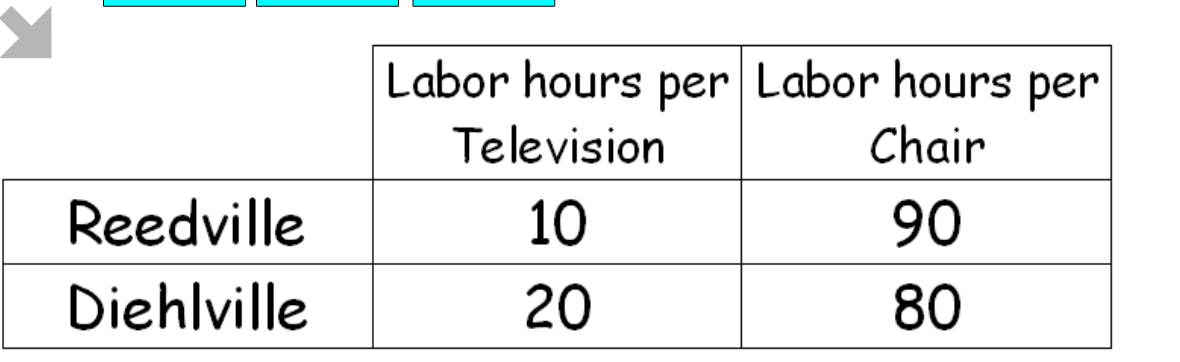
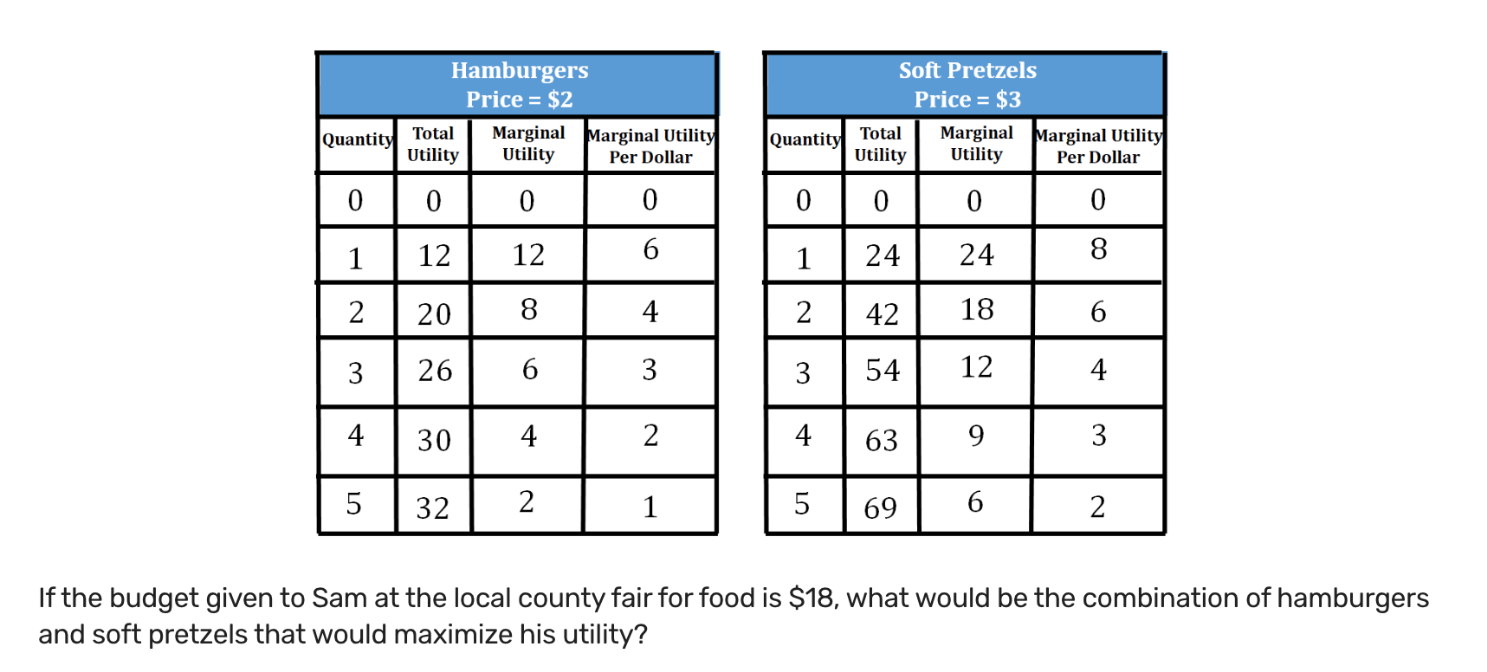
3 hamburgers 4 soft pretzels
Explanation
- He would first buy ONE soft pretzel because the MU/P of 1 soft pretzel is 8 and the MU/P of one hamburger is 6. He will be left over with $15.
- Next, he will buy a SECOND soft pretzel (MU/P = 6) and a FIRST hamburger (MU/P = 6). He will have $10 at this point.
- Then, he will buy a SECOND hamburger (MU/P = 4) and a THIRD soft pretzel (MU/P = 4). He will end up with $5 after this.
- Finally, to use the last of his budget, he would buy his THIRD hamburger (MU/P = 3) and the FOURTH soft pretzel (MU/P = 3)
The ideal combination would be 3 hamburgers and 4 soft pretzels. MU/P of 3 hamburgers = MU/P of 4 soft pretzels (3 = 3), while still staying in budget.

3 Pepsis