This is the law that states that as variable resources are added to fixed resources, marginal product will eventually fall
What is the law of diminishing marginal returns
These are the four kinds of costs firms face in the short-run.
What are fixed costs, variable costs, total costs, and marginal costs?
This is the profit maximizing point for a firm
What is MC=MR
This is what firms will do if other firms are earning a profit in a particular market.
What is entering that market?
These are 3 characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Markets
What are no barriers to enter/exit, many buyers/sellers, identical products, firms are price-takers, firm's demand curves are horizontal?
This is the difference between the short-run and the long-run in economics.
What is the fact that in the short-run at least one input is variable, while in the long-run there are no variable inputs?
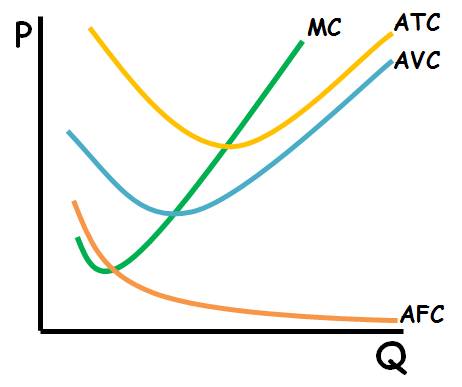
This is what a graph with a firm's marginal cost curve, an average total cost curve, a average variable cost curve, and an average fixed cost curve.
What is: Total Revenue-Total Explicit Costs?
This is one of the two scenarios in which a firm will shut down in the short-run?
What is when price is less than average variable costs OR when total revenue is less than total variable costs?
These are the places on a graph in which allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are achieved in a perfectly competitive market.
What is where MC=MR=D=AR=P for allocative efficiency and where MC=Minimum ATC for productive efficiency?
This is an example of a marginal product curve.
What is:

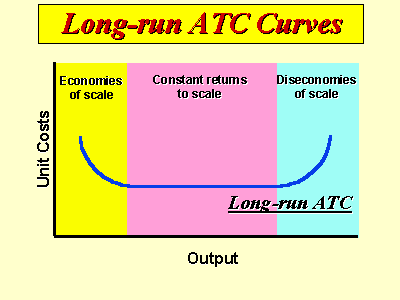
This is what a firm's long-run average total cost curve looks like with Economies of Scale, Constant Returns to Scale, and Diseconomies of Scale.
What is:
This is an entrepreneur's economic profit in the following scenario:
Instead of working as a web designer earning $60,000 per year, they start their own web design business. He uses savings that could have earned $5,000 in interest to buy equipment for their company. Their annual expenses for employees, software, and utilities total $80,000. If their total revenue from clients during the first year is $150,000, their total economic profit is:
What is $5,000?
This is why firms sometimes continue to operate despite earning loses?
What is because the loss they receive by operating is less than the loss they'd receive by shutting down due to their fixed costs?
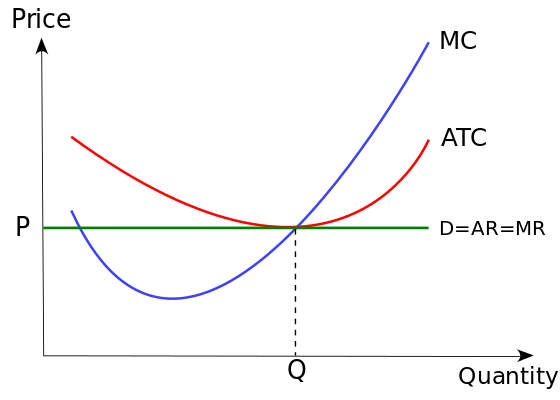
This is an example of a graph including a firm's marginal cost, average total cost, marginal revenue, average revenue, demand, price, and quantity in a perfectly competitive market in long-run equilibrium
What is:
This is what happens to total product when marginal product is at 0.
What is total product is at a maximum?
This is the total cost of producing a 6th unit of output according to the table below.

What is $230?
This is what a firm should do with their output if the marginal cost of producing a good is $15 and the marginal revenue is $10.
What is reducing their output since MC exceeds MR?
This where a firm's supply curve is on graph below:

What is the MC curve beyond Q1/P1?
Imagine a firm was earning economic losses in a perfectly competitive market. This is what would happen to the amount of firms in the industry, the price the firm charges, and the quantity the firm produces in the long run
What is that the number of firms would decrease, and the amount the firm produces and the price they charge will increase?
This is the relationship between marginal product and marginal cost.
What is that when marginal product is increasing, marginal cost is decreasing OR when marginal product is decreasing, marginal cost is increasing.
This is the average variable cost of producing a 3rd unit of output according to this chart

What is $16.66?
This is how much revenue that Jordan needs to net 0 economic profit in the following scenario:
Jordan decides to open a small bakery. He pays $40,000 per year to rent his storefront, spends $35,000 annually on ingredients and utilities, and hires a part-time worker for $25,000 per year. If Jordan could have earned $60,000 working as a chef elsewhere, what amount of annual revenue must his bakery earn for him to make zero economic profit?
What is $160,000
This what a profit-maximizing firm would do in the following scenario:
Imagine a business's marginal cost equals AVC at $25, its marginal cost equals ATC at $30, and its marginal cost equals marginal revenue at $28
What is continuing to operate in the short-run, despite losing money?
Imagine a firm was in a perfectly competitive market in long-run equilibrium. This is what would happen to its marginal revenue, quantity produced, and economic profit if demand for their good increased in the short-run.
What is that marginal revenue, quantity produced, and economic profit would all increase?