Those functions of the body necessary for life.
Vital Functions
What is the most inferior of the brainstem?
Medulla oblongata
Letter D.
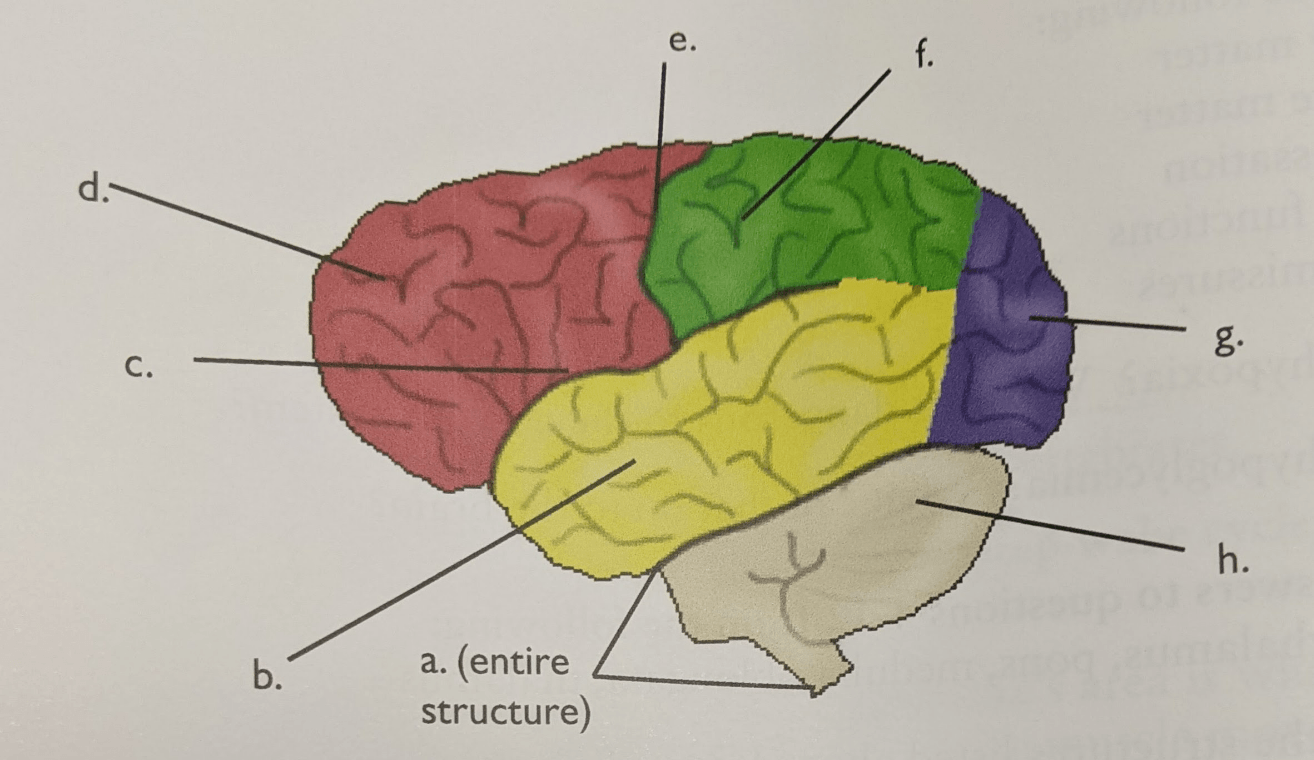
Frontal lobe
The hills of the brain?
Gyri
The anatomical crossing over of neurons from left to right.
Decussation
Which structure have nuclei dedicated to reflexes involving the senses of hearing and sight?
midbrain
Letter b.

Temporal lobe
The valleys of the brain?
Sulci
Collection of neuron cell bodies and their associated neuroglia.
Gray matter
Which structure relays messages from the cerebrum to the cerebellum?
Pons
Letter g.

Occipital lobe
Condition in which the glucose levels in blood get too low.
Hypoglycemia
bundles of parallel axons and their coverings
White matter
What structure controls the pituitary gland?
Hypothalamus
Letter f.

Parietal lobe
The part of the brain that performs subconscious motor function
Cerebellum
Connections of neuron axons that allow the two hemispheres of the brain to communicate with one another.
Commissures
Performs crude interpretation of sensory information
Thalamus
Letter h.

Cerebellum
Condition in which the brain is not getting enough oxygen due to poor blood supply
hypoxia