determines the orientation of the head relative to the pull of gravity
Static equilibrium
Letter f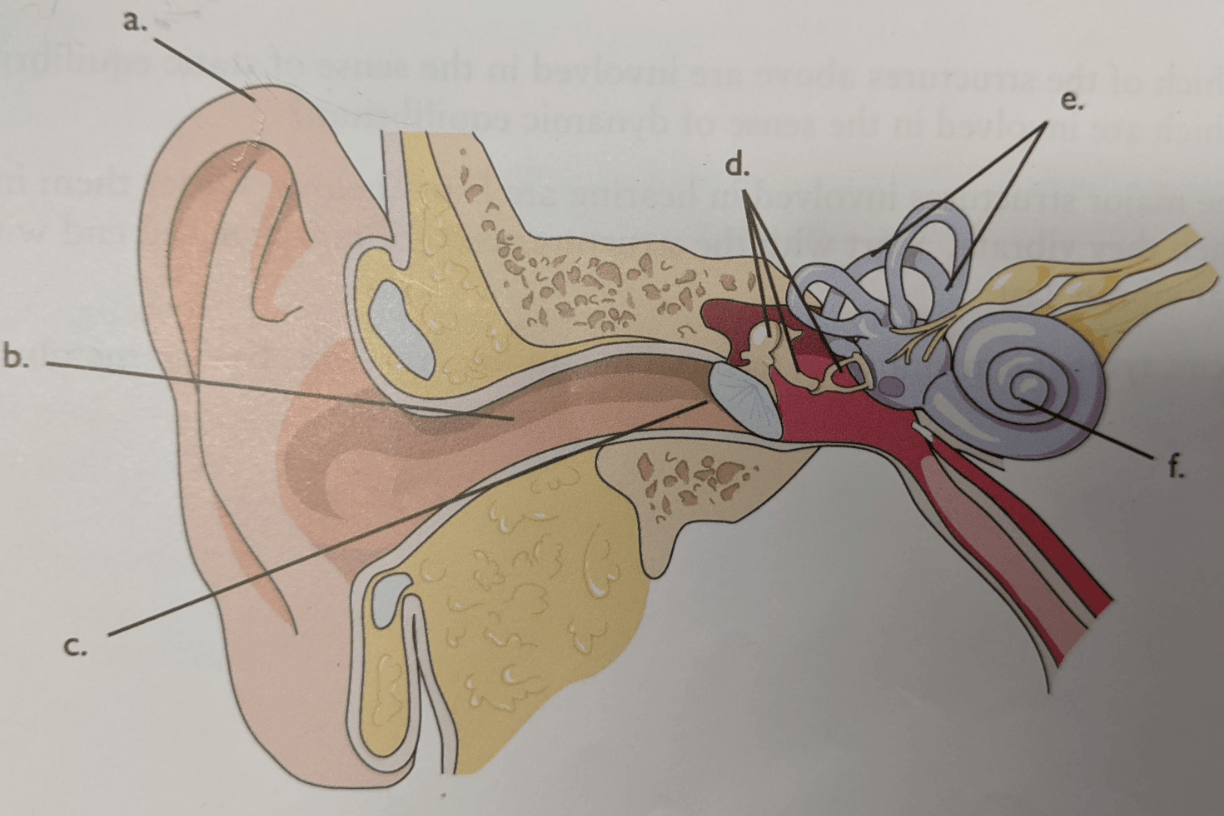
Conchlea
contains light receptors that detect light
Retina
contains muscles that control the size of the pupil
Iris
Cells responsible for the detection of color
Cones
helps determine the rotation and acceleration of the head.
Dynamic equilibrium
Letter e
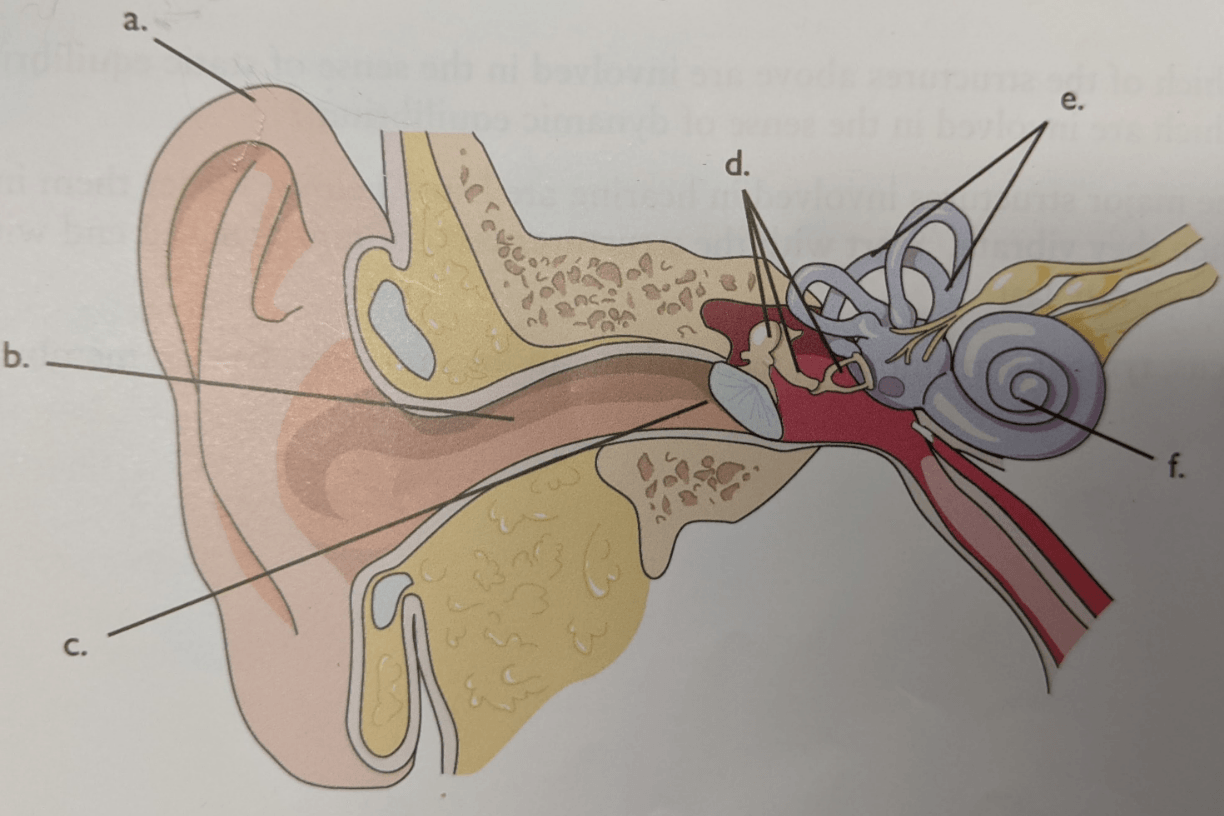
Semicircular canals
allows light to enter the eye and constricts or dilates to regulate light entry
pupil
bends light to focus it on the retina
Lens
Cells responsible for the detection of low light
Rods
the height of a sound wave that is associated with loudness
amplitude
Letter c
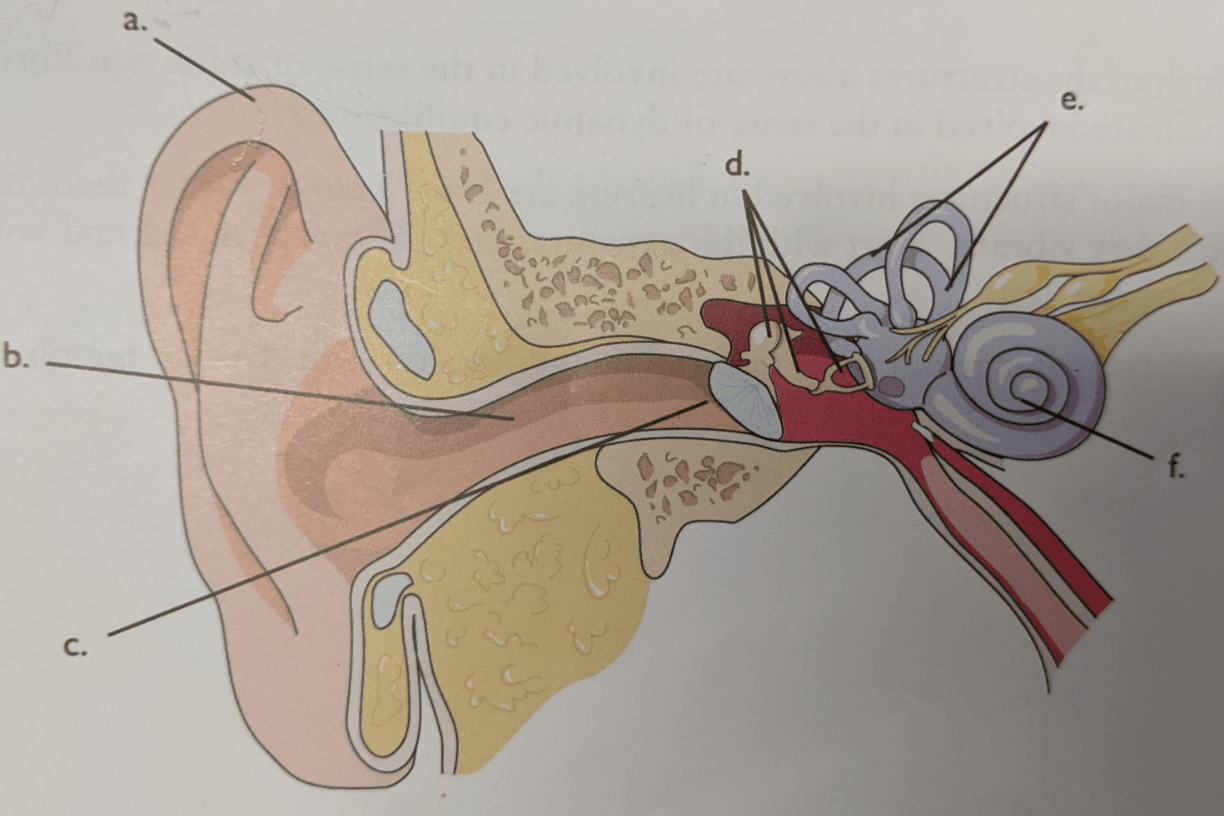
Tympanic membrane
Carries action potentials to the brain
Optic nerve
maintains the shape of the eyeball, protects the inner components of the eye
Sclera
The first structure in the ear to vibrate
Tympanic membrane
how often a sound wave passes by a given location. associated with pitch
Frequency
Letter a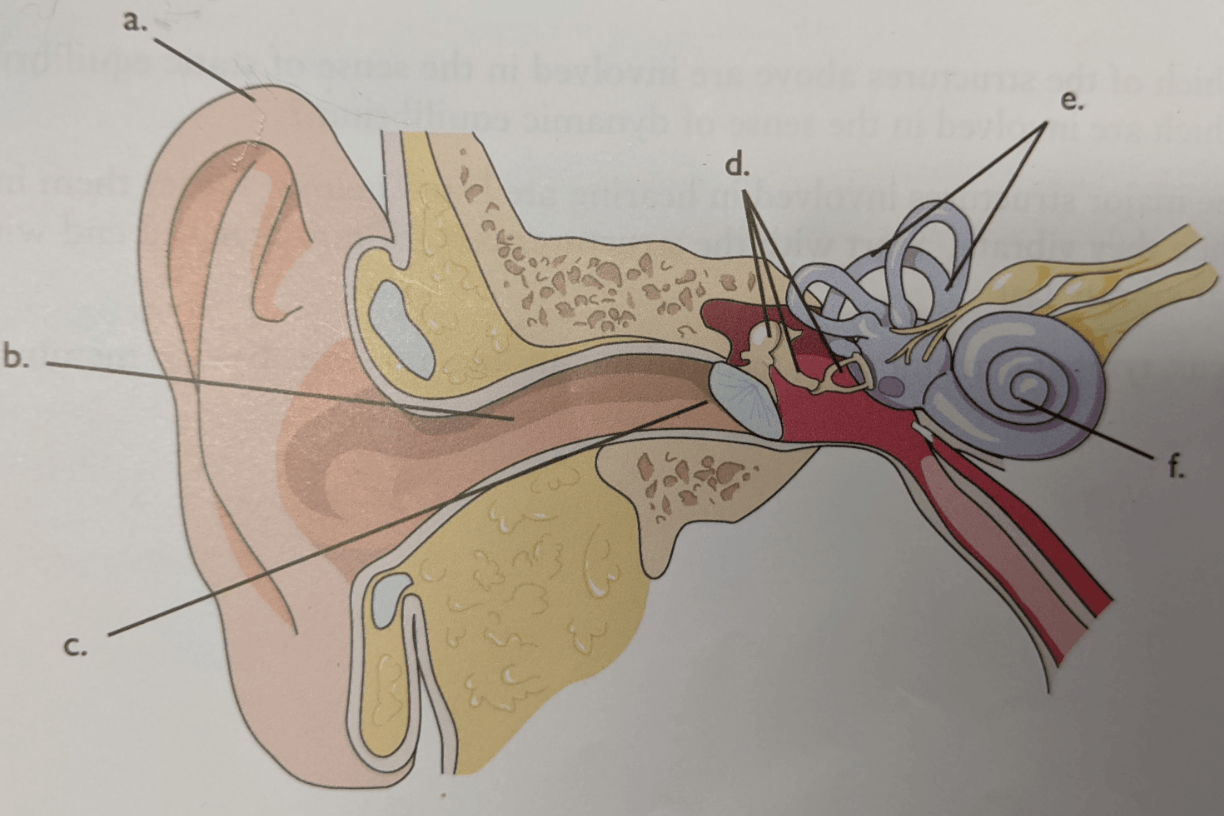
Auricle
connects the ciliary body to the lens
Suspensory ligaments
Maintains general eye shape and pressure as a filler
Vitreous humor
The ability to see objects far away but cannot focus on things closer
Farsighted
Otoliths
tiny rocks suspended in maculas to help with static equilibrium
Letter d
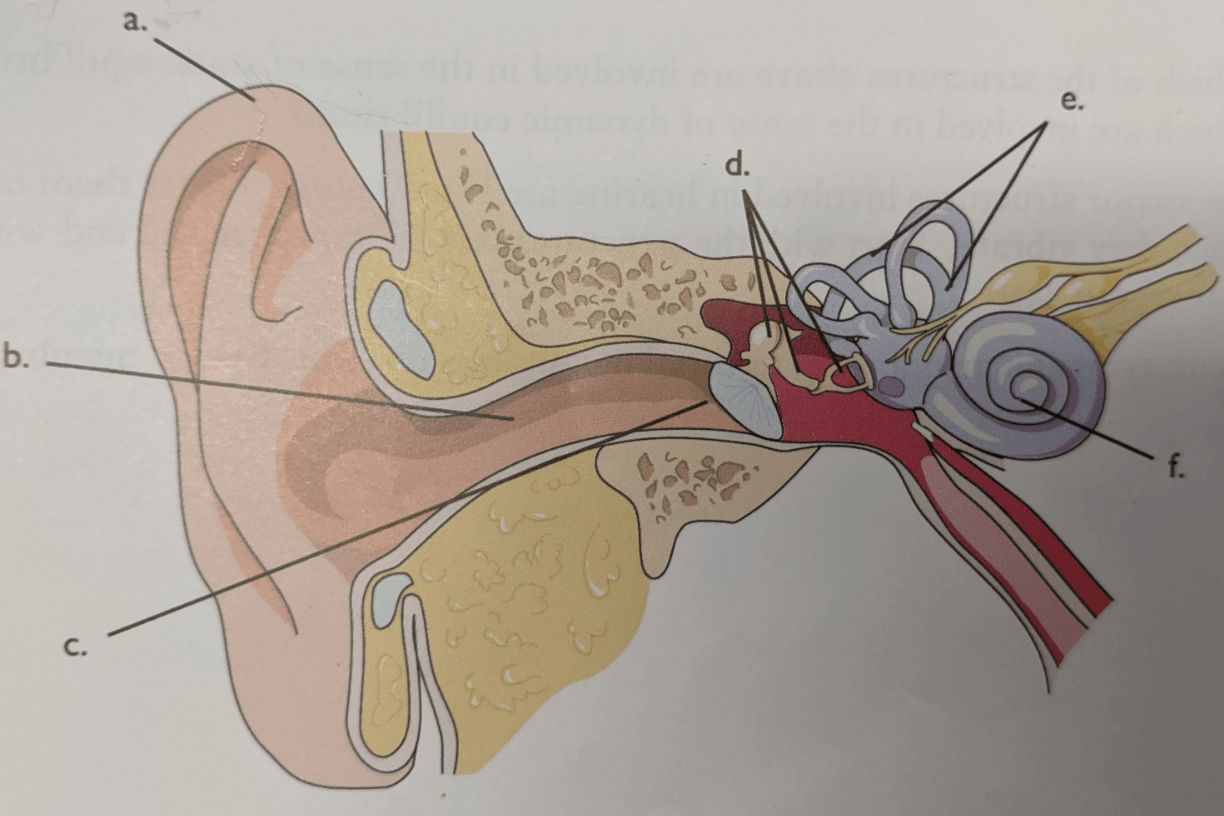
Auditory ossicles
contains a muscle which changes the shape of the lens
Ciliary body (muscle)
Protects and lubricates the exposed part of the sclera
Conjunctiva
The process of the lens changing shape to adjust the eye's focus at near distances
Accommodation