:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13055/Occipitofrontalis_muscle.png)
Frontalis
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12986/jt6lkyuTYizDZFWnsiHpng_Musculus_rectus_abdominis_01.png)
What provides the energy for the myosin head to move?
ATP
What does ATP become when energy is released?
ADP + P
What type of muscle lines your digestive tract?
Smooth
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13946/aHliOOl62koJhumoZcUysg_vsBTp2iDc2_M._triceps_brachii_1.png)
Triceps brachii
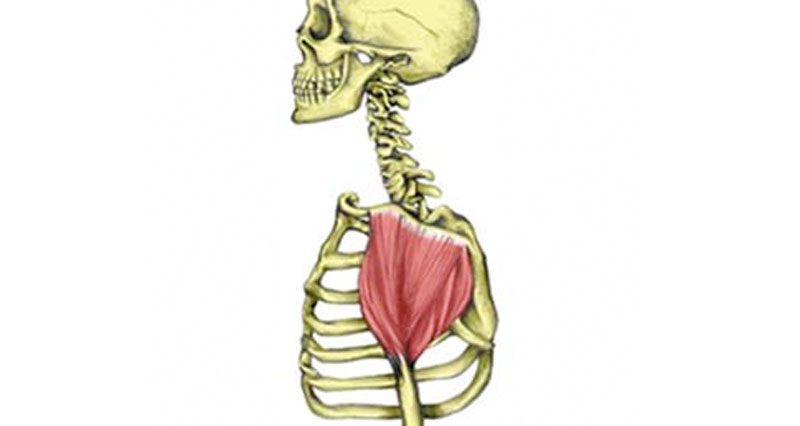
Deltoid
The myosin head forms a __________ with the actin filament and moves it.
Cross-bridge
In our experiment, the pipe cleaner served as the _______________ (2 words).
Myosin head
What type of muscle is voluntary?
Skeletal
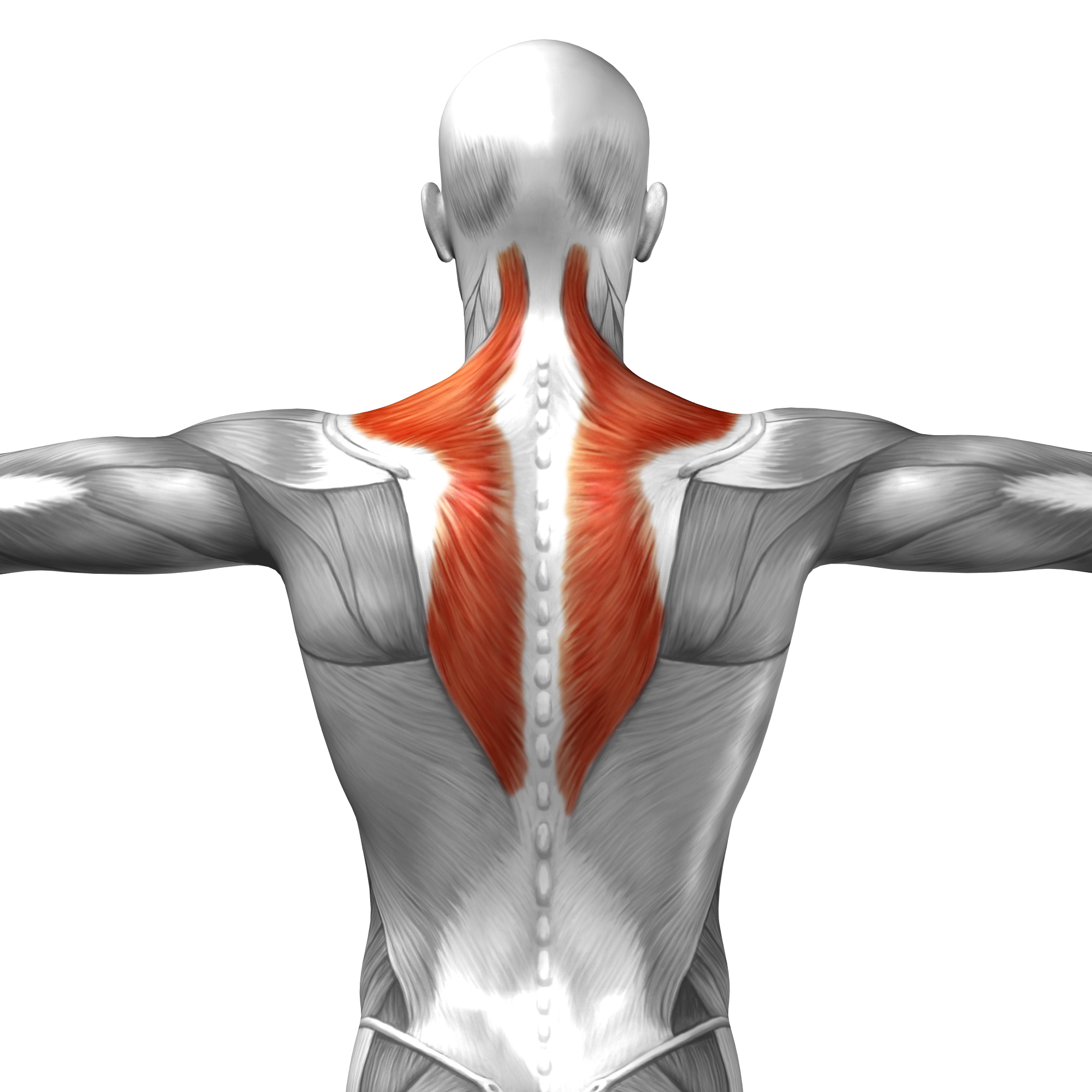
Trapezius
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/biceps-brachii-muscle/Z2RGP51azUCAFCn357O30g_Biceps_brachii_muscle.png)
Biceps brachii
The energy from the ATP molecule is used by the myosin head to release from the actin filament and return to its original position. This is called the _____________________ (2 words).
Return stroke
______________ exits the cell after the return stroke.
Calcium
A bundle of muscle fibers is called a...?
Fascicle
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13535/Wt6B7qUeKq5WqFGlzsQ_Musculus_pectoralis_major_01.png)
Pectoralis major
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13052/L77GpC0EIuzBqMfN8dU8xw_833_Thoraxmuskeln_ventral_NN.png)
External obliques
What type of membrane covers a fascicle?
Perimysium
What type of membrane covers an individual muscle fiber?
Endomysium
What build up in your cells to make your muscles sore?
Lactic acid
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/gastrocnemius-muscle/DLZb0oIzs3boKZ6CRge3Q_UBNnWrJfEfzi1t893NoOyg_Pzr4hPK6pL_M._gastrocnemius_NN_2.png)
Gastrocnemius
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13441/IrtirBf6PsVLImfncXQHWQ_Musculus_latissimus_dorsi_1.png)
Latissimus dorsi
The attachment of the tendon to the more stationary bone is called the __________.
Origin
The attachment to the more movable bone is called the _________________.
Insertion
___________ attach muscles to bones.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13458/2ZRAUJCRUT2KYlPmeve3g_M._gluteus_maximus_02.png)
Gluteus maximus
Soleus
___________ rushes in from a nerve cell to remove the blocking molecules and make the active site available to be engaged
Calcium
What is this called? 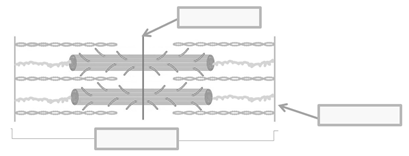
Which type of membrane surrounds the entire muscle?
Epimysium
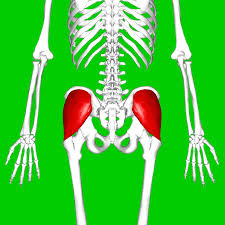
Gluteus medius
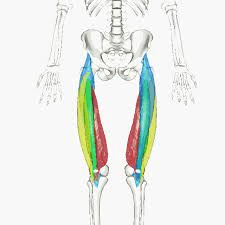
Quadriceps
Which two structures engage to create a muscle contraction?
Actin & myosin
Which two structures block the active site on an actin filament?
Troponin & tropomyosin
What type of respiration happens when your muscles are worked strenuously and the glucose supply is exhausted?
Anaerobic respiration