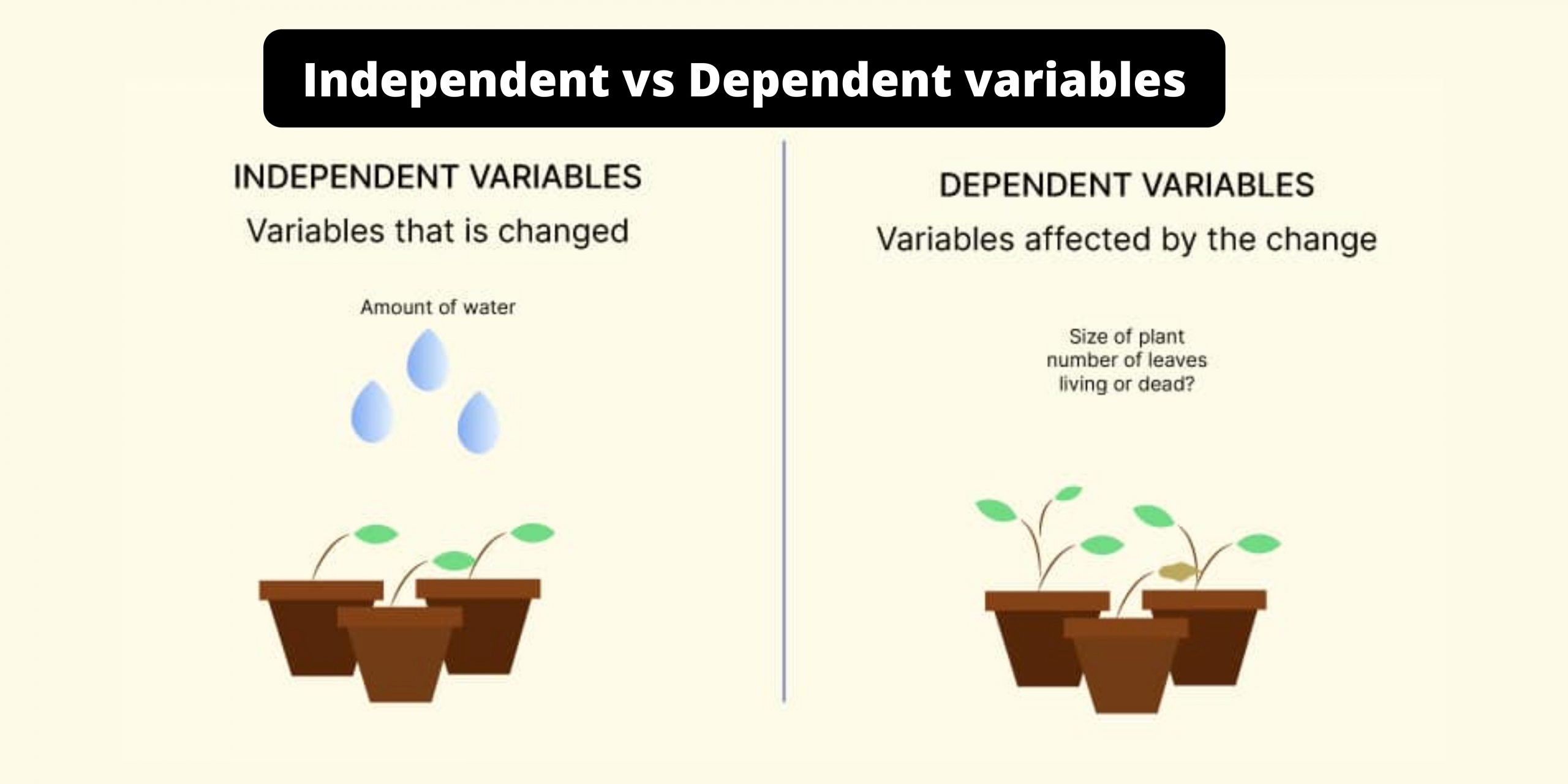
The variable that researchers manipulate in an experiment.
What is the independent variable?
Explanation: The independent variable is controlled or changed by the researcher to examine its effect. For example, giving participants different amounts of caffeine to measure alertness.
This part of the brain is responsible for heartbeat and breathing.
What is the medulla?
Explanation: Located in the brainstem, the medulla controls vital autonomic functions.


The part of the eye that contains photoreceptors (rods and cones) that detect light and start the visual process.
What is the retina?
Explanation: The retina contains photoreceptors (rods and cones) that detect light and start the visual process.

Learning by association is known as...
What is classical conditioning?
Explanation: Pavlov’s dogs learned to salivate to a bell when it was paired with food.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2794859-article-classical-conditioning-5ac50cc9c5542e0037d54692.png)
This is the process of getting information into memory.
What is encoding?
Explanation: Encoding is the first step in memory formation. Example: Reading notes before a test to commit information to memory.

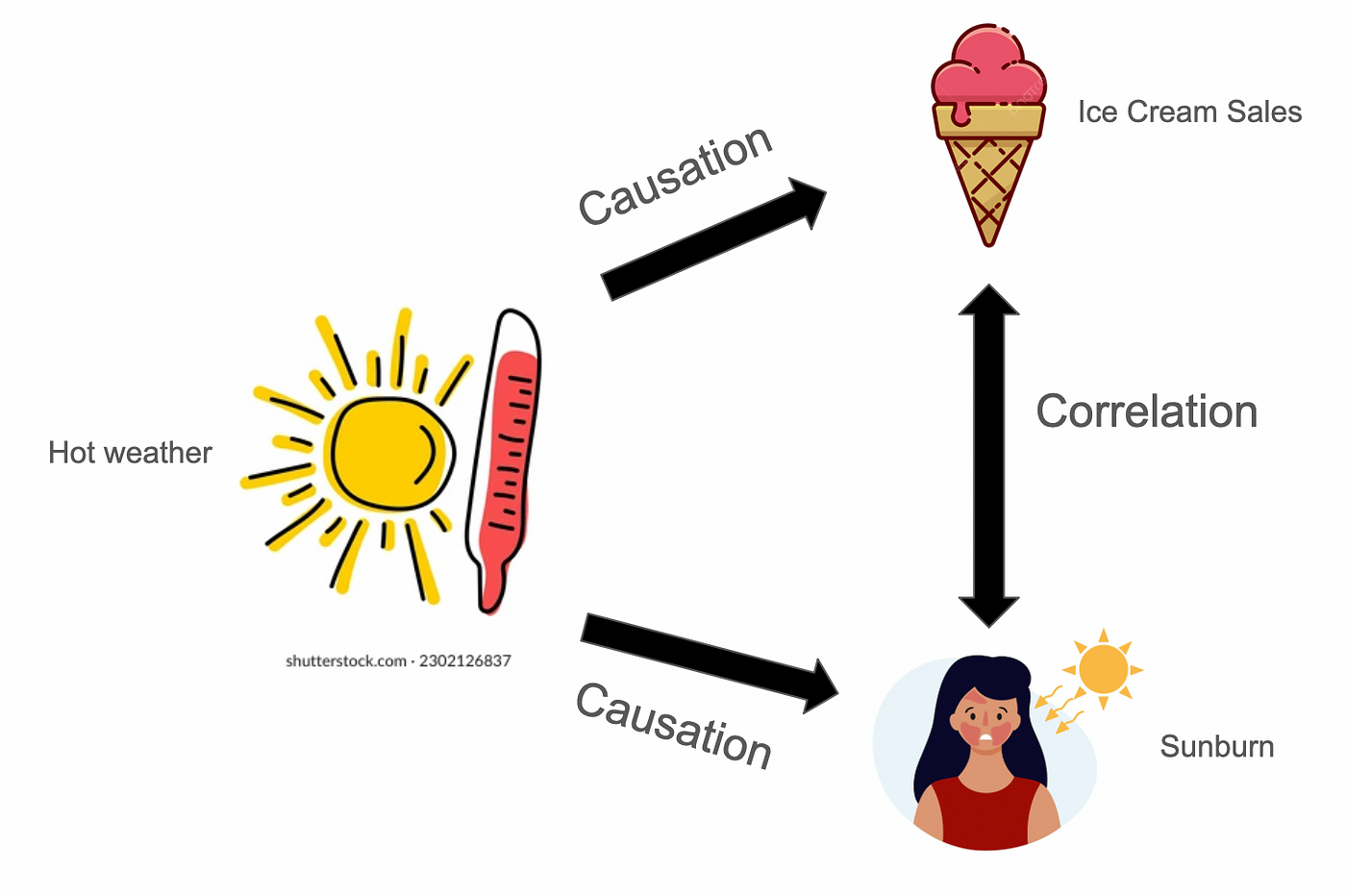
A study finds that as stress increases, sleep decreases. What kind of correlation is this?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY: Correlation does NOT equal ___________.
What is a negative correlation?
Explanation: Negative correlation means one variable increases as the other decreases. This doesn't imply causation.

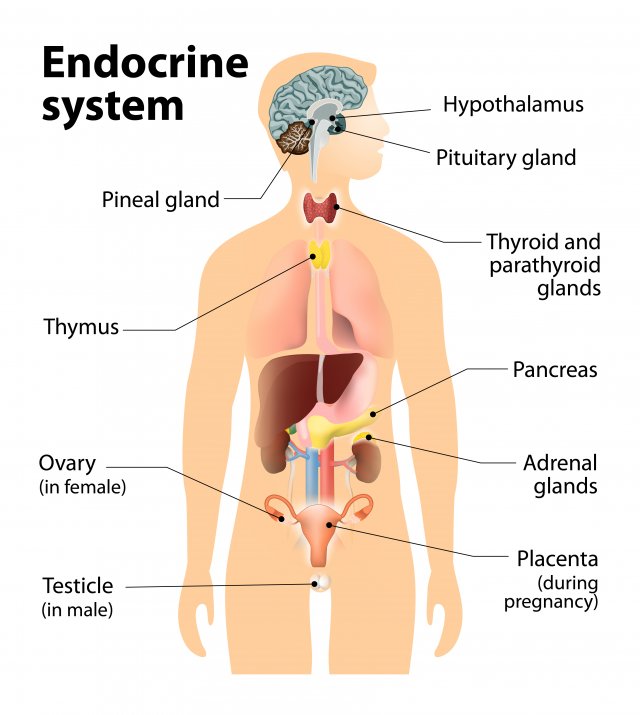
The brain structure that regulates hunger, thirst, and body temperature
What is the hypothalamus?
Explanation: The hypothalamus maintains homeostasis and controls the endocrine system via the pituitary gland.

The process that converts sensory input into neural signals
What is transduction?
Explanation: Transduction happens in sensory organs, like rods and cones in the eye, converting light into signals.


The psychologist most associated with operant conditioning.
Who is B.F. Skinner?
Explanation: Skinner used reinforcement and punishment to shape behavior using the operant chamber (“Skinner box”).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)

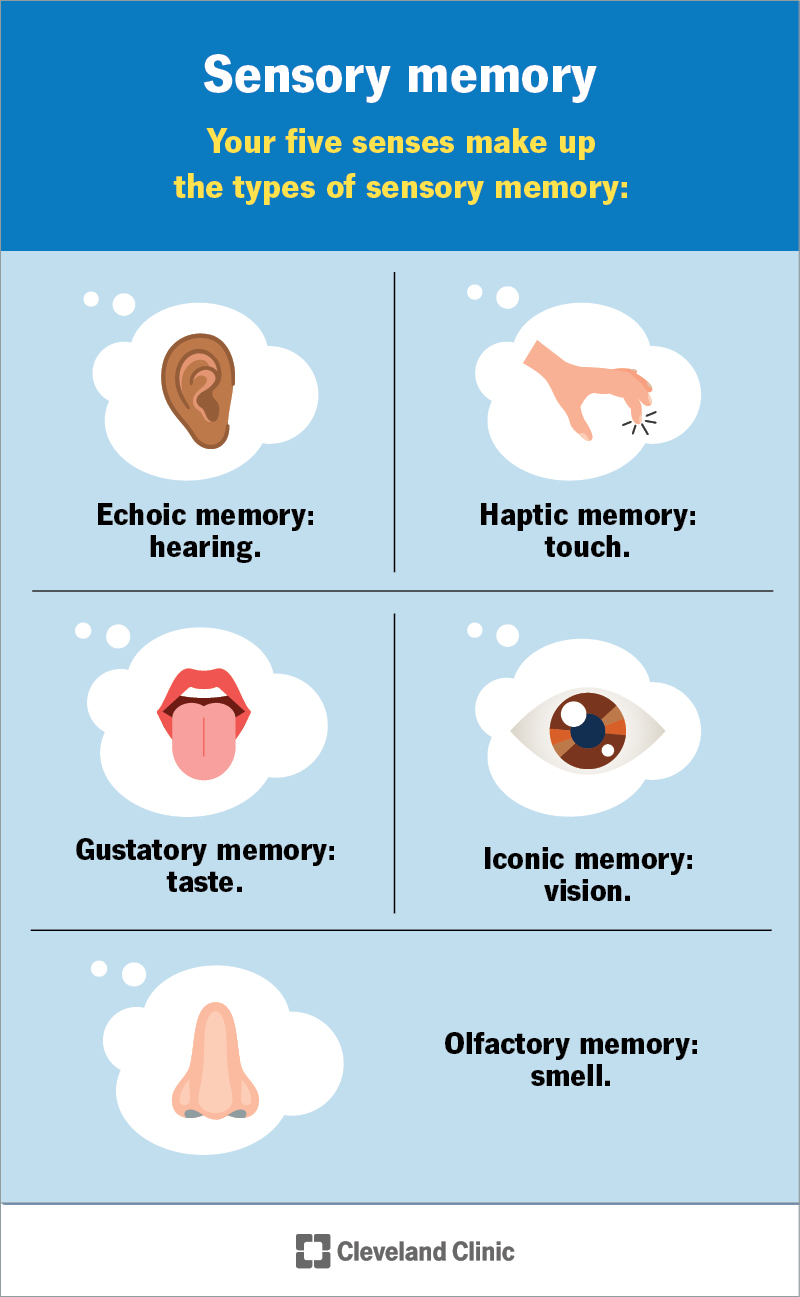
The memory system that lasts only a few seconds and holds sensory info
What is sensory memory?
Explanation: It briefly holds stimuli (e.g., a sparkler’s light trail), allowing perception to continue smoothly.

Ethical guideline for psychological research in which participants must voluntarily agree to take part in research after understanding risks and procedures.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY: List the rest of the APA Ethical Guidelines
What is informed consent?
Explanation: Participants must voluntarily agree to take part in research after understanding risks and procedures.
Example: A sleep study informing participants of the conditions they'll experience.
APA Ethical Guidelines:
1. Informed Consent
2. Debreifing
3. Limited Deception
4. Confidentiality
5. Institutional Review Board (IRB) Approval
6. Protection from Harm
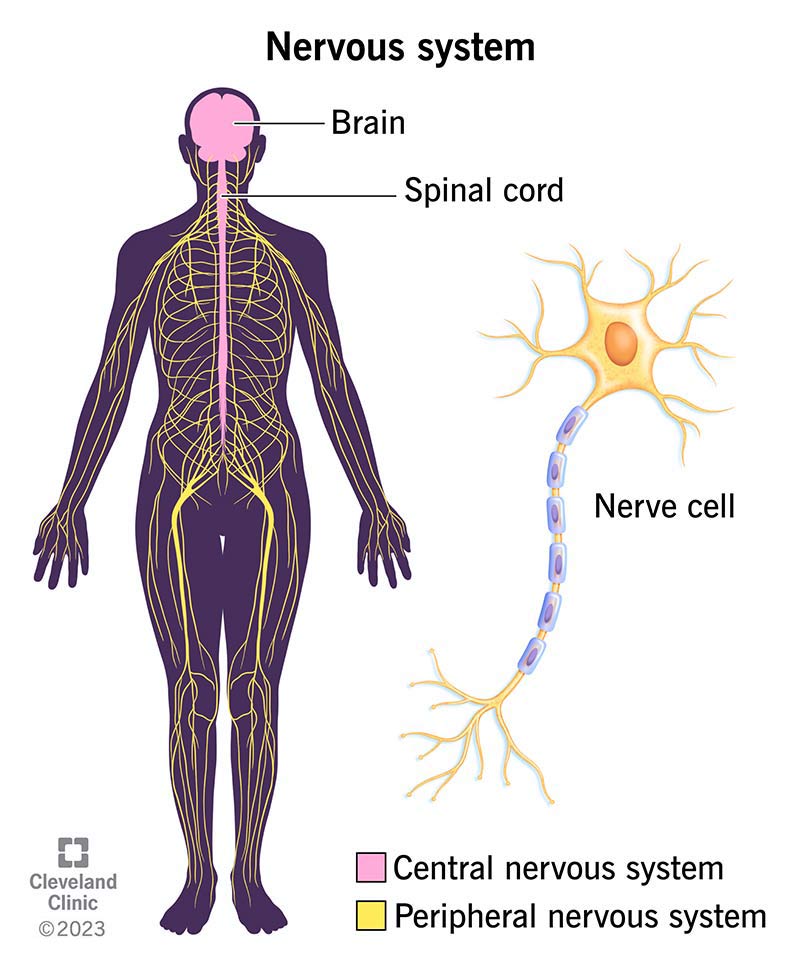
The type of neuron that carries information from the senses to the brain.
What is a sensory (afferent) neuron?
Explanation: Sensory neurons detect external stimuli and transmit signals to the CNS.

____________ is raw input, ____________ is meaning-making
What’s the difference between sensation and perception?
Sensation is raw input, perception is meaning-making.
Explanation: Sensation is detecting stimuli; perception interprets them. For example, sensation detects a loud sound; perception recognizes it as a fire alarm.

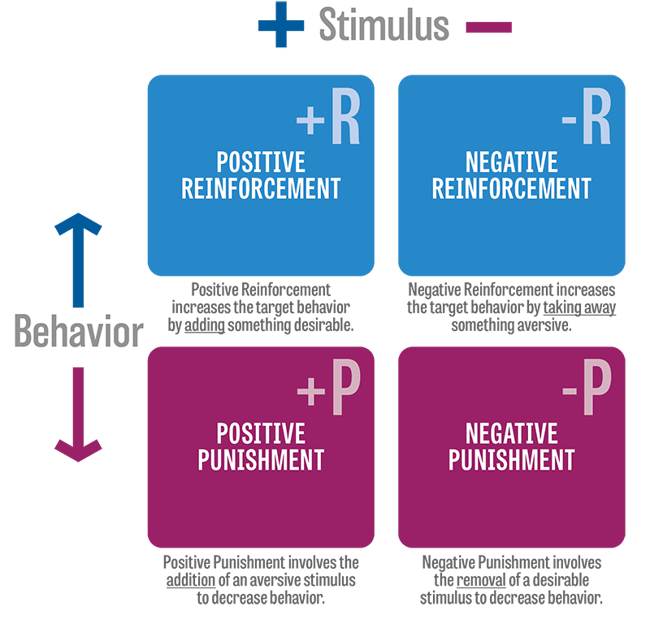
_____________ increases behavior, _____________ decreases behavior.
Reinforcement increases behavior, punishment decreases behavior.
Examples: NR = taking aspirin to reduce headache. NPt = time-out for misbehavior.
__________ is retrieving info without cues, __________ is identifying info with cues.
What’s the difference between recall and recognition?
Recall is retrieving info without cues, recognition is identifying info with cues.
Explanation: Recall = essay test; Recognition = multiple choice.

This perspective emphasizes unconscious drives and childhood experiences.
What is the psychoanalytic perspective?
Explanation: Originating with Freud, this perspective suggests behavior is driven by unconscious desires, fears, and early childhood events. Example: A person’s fear of abandonment may stem from early childhood trauma.

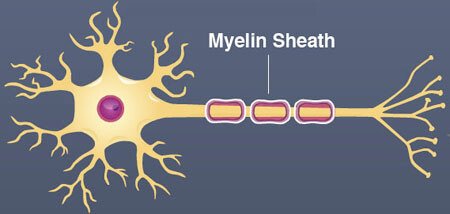
Part of the nerve that speeds up neural transmission.
What is the myelin sheath?
Explanation: The fatty myelin sheath insulates the axon, enabling faster transmission of action potentials. Damage leads to disorders like MS.
States that the difference threshold is a constant proportion.
What is Weber’s Law?
Explanation: The just noticeable difference (JND) depends on the magnitude of the original stimulus. Example: Adding 1lb to a 10lb weight is noticeable; 1lb to 100lbs isn’t.

Learning that remains hidden until there’s a reason to demonstrate it.
What is latent learning?
Explanation: Rats in a maze learn layout without rewards but show the knowledge once food is introduced (Tolman’s study).

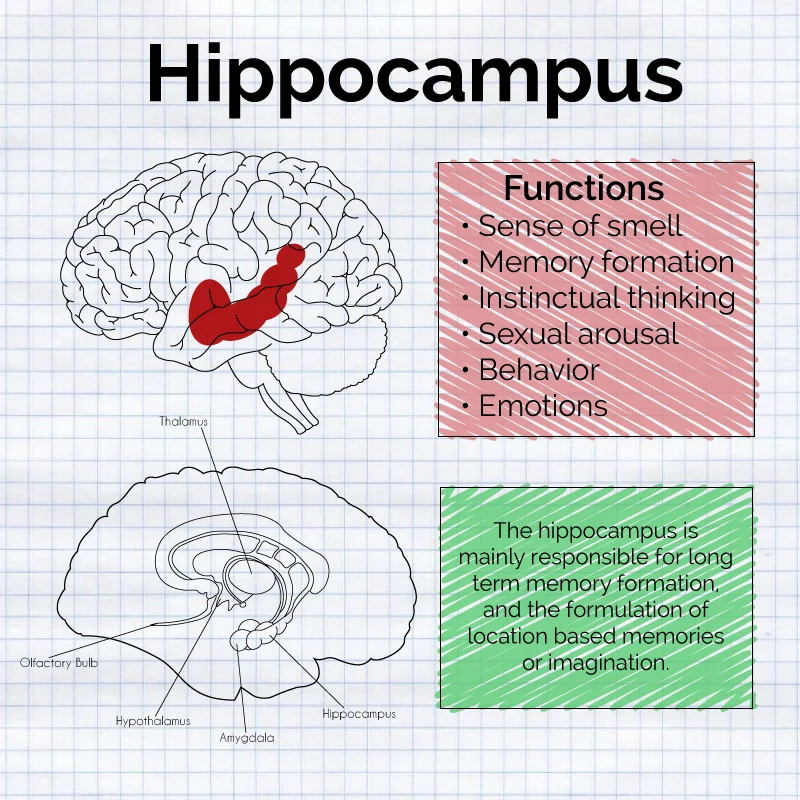
The brain structure most involved in forming new memories.
What is the hippocampus?
Explanation: The hippocampus helps encode explicit (declarative) memories. Damage impairs new memory formation.
The purpose of random assignment in an experiment.
To control for confounding variables.
Explanation: Random assignment helps ensure groups are equivalent, reducing bias. This makes the results more reliable.

Neurotransmitter that affects mood, sleep, and appetite.
What is serotonin?
Explanation: The neurotransmitter serotonin affects mood, sleep, and appetite. Low serotonin is linked to depression; SSRIs increase serotonin to alleviate symptoms.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/what-is-serotonin-5189485_color_v1-0cf1021dcefb4410865f4cea18254b5e.jpg)

The gate-control theory of pain states that pain are regulated by a “gate” in the __________.
The gate-control theory of pain states that pain signals are regulated by a “gate” in the spinal cord.
Explanation: The theory suggests psychological factors and competing stimuli (like rubbing a sore spot) can reduce pain perception.

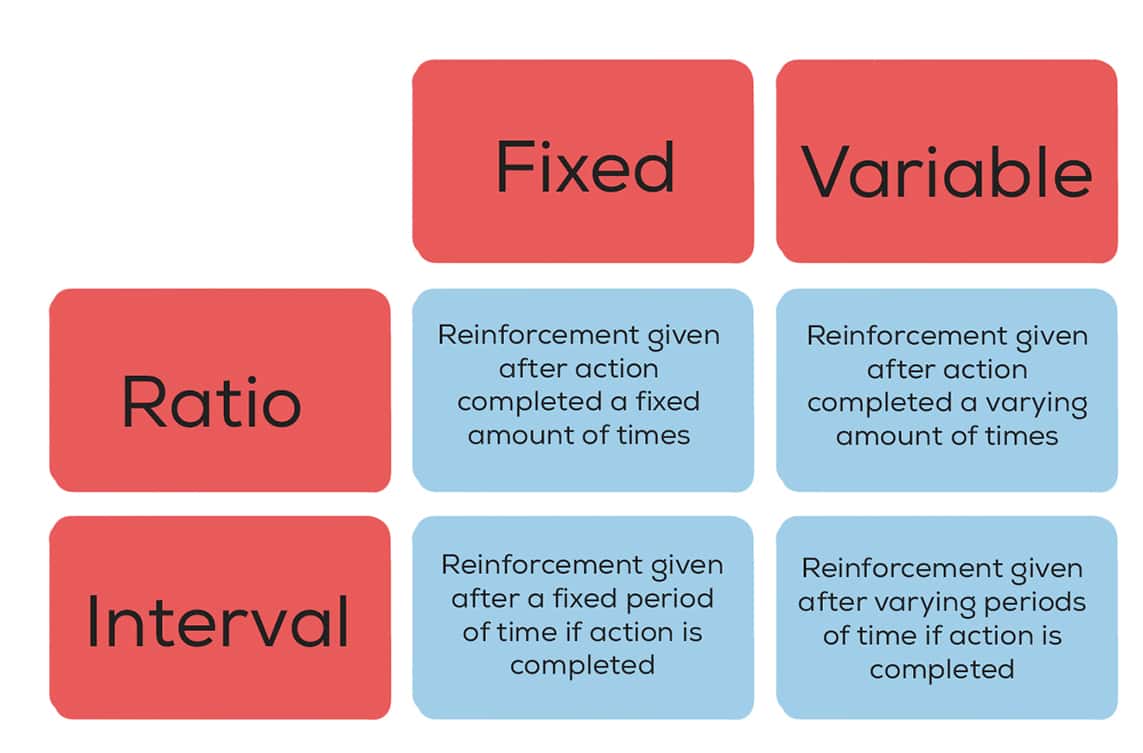
Reinforcement schedule with the highest response rate.
What is variable ratio?
Explanation: Like gambling, it provides rewards after an unpredictable number of responses, reinforcing behavior strongly.

The altering of memory due to misleading information.
What is the misinformation effect?
Explanation: Loftus' studies show that language (e.g., "smashed" vs. "hit") can change eyewitness recall.