The receptors located toward the center of the retina that are responsible for day and color vision
What are cones?
(name the Gestalt principle)

What is figure-ground?
The perceived pitch of a tone is largely determined by its (number of repetitions of a periodic waveform in a given unit of time)
What is frequency?
Someone who tends to be extremely sensitive to sweet and bitter tastes and spicy foods
What is a supertaster?
Where tactile receptors are located
What is skin?
The outer protective "window" of the eye through which light enters
What is the cornea?
The perceptual process that allows us to accurately read a series of words with jumbled up letters
What is top-down processing?
The three tiniest bones in your body, collectively known as the ossicles, that transmit sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane (eardrum) to the cochlea are called
What are the hammer, anvil, and stirrup? (or malleus, incus, stapes)
The proper name for our sense of taste
What is gustatory system/gustation?
The lobe and cortex responsible for processing tactile sensory input
What is the parietal lobe; somatosensory cortex?
After the opening number, Rachel's eyes are no longer bothered by the bright stage lights (what has occurred?)
What is sensory adaptation?
The binocular depth cue that contrasts differing views of the same object from each eye
What is retinal disparity?
The brightness/intensity of a light is analogous to this feature of a sound
What is loudness?
This sense is not routed through this brain structure before being processed in the cerebral cortex
What is olfaction?
The body sense that gathers sensory input from your semicircular canals that send signals to the cerebellum to maintain balance
What is the vestibular sense?
This is complete color blindness and the rarest form of color blindness where people only see in shades of gray, black, and white
What is monochromatism?
The tendency to experience a stable perception despite constantly changing sensory input (ex: your friend gets smaller as they walk away but you don't perceive them shrinking)
What is perceptual constancy?
The ear structure labeled D
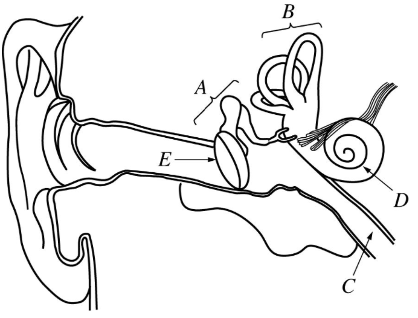
What is the cochlea?
1) What is the name of the taste associated with fats: creaminess or richness of food?
2) Which is the taste associated with savory/meaty flavors?
3) What is not a taste, but is related to endorphins because the active food compound, capsaicin, triggers pain receptors in the mouth, which can lead to a release of endorphins—natural painkillers produced by the body.
What is oleogustus?
What is umami?
What is spiciness?
The theory that explains why biting your tongue while getting an injection blocks your experience of pain from the needle
What is gate-control theory?
Which theory of vision takes place in the cones (all color perception involves 3 different color receptors)? Which theory takes place in the ganglion cells (Afterimages result when certain ganglion cells in the retina are activated)?
Trichromatic = cones; opponent-process = ganglion cells
The term that explains why placing the below figure between "A" and "C" would lead you to perceive the figure as "B" instead of "13"

What is context effects? (contextual perception)
The theory that says pitch perception depends on the rate that the entire basilar membrane vibrates
What is frequency theory?
The process of converting sensory input into signals that can be processed in the brain
What is transduction?
You see a white dress in bright sunlight, but in a shadow, it appears gray. This is why you still perceive the dress as white
What is color constancy?
