What research design randomly assigns participants to different conditions and manipulates an independent variable to determine causal effects?
An experiment
Define "operational definition" in one sentence and state why operational definitions are important for replication.
An operational definition specifies how a variable is measured or manipulated so others can replicate the procedure.
What is informed consent and why is it required?
Informed consent is participants' voluntary agreement to participate based on full disclosure of procedures, risks, and benefits.
What does a correlation coefficient of +0.85 indicate about the relationship between two variables?
+0.85 indicates a strong positive relationship: as one variable increases, the other tends to increase (large effect).
Calculate the mean, median, mode, and range for this data set: 4, 7, 7, 9, 12.
Mean =7.8
Median = 7
Mode = 7
Range = 8
Name two non-experimental methodologies commonly used in psychology that do NOT involve random assignment.
Case study, correlation, naturalistic observation, meta-analysis
In a study measuring "stress," provide two different operational definitions (one physiological and one self-report) that a researcher might use.
Physiological: cortisol level in saliva, blood pressure
Self-report: score on a validated 10-item stress questionnaire (Likert scale).
Explain the difference between confidentiality and anonymity in research.
Confidentiality: researcher keeps data private and links to identity secure (password protected)
Anonymity: data collected cannot be linked to participants at all
Explain why correlation does not equal causation, giving one possible alternative explanation when two variables are correlated.
Correlation doesn't prove causation; third variables or reverse causation could explain the relationship (e.g., socioeconomic status drives both variables).
Given a data set with mean μ=50 and scores clustered closely around the mean, explain whether the standard deviation is likely to be large or small and why.
Small standard deviation because scores are close to the mean, indicating low variability.
Given a study that compares test scores of students before and after a new teaching method without a control group, identify whether this is experimental or non-experimental and name a key limitation.
Non-experimental (pretest–posttest without control)
limitations: cannot rule out maturation, history, or testing effects
In a study that operationally defines "motivation" as minutes spent on homework, evaluate whether the operational definition is precise and how you might improve it to increase reliability.
Example critique: "Minutes on homework" is observable but may not capture quality or motivation—improve by defining tasks, timing procedures, and specifying allowed materials.
A study uses mild deception and places participants under stress for data collection. List three ethical safeguards researchers must use before, during, or after this study.
Safeguards: IRB approval, thorough informed consent, provide exit options/stop rules, careful debriefing and post-study support.
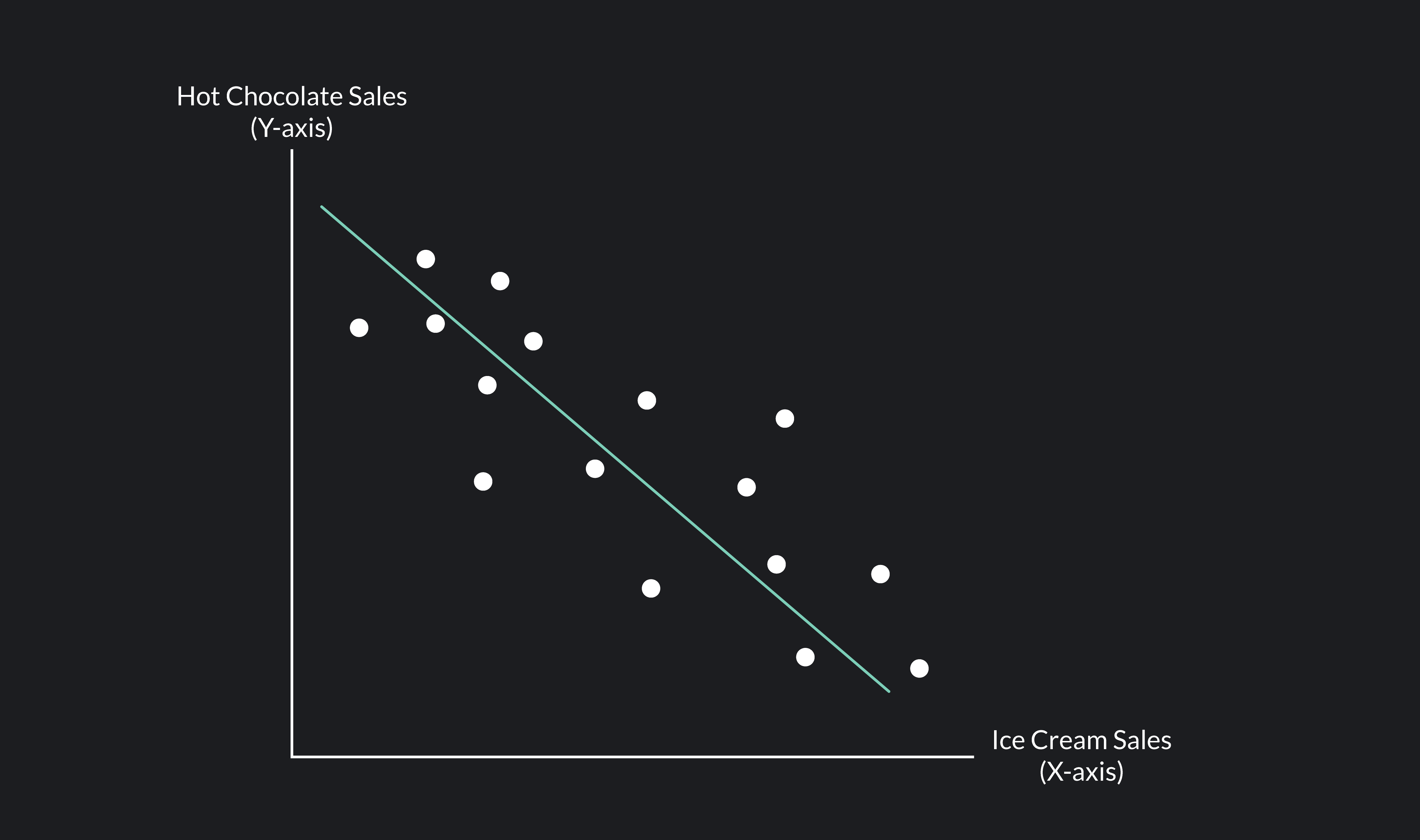 Give a potential correlation coefficient for this scatterplot.
Give a potential correlation coefficient for this scatterplot.
R= -.45
Explain what a bimodal distribution is and give an example of a psychological measure that might produce it.
Bimodal distribution has two distinct peaks
example: test scores from two different instructional groups mixed together
Describe how a double-blind procedure is implemented and explain which two sources of bias it aims to reduce.
Double-blind: both participants and experimenters who interact with participants do not know condition assignments; reduces experimenter bias and placebo effects.
Identify the independent and dependent variables and write clear operational definitions for each in this scenario:
"Researchers test whether listening to classical music while studying affects number of math problems solved in 30 minutes."
IV: presence of classical music
(operational definition: playlist X played at 60 dB during study session).
DV: number of correctly solved math problems in 30 minutes
(operational definition: count of problems solved correctly on a provided worksheet).
Describe the purpose of institutional review boards (IRBs) and name two criteria they consider when approving a human-subjects study.
IRBs protect participants by evaluating risks vs benefits and ensuring informed consent, confidentiality, and minimization of harm.
Given a study reporting a correlation of 0.02 between sleep hours and test performance, interpret this effect size and explain whether it is meaningful.
0.02 is near zero, indicating virtually no linear relationship; likely not meaningful.
Define effect size and interpret the meaning of an effect size statistic of 0.35 in psychological research.
Effect size measures strength of the statistical significance; 0.35 is a medium effect, indicating a modest practical relationship.
You are given a study with an independent variable, a dependent variable, and a potential confounding variable that varies systematically with groups. Explain how random assignment helps address the confounding variable and describe one additional design change that could further reduce its impact.
Random assignment distributes confounders across groups on average; additional change: include a control group or use stratified random assignment.
A researcher measures "social anxiety" via classroom participation frequency.
Critique this operational definition for construct validity and propose a multi-method operationalization that would strengthen the study.
Critique: classroom participation frequency may conflate opportunity with anxiety;
multi-method operationalization: COMBINE
self-report anxiety inventory + behavioral avoidance measures + and physiological indicators (e.g., heart rate) to improve construct validity.
A researcher uses a vulnerable population (minors) in an experiment with deception. Explain the additional ethical steps required (including assent, parental consent, and debriefing) and why each is necessary.
Additional steps:
-obtain parental consent and child assent
-minimize risks
-provide full debriefing including justification for deception
-provide options to withdraw data
these protect vulnerable participants and respect autonomy
A researcher finds a strong positive correlation between ice cream sales and drowning incidents. Provide at least two plausible third-variable explanations.
Third-variable examples: hot weather increases both ice cream sales and swimming activity, seasonal effects or population increases could also be driving the variables upwards
Given the following sample data: 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 — calculate the mean, median, mode, range, and explain briefly whether regression toward the mean would be expected if these scores were followed up with additional measurements over time.
For 10, 12, 14, 16, 18:
Mean=14
Median = 14
Mode = none (no repeated values) or "no mode" Range-=8
Regression toward the mean: if any extreme scores were due partly to random error, future measurements would likely move closer to the population mean (so moderate movement toward mean expected).