What type of reinforcement increases a behavior by removing an unpleasant stimulus?
What is negative reinforcement
This refers to the reappearance of an extinguished conditioned response after a period of time.
What is spontaneous recovery
Who is the psychologist best known for the Bobo doll experiment?
Who is Albert Bandura?
This term refers to the mental activities involved in acquiring, processing, and storing information
What is cognative processing
This psychologist conducted the controversial "Little Albert" experiment on classical conditioning.
Who is John B. Watson?
This schedule of reinforcement provides reinforcement after a fixed number of responses.
What is a fixed ratio schedule
In Pavlov’s experiment, what was the neutral stimulus?
What is the bell
This term refers to the process of imitating observed behaviors
What is modeling
This refers to the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information to give it meaning.
What is perception
Who developed the concept of operant conditioning?
Who is B.F. Skinner?
Giving a child candy for completing homework is an example of what.
What is positive reinforcement
This process involves a conditioned stimulus eliciting a response to stimuli similar to the original CS.
What is generalization
This social psychology concept refers to the tendency for people to exert less effort when working in a group compared to when working alone.
What is social loafing?
What term describes learning that occurs but is not demonstrated until there is motivation?
What is latent learning
This psychologist's famous conformity experiments involved participants judging the length of lines.
A: Who is Solomon Asch?
Who is Solomon Asch?
This principle states that behavior followed by favorable consequences is likely to be repeated
What is the Law of Effect
The process of linking a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus is known as what
What is acquisition
This bias occurs when people attribute their own actions to external factors but attribute others' actions to internal factors.
What is the fundamental attribution error?
This type of memory involves the unconscious recall of skills or information, such as how to ride a bicycle.
What is procedural memory?
This psychologist's obedience experiments involved participants administering fake electric shocks.
Who is Stanley Milgram?
A teacher stops giving attention to a student who frequently interrupts. Over time, the interruptions decrease. This is an example of what operant concept?
What is extinction
In Pavlov's famous experiment, this was the unconditioned stimulus.
What is food
Observational learning involves which four key processes
What are attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation
This technique involves organizing information into meaningful groups to enhance memory recall.
What is chunking?
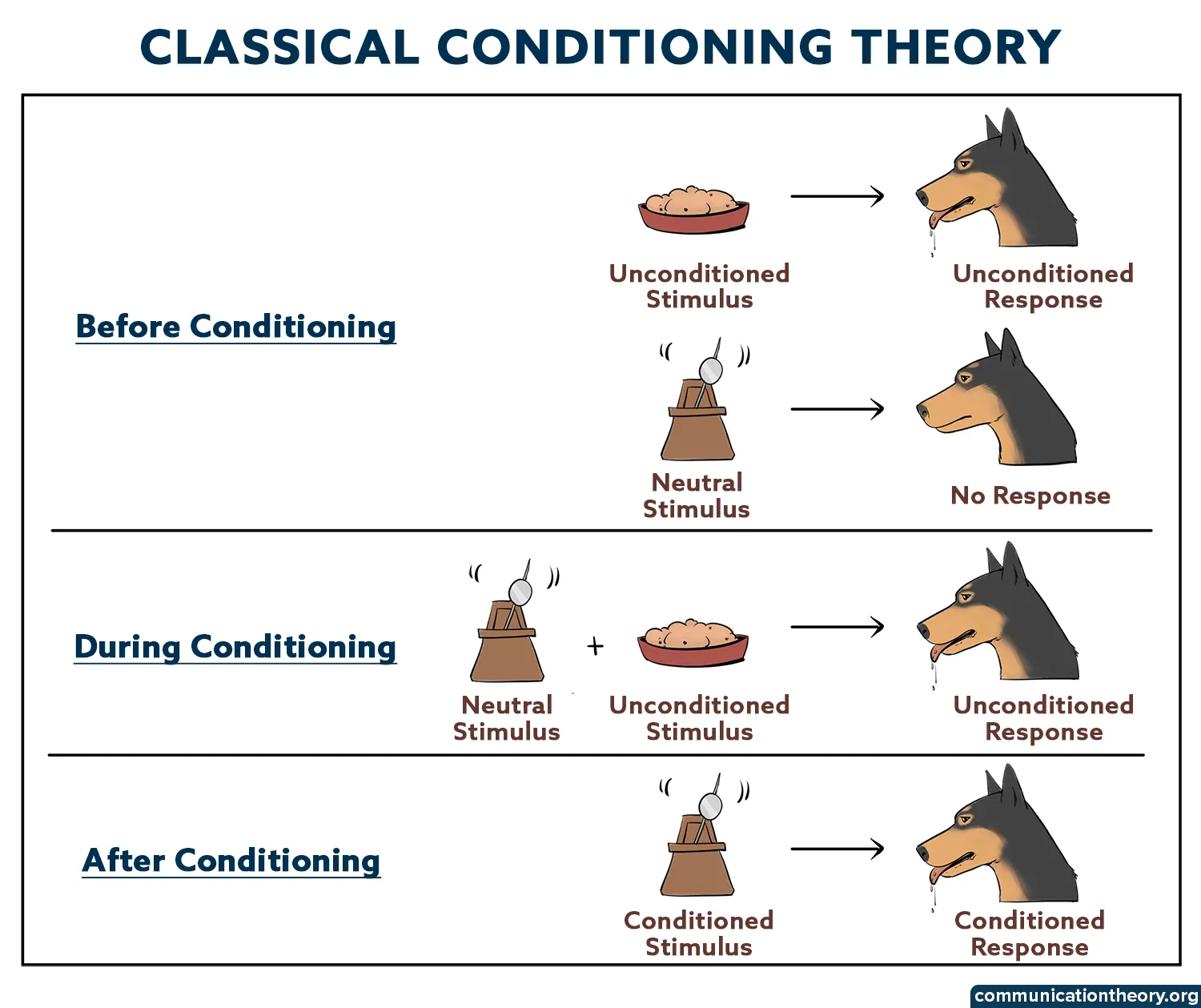 The experiment is associated with which psycholois?
The experiment is associated with which psycholois?
Who is Ivan Pavlov