The the senses that rely on chemical receptor cells.
What are taste and smell
The term for chemicals that travel from one neuron to another, affecting nearby neurons.
What is neurotransmitters?
The primary connection between the left and the right hemisphere
What is the corpus callosum?
Patient reports that he has no trouble falling asleep; however he has multiple awakenings during the night and does not know why. He awakes feeling unrefreshed. He experiences daytime sleepiness. He awakes with his mouth feeling dry.
What is sleep apnea?
The _____ side of the brain is responsible for recognizing faces and the _____ side of the brain is responsible for language
What is the right side and the left side?
Riley has concerns about her sleeping habits. Last night she woke up in his backyard fishing in her pond. She recalls that she was just dreaming that she was on vacation fishing. The previous week she experienced a similar situation in which she woke up cooking Mac and Cheese when she was having a dream that she was making her 4th block meal.
What is sleepwalking?
The sensation process that deals with examining small details and piecing them together into a larger picture.
What is bottom up proccessing
This determines pitch in hearing.
What is frequency
Injury to this part of the brain is likely to cause someone to have great difficulty maintaining their balance and coordinating their movements
What is cerebellum?
The primary connection between the left and the right hemispheres
What is the corpus callosum?
The approximate amount of hours of sleep adolescents need.
What is 9 +/- 1 hours?
During this stage your brain experiences delta waves and you may sleep walk
What is NREM stage 3?
During this stage your brain experiences alpha waves and you may have hallucinations
What is NREM stage 1?
A wave's amplitude determines it's _____.
brightness or intensity (loudness)
The place in the eye where the optic nerve leaves the eye and we cannot see anything.
What is the blind spot
This part of the brain regulates someone's sense of fear
What is amygdala?
The literal content of your dream
What is manifest content?
The lobe that contains the auditory cortex
What is the temporal lobe?
During this stage of sleep you experience the most vivid dreams
What is REM?
Area of the eye that only contains cones
The conversion of one form of energy to another through neural impulses
What is transduction?
What is the red (52) part of the brain?
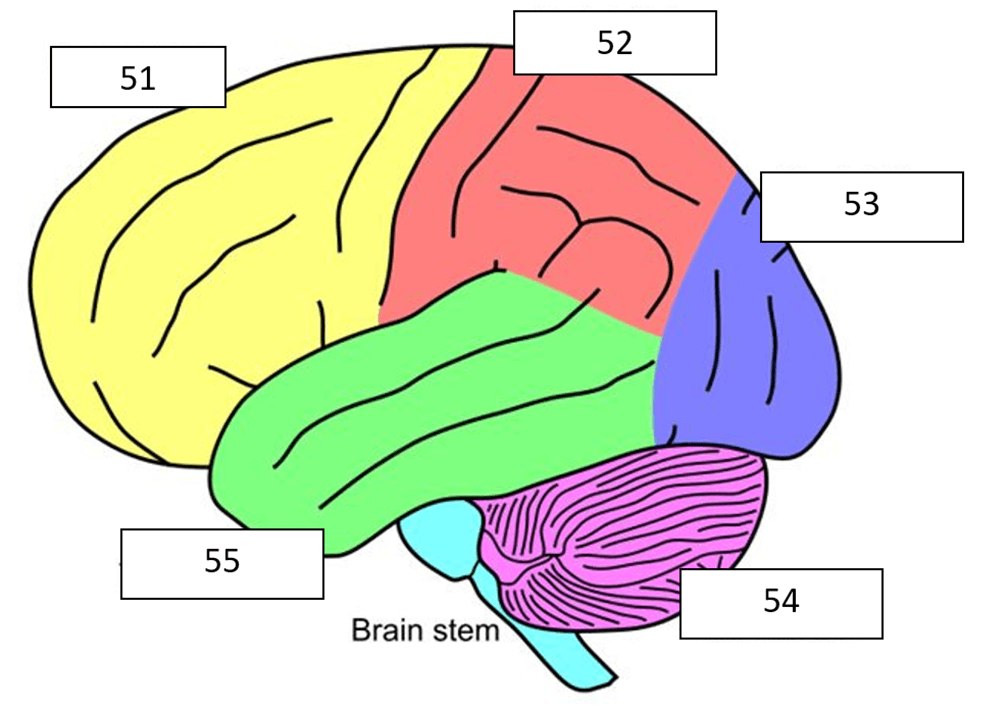
What is parietal lobe?
What is the yellow (51) part of the brain?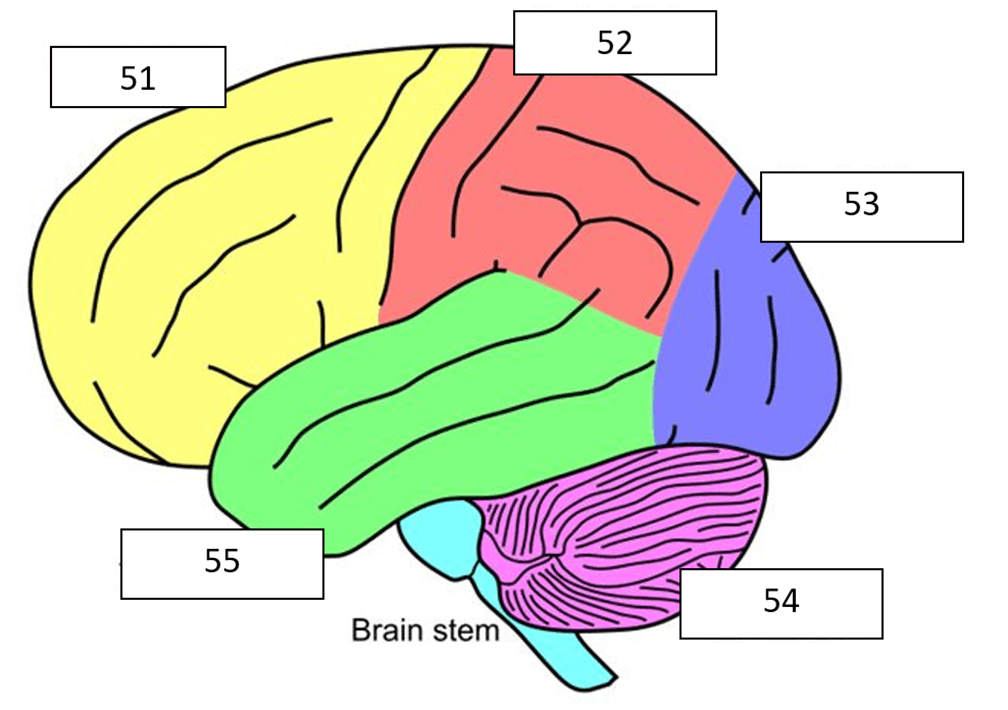
What is frontal lobe?
During this sleep stage, your brain experiences sleep spindles and you can still be awakened without difficulty
What is NREM stage 2?
What is the Circadian rhythm?
The patient suffers from excessive fatigue and sleepiness during the day. She often has difficulty concentrating and performing tasks. The patient drinks several cups of coffee and diet sodas to stay awake during the day. She also has an alcoholic beverage or two to help her sleep. She can fall asleep okay, but cannot stay asleep for very long and wakes up numerous times and cannot fall back asleep.
What year did I graduate high school?
2009
When your eye's lens focuses on nearby objects and are seen more clearly than distant ones.
What is nearsightedness?
What is the blue (53) part of the brain?
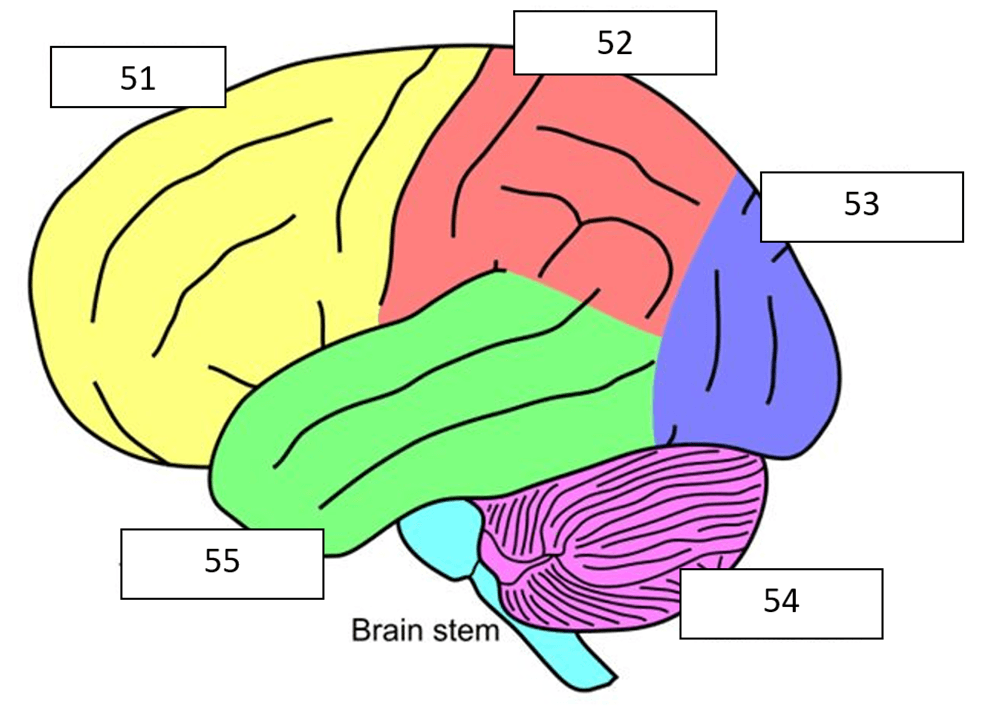
What is the green part of the brain?
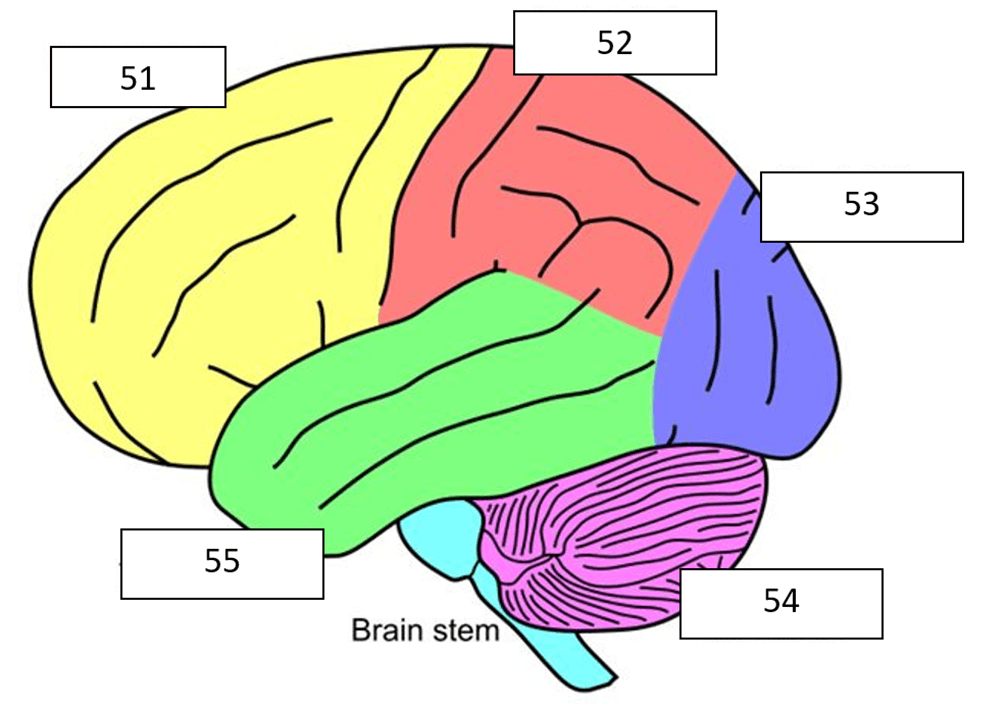
What is temporal lobe?
.
Description of sleep when you are internally (heart rate/breathing) active and externally (movement) inactive
What is paradoxical sleep?
Patient feels excessively sleepy during the day. She sometimes cannot tell if she is dreaming or hallucinating. When she wakes up in the morning she feels glued to her bed as if she cannot move. She mentions that she feels weak when she laughs or is being tickled.
What is narcolepsy?
double your score
.
The distance from one peak to the next describes ____ which determines the ___ of the light we see.
wavelength hue (color)
The _______ hemisphere of the brain controls the right hand and the _______ hemisphere controls the left hand
What is the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere?
What is the purple (54) part of the brain?
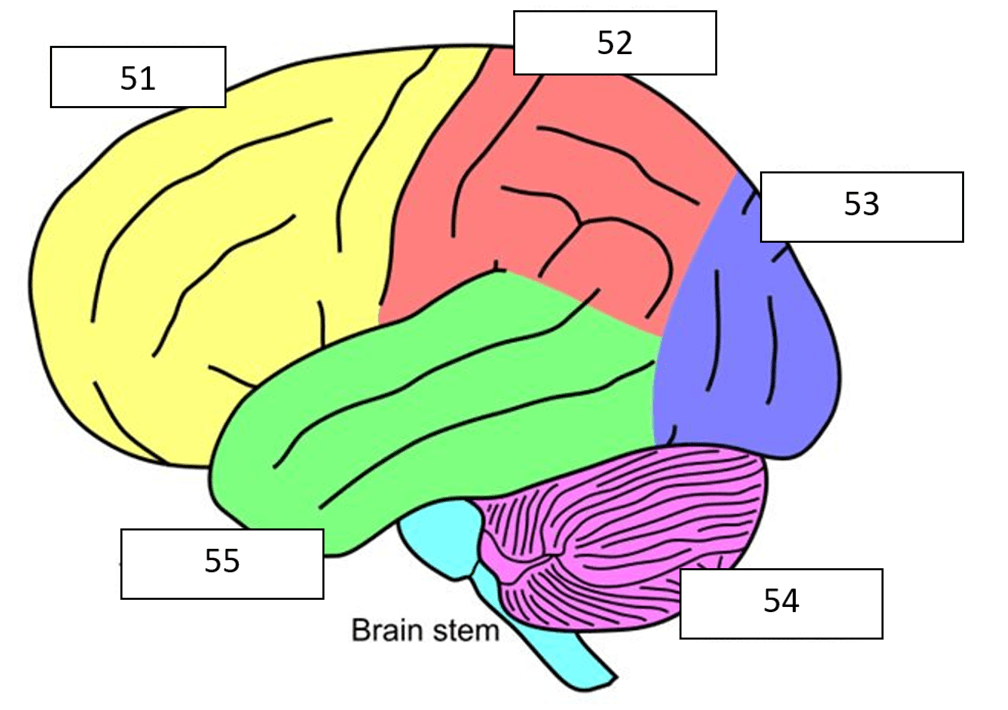
What is cerebellum?
When our body wants us to sleep our body temperature _____ and when our body wants us to wake up our body temperature _____
What is falls and rises?
During this stage of sleep your body experiences paradoxical sleep
What is REM?
When you don't sleep enough for many days and then you finally final asleep, you are likely to experience ________________.
What is REM rebound?
The sense that helps us balance.