What is the organelle that converts chemical energy from food to ATP in a process called cellular respiration?
Name the four types of tissues
1. Epithelial
2. Connective
3. Muscle
4. Nervous
What type of joint is very moveable? What are the names of these area of movement and provide examples for each.
1. Ball and socket (shoulder, hip)
2. Hinge (elbow, knee)
3. Pivot (lower arm)
4. Saddle (thumb)
Myosin vs Actin
Myosin - thick filaments, dark, A-bands
Actin - thin filaments, light, I-Bands
Draw a neuron and identify a cell body, dendrites, and axons. What do each component do?
The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles, dendrites receive information from other neurons, while axons sends information to other neurons.
What are the three characteristic of the cell membrane?
1. Has a phospholipid bilayer
2. Consists of phospholipids and embedded proteins
3. Regulates what enters and leaves the cell, aka selectively permeable
What is the difference between tendons and ligamenst?
Ligaments = bones to bones
Label the sutures of the skull.

Top Right: Coronal suture
Middle Right: Sagittal suture
Bottom Right: Lambdoidal suture
Top left: Frontal bone
Middle Left: Parietal Bone
Where can you find these types of muscle tissue? Skeletal, smooth, cardiac
Skeletal (attached to bones via tendons), Smooth (in gastrointestinal, reproductive, urinary, vascular, and respiratory systems), Cardiac (in heart)
What is the overall function of the nervous system?
to coordinate the body's system by receiving and sending information; maintaining homeostasis
What is exocytosis and endocytosis? Draw an image of each term occurring.
Exocytosis: Secretion; things exit the cell
Endocytosis: Things enter the cell
What are the three types of cartilage and what is their location?
1. Hyaline Cartilage: covers ends of joints, nose, and respiratory passages
2. Elastic Cartilages: external ear and larynx (throat)
3. Fibrocartilages: between vertebrae
What is the long bone structure?
Epiphysis - ends of bones
Diaphysis - shaft (middle) of bone)
Articular cartilages (cartilage covering the end of bones)
Periosteum - membrane covering entire bone
medulla - within the diaphysis, contains bone marrow
What is muscle dystrophy?
A disorder causing muscle weakness and leads to reduce mobility.
In patients with muscular dystrophy, the muscles can become larger even as they become weaker. This is due to scar tissue and fat replacing working muscle cells.
What is the function of oligodendrocyte, astrocyte, microglial cells?
oligodendrocyte - make myelin sheaths that provide insulation around axons
astrocyte - connect blood vessels to neurons
microglial cells - immune functions, digest debris, kills bacteria
Describe the relationships between cancer and mitosis.
Cancer is a disease of mitosis meaning the normal "checkpoints" regulating mitosis are ignored. Changes in DNA (mutations) cause checkpoints to be ignored. This causes uncontrolled cell division.
What is the function of
1. Elastic fibers
2. Fibroblasts
3. Macrophages
4. Collagen fibers
5. Mast cells
1.Allow tissues in your body to stretch out and shrink back
2. Production of fibers
3. Consumes debris and foreign objects
4. Fiber that makes up tendons
5. Prevents blood clots
What are the bones of the pectoral girdle?
Clavicles (collar bones), Scapulas (shoulder blades), Humerus (upper arm), Ulna goes to pinky and radius goes to thumb, carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (palm of hand), phalanges (fingers)
Draw the muscle structure hierarchy
muscle (surrounded by epimysium)
fascicle (surrounded by perimysium)
muscle fiber (endomysium)
myofibrils
myofilaments (actin and myosin)
What are the general functions of the lobes of the brain?
Look at brain hat!
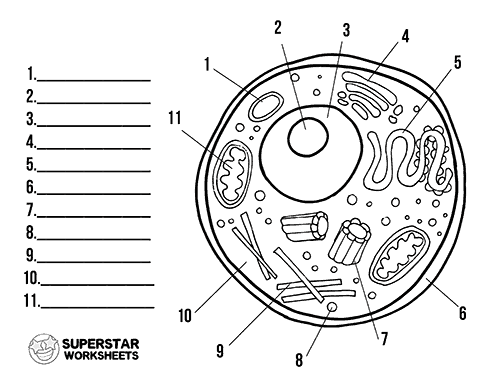
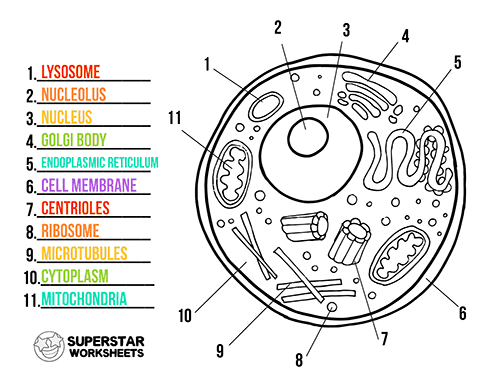
Draw a cell and label each item below:
1. Lysosome
2. Nucleolus
3. Nucleus
4. Golgi Apparatus
5. Smooth ER
6. Cell membrane
7. Centrioles
8. Ribosomes
9. Cytoskeleton
10. Cytoplasm
11. Mitochondria
What is Epidermolysis Bullosa?
Is a connective tissue disorder where a mutation in the COL7A1 gene affects the protein collagen (the glue that holds tissues together). Collagen is responsible for anchoring the epidermis to the dermis, so when that is not happening blisters form. This causes individuals to experience redness, pain, and lack of strong skin tissue.
Label the bones of the skull.

Describe the parts of the sliding filament theory.
Neuromuscular junction - where a nerve and muscle fiber come together
Motor end plate - folded area where muscle and neuron communicate
Synapse - gap between the neuron and motor end plate
Synaptic vesicles - where neurotransmitters are stored
What is multiple sclerosis and its symptoms?
A chronic neurological disorder. It is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that in MS the immune system—which normally protects us from viruses, bacteria, and other threats—mistakenly attacks healthy cells.
Symptoms: legs and arms feel heavy. Blurred vision. Lehs unable to lift. Slurred words.
