This condition allows us to establish causation between treatments and the response variable should statistically significant results occur.
What is the Random (assignment of treatments) Condition?
This the number of standard deviations above (or below) the mean a value is.
What is a z-score?
This sampling method selects a random starting point and then surveys every nth individual.
What is a systematic random sample?
Calculate the expected number of ATMs working when the mall opens. 
What is
0(0.15)+1(0.21)+2(0.40)+3(0.24) = 1.73 ATMS
This should be included in all written responses.
What is context?
This condition allows us to act as if trials are independent even when sampling without replacement.
What is the 10% Condition?
This describes how much data values typically vary from the mean.
What is standard deviation?
This sampling method consists of groups where some groups are randomly selected and then ALL the members of those groups are surveyed.
What is a cluster sample?
This is the main difference between a Binomial and Geometric distribution.
What is fixed trials or not fixed trials?
Binomial: Fixed
Geometric: until first success
This condition allows us to assume the sampling distribution of the SAMPLE PROPORTION is approximately normal.
What is the Large Counts Condition?
np>=10, n(1-p) >=10
This occurs when the null hypothesis is rejected when in actuality, the null hypothesis is true.
What is a Type I Error?
This sampling method divides the population into groups. These groups are chosen based off a variable that will affect the responses the MOST. Then, a simple random sample from each group is selected and surveyed.
What is a stratified random sample?
What is the SD for Y + Y + Y?
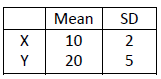
CANNOT ADD SDs, can add variances
\sqrt (5^2+5^2+5^2)=\sqrt(3(5)^2)=8.66
This Chi-Square test is the only test appropriate when there are 2 or more samples to consider.
What is a Chi-Square test for homogeneity?
This condition allows us to assume the sampling distribution of the SAMPLE MEAN is approximately normal even if the population distribution is skewed (or any other shape) so long as the sample size is sufficiently large.
What is the Central Limit Theorem?
This is the probability of getting the sample statistic or more extreme if we assume the null hypothesis is true.
What is the p-value?
This experimental design divides experimental units into groups first and then within each group, randomly assigns treatments.
What is a randomized block design?
These are 2 ways to decrease the margin of error of a confidence interval?
What is
1) increasing sample size
2) decreasing confidence level
What is a plot of the sample data that shows no strong skewness nor outliers?
This is the percent of all intervals we'd expect to capture the population parameter if the random sampling procedure was repeated many, many times and an interval calculated for each of those samples.
What is confidence level?
When describing bias, what should you include in your description.
What is the direction of the bias? (is population parameter over or underestimated?)
Should also include in description of bias how the sampling method leads to the overestimate/underestimate.
What is the probability all three ATMs are working when the mall opens, GIVEN that at least one ATM is working?

P(at least 1 ATM is working) = 0.21 +0.40 + 0.24 = 0.85
0.24/0.85=0.282
This is the proportion of variation in the response variable that can be explained by its linear relationship with the explanatory variable?
What is the coefficient of determination?
r^2