What is the variance?
The type of significance test used for the mean of a single population.
What is a T test (or T procedure)?
The fact that the data will change from sample to sample is called this.
What is sampling variability?
The formula to calculate the one-sample z statistic.
What is
z=(barx-mu_0)/sqrt(n)
These four things must be included in the description of the distribution of quantitative data.
What are shape, center, spread and outliers?
Outliers on a scatterplot that affect the slope of the regression line.
What are influential points?
This type of error could be committed when the decision is made to fail to reject the null hypothesis.
What is a Type II error?
When a distribution is skewed to the right, this measure of center will be higher.
What is the mean?
Using a regression model to make predictions about future values
What is extrapolation?
The 3 basic principles of experimental design.
What are control, randomize, and replicate?
The condition involving the population size that must be satisfied to use sigma divided by the square root of n as the standard deviation of a sampling distribution.
What is 'the sample is less than10% of the population'?
Two of the conditions to be verified for inference about a proportion.
What are (1) the sample size must be less than 10% of the population; (2) Simple Random Sample; (3)
n xx hatp>=10 and n xx hatq>=10
Given the following output, this is the slope of the regression model.
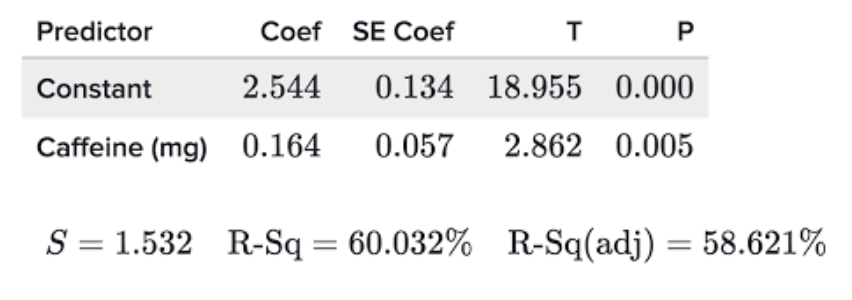
What is 0.163?
This type of bias is present in the following example:A call-in radio shows solicits audience participation in surveys on controversial topics (affirmative action, gun control, etc.) and the resulting sample tends to overrepresent individuals who have strong opinions.
What is voluntary response bias?
When two events, A and B, are independent then these two probabilities are equal.
P(A) = P(A|B) OR P(B) = P(B|A)
The type of pvalue for which you would reject a null hypothesis.
What is a low pvalue?