The steps in the signal transduction pathway
Reception, Transduction, Response
The resting state in the cell cycle
What is the G0 Phase?
Type of feedback that maintains homeostasis
What is negative feedback?
Parts of the phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid Heads facing the outside - polar
Phopholipid Tails on the inside - nonpolar
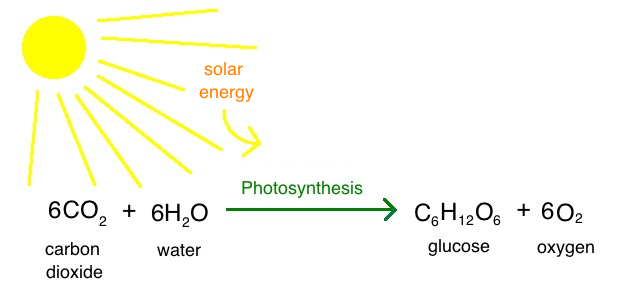
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
Type of cell signaling over long distances, includes growth hormones
What is endocrine signaling?
Steps of Cell cycle in order
G1, S, G2, M(mitotic)
Amplification of change in response to action
What is positive feedback?
Small nonpolar
O2, CO2
Leads to the denaturation of enzymes
What are high temperatures and non-optimal pH levels?
Enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups
What is a kinase?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Two examples of Negative Feedback
Temperature Regulation, Osmoregulation, blood pressure regulation
Joins monomers into polymers by removing a water molecule
Steps of Cellular Respiration in Order
Glycolysis - Pyruvate Oxidation - Citric Acid Cycle - Oxidative Phosphorylation
Allows molecules to pass between adjacent cells
What is cell junction?
The 3 components of Interphase
G1 Phase, S phase(DNA is synthesized,) G2 Phase
Two examples of positive feedback
Bloodclotting, Child Birth, Fruit Ripening
Linear sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acids
Products of Calvin Cycle
What are glucose, 2 molecules of G3P, NAD, & ADP?
Name the 4 types of cell signaling and what they do
Endocrine - signaling over long distances
Paracrine - signaling over cells in close proximity
Autocrine - signaling within the own same cell
Signaling by direct contact - it's in the name
Phase in cell cycle where centrosomes help seperate DNA
What is the M(mitotic) phase?
How are glucose levels maintained through negative feedback?
Pancreas detect high glucose levels -> Release of insulin -> Glucose is reduced and stored -> More stable levels of glucose/sugar
List all macromolecules and their monomers
Carbohydrate - Monosaccharides
Lipids - Fatty Acids
Protein - Amino Acids
Nucleic Acids - Nucleotides
How are the light-dependent reactions involved in the capturing and transforming of energy?
Transform light energy into chemical energy, stored as NADPH