If a plant cell is placed in a solution with a higher water potential than the cell, water will move in this direction.
Into the cell
This organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell, producing ATP through cellular respiration.
bonus: draw the organelle
Mitochondrion
There are two layers of this plasma membrane component, allowing for fluidity and flexibility.
bonus: draw and label this component and include polarity
Phospholipid
What term describes a solution that has a higher concentration of solutes compared to the inside of a cell?
hypertonic
Contrast active and passive transport by discussing how they are different:
a) in concentration movement
b) in the use of energy
a) passive moves high to low, active moves low to high
b) passive uses no energy, active uses energy in the form of ATP
The solute concentration inside a cell is 0.3M and outside the cell is 0.6M. Which has a higher water potential?
bonus question: what is the tonicity of the CELL?
The cell has a higher water potential. The cell is hypotonic.
This organelle forms vesicles, which are used to package and transport molecules for export. It also forms lysosomes.
bonus: draw the organelle
Golgi
These proteins embedded in the plasma membrane assist in transporting substances across the membrane.
bonus: identify the names of these two proteins and give a quick drawing
Transport proteins
bonus: carrier and channel proteins
A nurse messes up and gives distilled water in an IV instead of isotonic saline. This causes the cell to gain water and burst.
The cell is _______________, the environment is _____________.
cell: hypertonic
environment: hypotonic
Compare and contrast facilitated diffusion and protein pumps. Be sure to discuss energy requirements and the concentration gradients in each.
Compare: Both use transport proteins to move molecules through a membrane.
Contrast: Facilitated diffusion is passive transport, molecules move from high to low through the protein with no energy. Protein pumps are active transport, molecules move from low to high through the protein with energy (ATP).
If the solute potential of a cell is -4.9 bars and the pressure potential inside the cell is 2 bars, what is the water potential?
-2.9 bars
Identify three things that are found in all cells
Cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes, DNA/RNA
The plasma membrane has many different molecules embedded within it. Identify one of these molecules that could be malfunctioning if the cell suddenly isn't communicating with its external environment.
Glycolipids, glycoproteins, peripheral proteins, protein receptors
When a plant has not been watered in a while, explain what is happening at the cellular level to make it wilt.
bonus: described what plasmolyzed means for a plant cell that has dehydrated
Water is being pulled from the large central vacuole, making it not push against the cell wall. This makes the plant's stems not as strong and the plant gets sad.
bonus: when too much water leaves the vacuole, the cell membrane becomes sucked away from the cell wall. This kills the cellA) Draw a picture of endocytosis and exocytosis.
B) Give a brief one sentence summary describing how the process works.
Endocytosis is making dip in the cell membrane and bringing in a large amount of molecules all at once. Exocytosis is fusing a vesicle with the cell membrane to expel a large amount of molecues all at once.
A beaker contains a solution with a solute concentration of 1M. If the temperature is 20C, what is the solute potential of the solution?
-24.35 bars
If a cell has malfunctioning lysosomes, it would struggle to do this, leading to the accumulation of waste materials.
Break down macromolecules and cellular debris
Draw the a phospholipid bilayer (ignoring all of the other things embedded within) and label the polar and nonpolar sections.
bonus: identify one molecule that cannot go through the membrane in large quantities and one that can. Be sure to label each.phosphate heads - polar
fatty acid tails - non polar
can go through: CO2, O2. Cannot: water, sugar, salt
A scientist places a 0.8M solution in chamber A and a 0.4M solution in chamber B. In which chamber will the water move?
bonus: identify a different concentration that would make the water move faster into the same chamber?
It will move into chamber A to balance out both sides and reach dynamic equilibrium.
bonus: any number greater than 0.8M would cause it to move faster.
Identify a molecule that would need active transport to bring it into the cell.
Any large, polar molecule. Sugar or Salt
A cell with a solute potential of -6 bars and a pressure potential of 3 bars is placed in a 0.4M solution of salt (i=2) at 22C.
What is the water potential for the cell and the solution?
bonus: in what direction with the water move?
Cell WP = -6 +3 = -3
Solution: = (-2)(0.4)(0.0831)(22+273)= -19.6 bars
bonus: Water will leave the cell
Two organelles are believed to exist thanks to the endosymbiotic theory.
a) Identify an organelle
b) List two observations of that organelle that supports this theory
Mitochondria or chloroplast
- ribosomes similar to prokaryotes
- they have their own DNA and it is circular like prokaryotes
- can divide through binary fission
- ribosomes inside the organelle are more similar to prokaryotes
- have two membranes
Explain the role of cholesterol in maintaining membrane fluidity and describe how temperature affects this relationship.
Cholesterol is embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, allowing the membrane to stay together while also being fluid.
At high temps, it prevents the membrane from being too fluid and falling apart.
At cold temps, it prevents the membrane from packing too tightly and becoming solid.
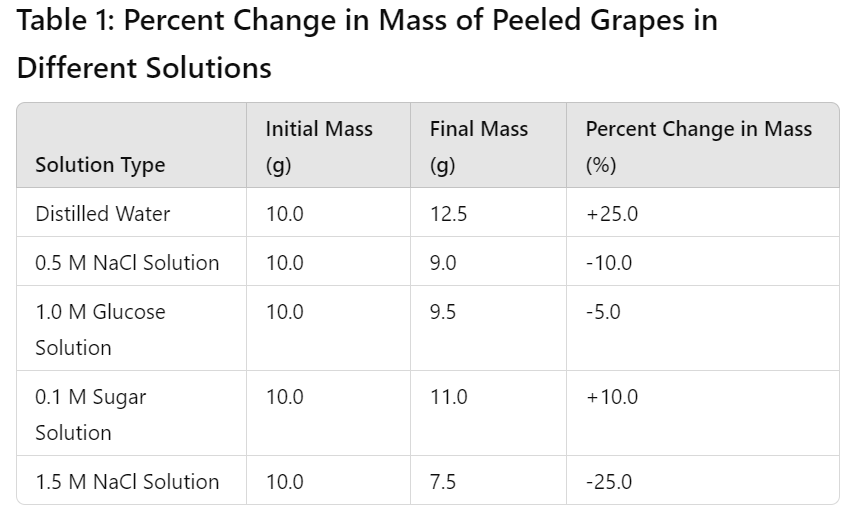
Peeled grapes were placed in various solutions and then their percent change in mass was measured.
a) identify the solution that has the highest water potential.
b) identify the solution that has the lowest water potential.
a) distilled water
b) 1.5 M NaCl solution
What type of transport allows oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse across the membrane? Give the characteristics about these molecules that allow this to happen.
Diffusion. They are small, nonpolar molecules so they can diffuse through the fatty acid tails in the membrane.
