Examples include taiga, shrubland, and tundra.
What are terrestrial biomes?
Any close and long-term interaction between two organisms of different species
What is symbiosis?
The power source of the hydrologic cycle.
What is the Sun?
The rate at which solar energy is converted into organic compounds via photosynthesis over a unit of time.
What is primary productivity?
A model of an interlocking pattern of food chains that depicts the flow of energy and nutrients in two or more food chains.
What is a food web?
This is the biome where rivers empty into the ocean.
What is an estuary?
One species benefits while the other is neither benefited nor harmed.
What is commensalism?
The major reservoir of the nitrogen cycle.
What is the atmosphere?
The total rate of photosynthesis in a given area.
What is gross primary productivity?
Organisms occupying the same feeding position in a food web.
What is a trophic level?
The 2 zones of the ocean.
What are photic and aphotic?
The relationship between a tapeworm and the host that is lives inside.
What is parasitism?
This biogeochemical cycle has no atmospheric component.
What is the phosphorus cycle?
The units for primary productivity.
What is energy/area/time?
The scientific law that is demonstrated in biogeochemical cycles, food chains, food webs, etc.
What is the 1st law of thermodynamics?
The factors that characterize terrestrial biomes.
What are annual temperature, precipitation, nutrient availability?
What is a keystone species?
The two carbon cycle processes that exchange carbon in living things.
What are photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
The rate of energy storage by photosynthesizers in a given area, after subtracting the energy lost to respiration.
What is net primary productivity?
An ecological event that involves changes to the structure of an ecosystem resulting from changes in animals or plants.
What is a trophic cascade?
The characteristics that define aquatic biomes.
What are salinity, depth, temperature and flow?
When species use limiting resources in different ways, places, or times to reduce competition.
What is resource partitioning?
The process in which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into a form of nitrogen (primarily ammonia) that is available for uptake by plants.
What is nitrogen fixation?
The gross primary productivity (GPP) of a meadow in southeastern Kansas is found to be 38,000 kcal/m2. Respiration which is measured by the amount of CO2 released is 13,500 kcal/m2, What is the net primary productivity (NPP) for this ecosystem, in kcal/m2/ year?
What is 24,500 kcal/m2/year?
Write out a food chain with 4 trophic levels from the following food web:
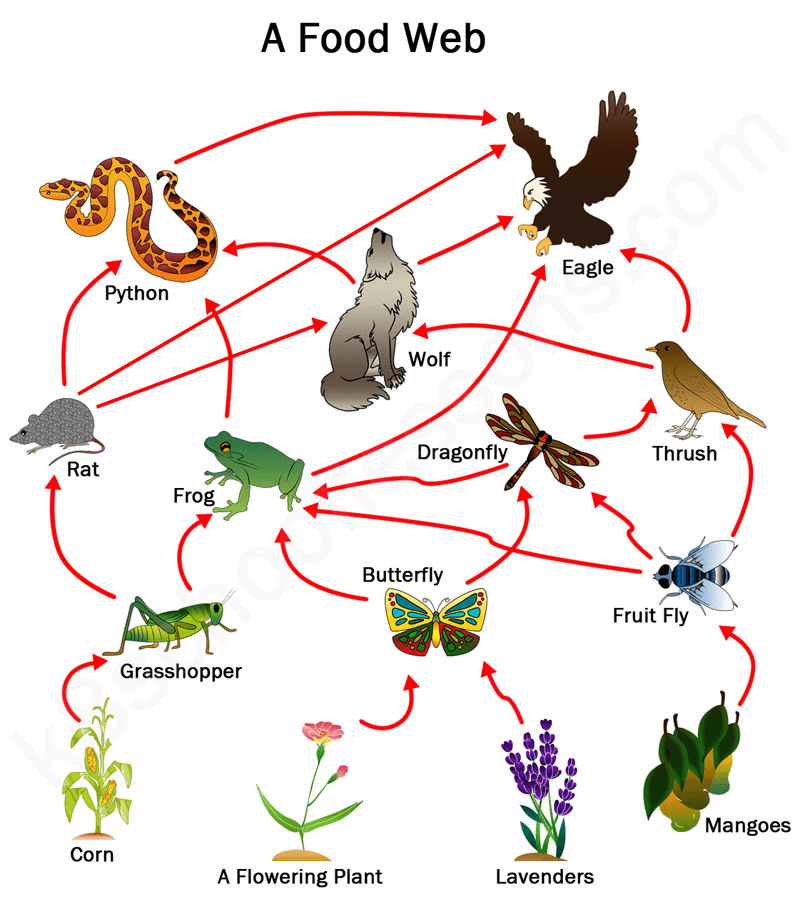
What is: lavender --> butterfly --> frog --> python