What happens to growth when a population approaches its capacity?
Growth slows and eventually stabilizes
Population influencing factors that change as population increases are called these types of factors.
Density dependent
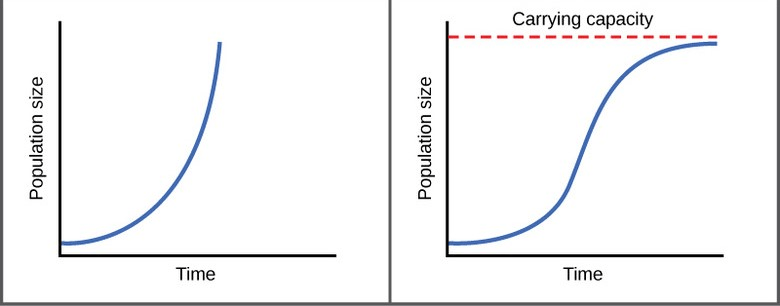 Exponential growth models don't consider carrying capacity and show this kind of curve.
Exponential growth models don't consider carrying capacity and show this kind of curve.
J Shaped Curve
These are the 2 factors used to describe people moving into or out of a population
Immigration and Emigration
The formula to find doubling time is also called the rule of this number
70
The maximum growth a species can have given unlimited resources is called this.
Biotic Potential
The type of survivorship curve is show by high survival throughout the lifespan, with individuals dying off at an old age
Type I
An age structure diagram separates a population by different age groups, but also by...... [usually color coded]
Gender
Give 2 of the defining characteristics of a population in stage 4 of demographic transition.
High Population, Low Death rates, Low birth rates, Slow population growth/declining population, healthcare, wealth, access to education.
These countries are more likely to have a greater impact on the environment, thanks to factors like higher wealth, greater resource consumption, meat heavy diet, industrial pollution, Amazon warehouses, Labubu's etc.
Developed
Mice have lots of offspring at once, reproduce quickly, and mature quickly. A mouse is an example of this type of species
R-selected
The resource in the ecosystem that is too low to allow further population growth is called this.
Limiting Resource
A developing country with a very wide base in the 0-4 range with a much smaller age range in 5-9 would likely be in this stage of development
Stage 1
The following equation is used to calculate this:
(CBR + Imm) - (CDR + Em)/10
Population Growth
High birth rate, and declining death rates with rapid population growth are signifiers of this stage of demographic transition.
Stage 2
If a population overshoots its carrying capacity, the population rapidly declines to fall back under it in an event called this
Dieback (Die-Off)
Sea turtles lay hundreds of eggs at once, then leave the eggs to hatch and fend for themselves. This behavior matches best with this survivorship type.
Type III
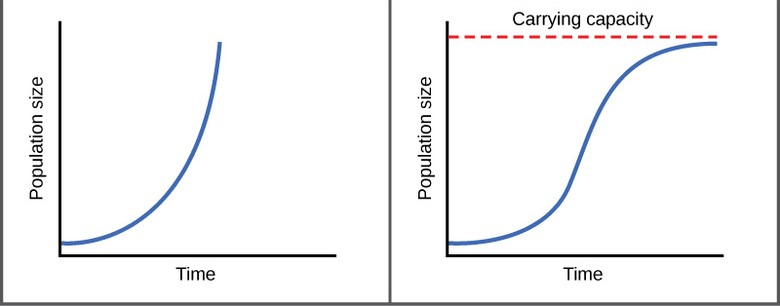 Population graphs that show an S-shaped curve are this type of growth model.
Population graphs that show an S-shaped curve are this type of growth model.
Logistic
The theory of environmental justice states that these populations more likely to be exposed to harmful ecological conditions. (Give 1)
Recent immigrants, People of Color, People with low socio-economic class.
What would the Total Fertility Rate need to be in order to be at Replacement level?
Around 2.1
A species with high fecundity has a high ability to?
Reproduce, especially abundantly with lots of kiddos.
A factor that is NOT dependent on the density of a population like a chemical spill polluting a pond for example is considered to be Density _____________
Density-Independent
An age structure diagram with in the shape of a column suggests that this is happening in the population.
Remaining Stable
The 3 factors are used to determine a country's impact on the environment
Population, Affluence, and Technology
What is the doubling time of a population that has a 5 percent growth rate
14