This term describes the total number of children a woman must have in order to replace her and her partner in the next generation. This can sustain a population and prevent it from decreasing.
What is replacement level fertility (RLF)?
This is the type of growth observed in this age structure diagram.
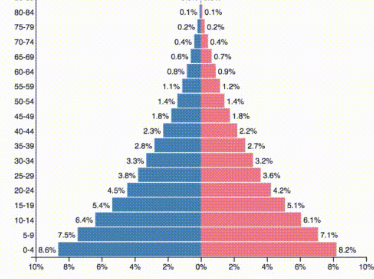
What is a rapidly growing population?
This is the type of growth curve that occurs when the growth rate is constant and limiting factors are not present.
What is exponential growth?
Species with this reproductive strategy are more likely to have low amounts of offspring with a high level of parental care at a young age.
What are K-selected reproductive strategy species?
Invasive species are likely to exhibit this type of reproductive strategy.
What is r-selected reproductive strategy?
Access to family planning, increased education for women, and access to contraceptives are all ways to decrease the _____ (three letter term that includes rate) of a country.
What is the total fertility rate (TFR)?
This is the type of population growth found in this age structure diagram.
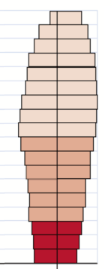
What is declining population growth?
Floods, natural disasters, and earthquakes are categorized as this type of limiting factor.
What are density-independent limiting factors?
Species with this type of reproductive strategy often have high biotic potential.
What are r-selected reproductive strategy species?
The term to describe the population exceeding the carrying capacity.
What is an overshoot?
This is the amount of years it would take a population with a growth rate of 4% to double in size.
What is 17.5 years?
This stage of the DTM is characterized by equal birth and death rates with emphasis on child labor in an agricultural society.
This is the maximum number of individuals of a population of a species that the environment and its resources can sustain for a long period of time.
What is carrying capacity?
Humans have this type of survivorship curve with lots of parental care at a young age to ensure high survival rates at a young age.
These are two reasons why a country's TFR (total fertility rate) can be lowered as it becomes more industrialized.
What are access to family planning, increase in women's education, increased use of contraceptives, widely available birth control, increased standard of living, etc.?
This is the growth rate of a population with a CBR of 32 and a CDR of 22.
What is 1% growth rate?
This stage of the DTM is characterized by low death rates and a drop in birth rates due to increase in women's education, family planning, and rise in contraceptive use.
What is Stage 3 of the Demographic Transition Model?
The type of population growth curve that is pictured here.
What is logistic growth?
The type of survivorship shown in the graph below.

Disease transmission, impact of predation, and access to food are examples of this type of limiting factor.
What are density-dependent limiting factors?
This term describes the number of children per 1000 individuals that do not survive past the age of 1.
What is infant mortality rate (IMR)?
This is the stage of the DTM that affluent countries (USA, Canada, South Korea) with increased wealth and education are in.
What is Stage 4 of the Demographic Transition Model?
This term describes the immediate population decline following the moment when the population exceeds the carrying capacity of the environment.
What is a dieback?
Small organisms with high biotic potential tend to have this type of reproductive strategy AND this type of survivorship curve (need to include BOTH correct answers).
What are r-selected reproductive strategy species and Type III survivorship?
These types of countries have higher infant mortality rates (IMR), higher TFR (total fertility rate), and comparatively more children in the workforce.
What are less developed countries or developing countries?
