Identify each boundary and Explain what changes to the lithosphere these boundaries provide.

Transform: (Earthquake) Two plates move along each other. The lithosphere is neither added-to nor destroyed at a Transform Boundary.
Divergent: Two plates move away from each other and create a mid-ocean ridge where magma rises up to form a new crust. (rift)
Convergent: When colliding, the two plates fold downwards and create a Subduction Zone. The denser tectonic plate slides under the less-dense plate. This sinking creates a trench. (Trench, Subduction zone, Volcanoes, and Mountains)
How do insolation, latitude, and wind patterns affect the climate of a region?
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
What are the three water resources?
Where is the majority of freshwater located on earth?
green water, blue water, gray water
Polar Ice Caps
Bottum-Up soil formation: Name the two types of weathering and describe how said weathering plays a part in soil formation. (Hint: Refer back to the environment succession events)
Top-Down soil formation: Explain how the organic component of soil is made and identify what soil horizon this formation takes place in.
Physical Weathering and Chemical weathering are key steps to erode rock into small sediments that end up being the mineral component of soil.
Humus: Primarily located in the O-Horizon; Made up of microorganisms (both dead and alive) with dead organisms in varying stages of decay and decomposition.
Each image relates to an aspect of the Atmosphere and how climate is affected by it. One displays the pattern of convention cycles while the other highlights on a larger scale how convection cycles tie into the overall climate.
Explain in each temperature area how climate is determined by both convention cycles and by the global circulation of winds (aka cells in the atmosphere)

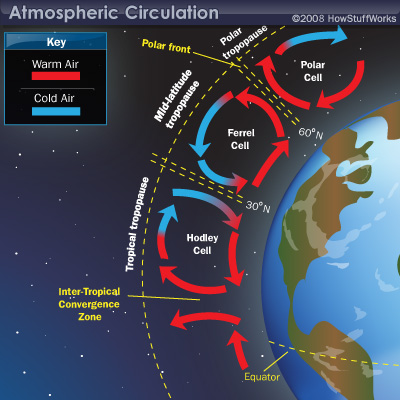
Yea, very tricky question. Discuss!!!!
Reminder for names: (Hadley Cell, Mid-latitude cell (Ferrel cell), (Polar cell))
Coriolis Effect in the simplest of terms: objects traveling long distances around the earth appear to move at a curve as opposed to a straight line.
Climate: (Wind patterns, convection cells, seasons:(how are seasons determined??))
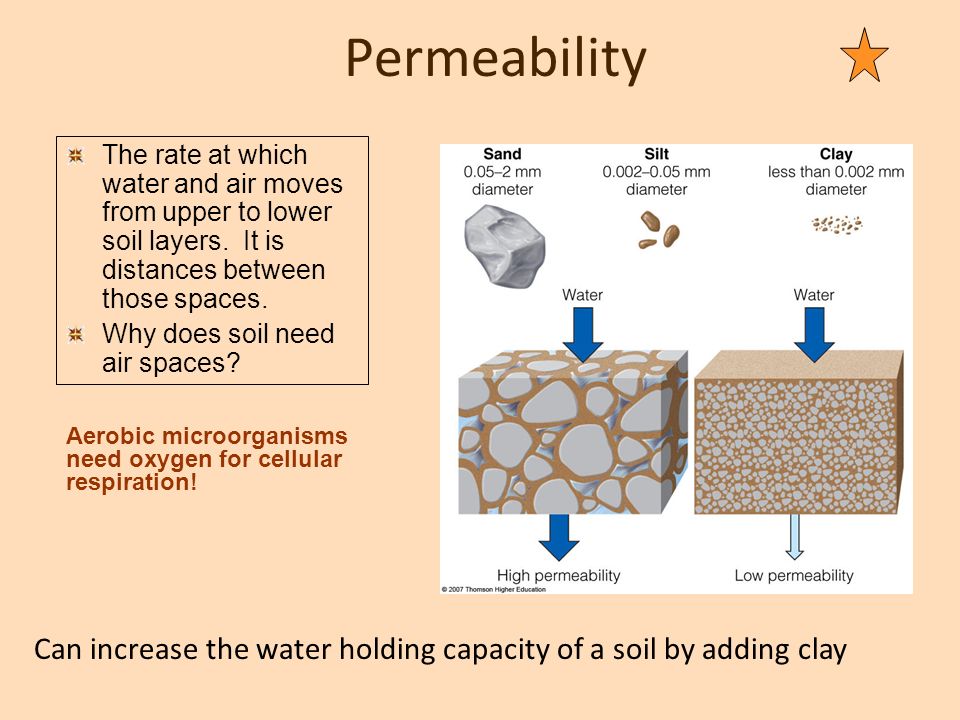
Pictured below is one of the optimal soils for gardening and growing crops. How do these three minerals play such a big role in the "perfectness" of soil?

The size affects the Permeability of the Soil, or its capacity to allow water to pass through.
Anyone except for a previous RO kid can answer this question: What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere?
Alright, real question incoming: There are four main layers of the atmosphere. What are they, and what's their key notable feature? (aka if asked in a question you'd instantly know the answer)
Troposphere: Almost all weather is in this layer; the Troposphere is the densest layer in the atmosphere.
Stratosphere: Ozone Layer
Mesosphere: The coldest atmospheric layer: temperature decreases as altitude increases.
Thermosphere: Most affected by solar activity; Aurora borealis.

How do geographic features in watersheds affect the movement of water?
Rivers, lakes, groundwater recharge
slope, land use, farms, wetlands, urban areas
((RUN-OFF AND SOIL EROSION)
Identify and define each soil layer and what they're composed of, what they contain, and what they are made of.
Also in reference because the image below didn't have these:
O Horizon (Humus): Top layer of soil profile composed of decaying organic material. (Think O for Organic)
A Horizon (Top Soil): Fully Decomposed Humus and a mixture of the three minerals that make up soil: Sand, Silt, and Clay.
(The O and A horizons are very important to farmers because they are the fertile areas of soil that support plant growth!!! The O, A, and E horizons can also be labeled as the "Zone of Leaching", where nutrients are washed down due to the movement of water through the soil profile)

Watersheds and more on how they are affected by the environment
understanding the geography of where watersheds start/end, (rain shadow effect)
Any other questions?
(Also Happy 300 Subscribers Mr. W!!!!)
