This process causes buildup of persistent organic pollutants in most aquatic organisms because POPs are fat soluble; so, they reside in fat tissue and are not removed.
What is Bioaccumulation?
This stage of sewage treatment removes organic matter using bacteria boosted by aeration.
What is Secondary Sewage Treatment?
Old phones, computers, monitors, etc., are considered this type of waste that contain POPs as well as several toxic heavy metals.
What is e-Waste?
Elevated levels of these, normally limiting nutrients, are the cause of eutrophication.
What are Nitrogen and Phosphorus?
Caffeine, Nicotine, Water.
Put these in order from highest (first) to lowest (last) LD50.
What are Water, Caffeine, and Nicotine?
This POP was once used globally to control mosquitos and also in American farms to control insect pests.
What is Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)?
Sewage, especially without tertiary sewage treatment, can cause this environmental problem in aquatic ecosystems?
What is Eutrophication?
This is one of the major alternatives to MSW and produces substantial air pollution as well as toxic waste residues.
What is Incineration?
The level of this gas (two words) drops during eutrophication.
What is Dissolved Oxygen?
The LD50 of a toxin (or disease) is defined this way.
What is the dose at which half of the test population is killed by the toxin (or disease)?
Many POPs are endocrine disruptors that have these two main effects.
What are Fertility Disorders and Developmental Disorders?
The last thing done to sewage before release involves either ultraviolet light or chemicals to do this.
What is kill pathogens?
These are three critical components of sanitary landfills that ensure waste pollution doesn't get into aquifers.
What are an Impermeable Liner, Leachate Collection System, and Monitoring?
Methane collection is often, but not always used (and isn't considered a necessary component).
Eutrophication can lead to ecosystem disruption because of toxic algae blooms and these two changes.
What are increased turbidity and decreased DO?
The LD50 of this toxin.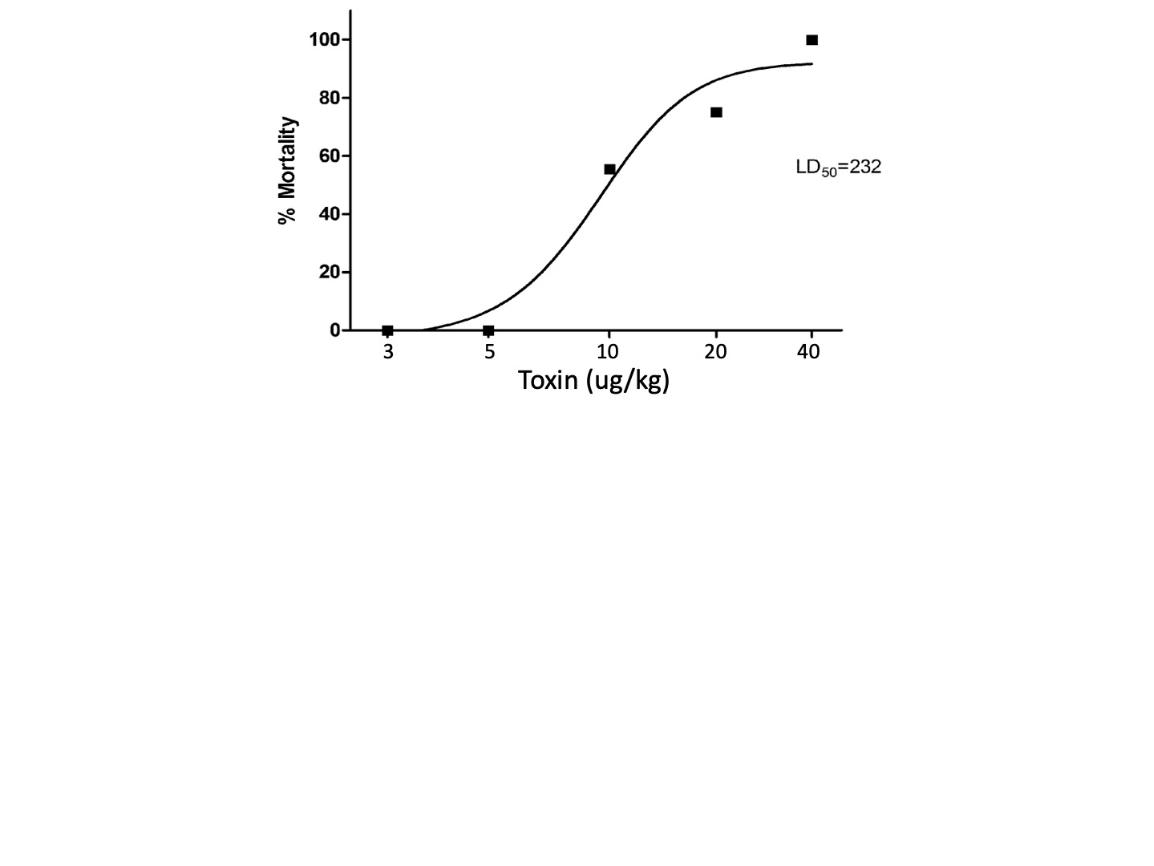
What is 10 micrograms/kg?
This process occurs in an aquatic ecosystem due to a combination of POPs in prey and the 10% Rule, resulting in very high levels of POPs in higher trophic levels.
What is Biomagnification?
These are two common waterborne diseases spread due to low water quality which can result from untreated sewage.
What are Typhoid, Cholera, Dysentery, Hepatitis A, and E. coli (choose 2)?
This law was enacted to regulate solid and hazardous waste.
What is the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)?
The name of this graph that describes DO levels in flowing water exposed to waste containing N and/or P.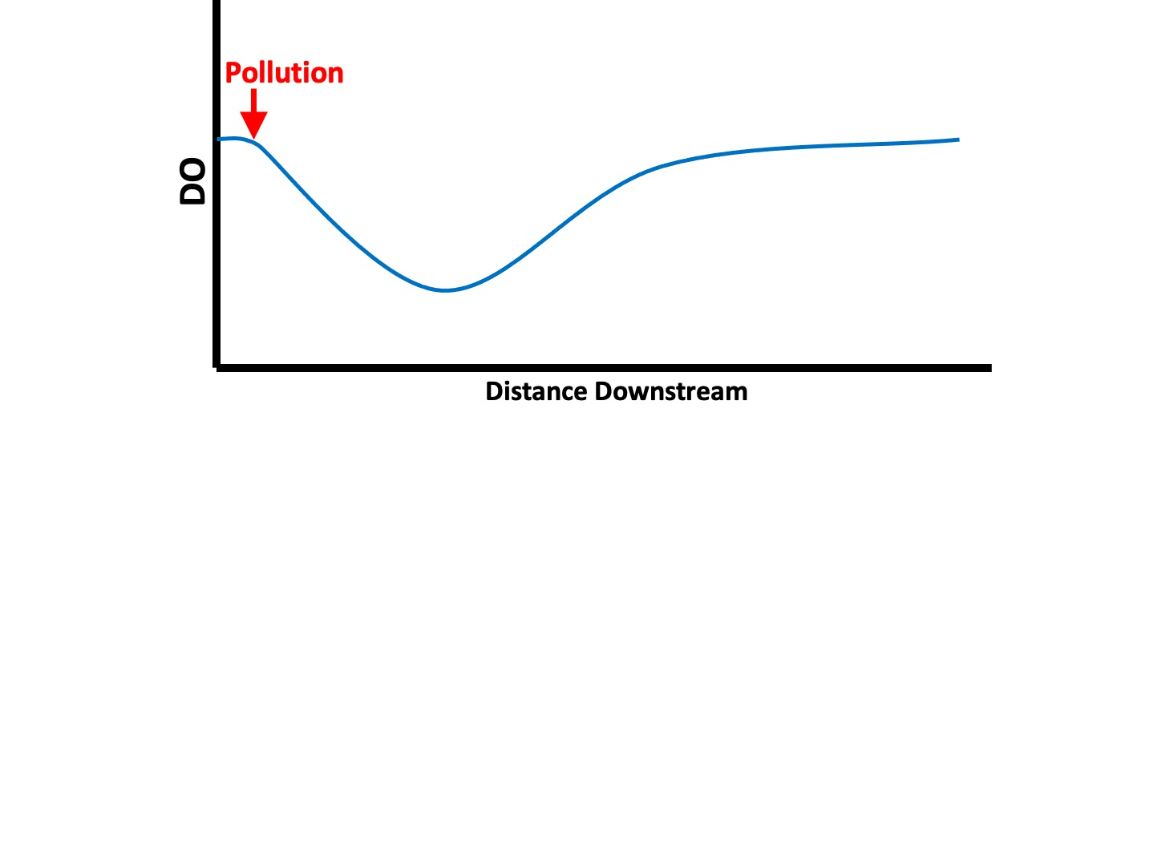
What is the Oxygen Sag Curve?
What are Arsenic, Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, and Chromium (any 3 of these 5)?
The "Dirty Dozen" POPs recognized by the Stockholm Convention are aldrin, chlordane, dieldrin, endrin, heptachlor, hexachlorobenzene, mirex, toxaphene, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), DDT, PCDD (dioxins) and PCDF (furans). This is a more recently identified POP that is used to make anti-stick coatings as well as foams.
What are Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl substances?
This stage of sewage treatment removes large particles in sewage using screens and gravity sedimentation.
What is Primary Sewage Treatment?
This law, also known as Superfund, regulates large cases of hazardous waste and its cleanup.
What is the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)?
This describes the amount of oxygen needed to support respiration of consumers and decomposers.
What is Biochemical Oxygen Demand?
Fleas spreading Bubonic Plague, for example.
What is a Vector?