normal language is controlled by this hemisphere
What is the left hemisphere?
lesions in this area result in impaired speech production and repeats, but preserved comprehension (except for syntax heavy meaning)
What is Broca's area?
this phenomenon occurs when there is bilateral damage beneath the calcarine sulcus near the occipital junction with temporal lobe
What is prosopagnosia?
*What is prosopagnosia?
impaired speech production, comprehension, and repeats
What is a global aphasia?
functional/psychogenic aphasia most commonly mimics this type of aphasia
What is Broca's aphasia?
these are important differences between the left and right hemisphere
L: language (linguistic content), skilled motor functions, verbal memory, processing detail, sequential and analytic musical skills
R: language (emotion/prosody), visual spatial analysis/attention, self-awareness, nonverbal memory, processing gestalt, music in untrained muscians
a transcortical aphasia results in a lesion disconnecting this area
What is Broca's area?
*Bonus: What is preserved in this aphasia?
deficit in attention to and awareness of contralateral personal extrapersonal space
What is neglect?
This triad of this syndrome is as follows:
1. optic ataxia
2. simultanagnosia
3. ocular apraxia
involuntary mimicry of examiner's movements
What is echopraxia?
the perisylvia language arc is all supplied by this artery
What is the MCA?
**BONUS: What are the structures in the perislyvian language arc?
adult onset stuttering is known as this type of aphasia
What is a psychogenic aphasia?
transcortical aphasias preserve this function
What is repetition?
lesions in this area result in impaired comprehension and repeats, but preserved speech production
What is Wernicke's area?
Simultanagnosia is a failure to perform this task
What is a failure to scan and integrate an entire visual scene/picture?
i.e. you can only see one object at a time
normal language is established by this age
What is age 5?
the definition of this term is as follows:
loss of normal inflection/emotional contet of speech
What is aprosodia?
a transcortical sensory aphasia results from a lesion to this area
What is a lesion disconnecting Wernicke's area?
*Bonus: What is preserved in this type of aphasia?,
Balint syndrome is the result of bilateral lesions to this area of the brain
What is the occipito-parietal junction?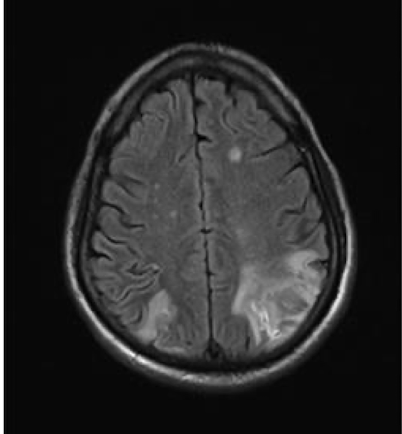
In visual processing, what is the difference between the dorsal and ventral pathway?
dorsal pathway = where
ventral pathway = what
this syndrome results from damage to the angular gyrus in the left parietal lobe and symptoms include finger agnosia, right-left confusion, agraphia, acalculia
What is Gerstmann syndrome?
idational apraxia is a hallmark of frontotemporal dementia. Describe ideational apraxia
cannot conceive/perform sequential steps in a task (i.e. can't follow steps to make coffee)
a L occipital plus a posterior corpus callosum lesion is usually associated with a R homonymous hemianopsia and this other aphasic finding
What is alexia without agraphia?
involuntary repetition of examiner's words
What is echolalia?
a lesion to the arcuate fasiculus results in this type of aphasia
What is a conduction aphasia?
*Bonus: What is preserved in this aphasia?