The study of relationships between people and their environments is known as _____.
Human Geography
What does the term "demography" refer to?
Demography refers to the statistical study of populations, including the structure, distribution, and trends.
What is culture, and what are its key components?
Culture is the set of beliefs, values, and practices shared by a group of people, including language, religion, and customs.
What is a state, and how does it differ from a nation?
A state is a politically organized territory with a permanent population and defined borders; a nation is a group of people with a shared identity. A state has legal borders.
What is subsistence agriculture?
Subsistence agriculture is farming that provides enough food for the farmer and their family, with little surplus for trade.
What is urbanization?
Urbanization is the process by which more people move to cities and urban areas, leading to growth.
What is industrialization?
Industrialization is the process of developing industries in a country or region on a wide scale.
What does "scale" refer to or measure?
"Scale" refers to the relationship between distance on a map and distance in the real world.
Describe the push-pull theory of migration.
The push-pull theory explains that people migrate due to "push" factors (e.g., war, famine) that drive them away and "pull" factors (e.g., job opportunities, better living conditions) that attract them.
Describe the concept of cultural diffusion. What are the different types of diffusion?
Cultural diffusion is the spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another.
Hierarchical (reverse), stimulus, contagious, relocation, and expansion.
Explain the significance of sovereignty in political geography.
Sovereignty is the authority of a state to govern itself and make decisions without external interference.
Describe the Green Revolution and its impact on agriculture.
The Green Revolution introduced high-yield crop varieties and modern agricultural techniques, significantly increasing food production.
Describe the concept of a central business district (CBD).
A central business district (CBD) is the commercial and business center of a city, characterized by high land values and concentrations of business activities.
Describe the role of globalization in economic development.
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness of economies, cultures, and populations, often leading to economic growth.
What is the difference between absolute and relative location?
Absolute location- exact location using coordinates
Relative location- the position in relation to other places
Difference: Absolute never changes, relative can change over time.
What are some factors influencing population growth rates? Name at least 3.
Factors influencing population growth rates include birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
Analyze how language can influence cultural identity.
Language shapes cultural identity by influencing communication, social interaction, and cultural practices.
Analyze a political map; what trends do you observe regarding borders?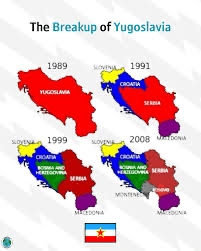
Trends may include changes in boundaries due to conflict, economic power shifts, or colonial legacies. In this case, we see different nations seeking soveignty.
Examine how urbanization affects rural land use.
Urbanization often leads to the conversion of rural land for housing and industrial uses, impacting food production.
Analyze the structure of a city using the concentric zone model.
The concentric zone model describes urban land use in concentric circles, each representing different social groups and land uses.
Analyze the relationship between resources and industrial location.
Resources, such as raw materials and energy sources, influence where industries are located due to accessibility and transportation costs.
Analyze a map showing population density; what trends can you identify?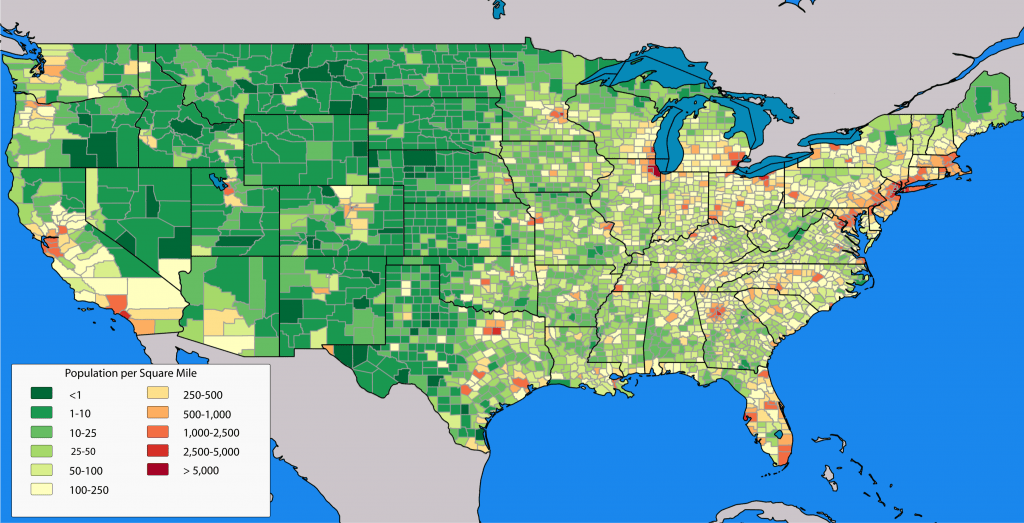
Higher population in urban areas. More people on the coasts or close to economic opportunity.
Examine a graph of migration patterns; what conclusions can be drawn?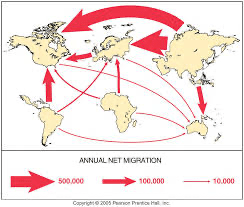
Answers may vary. Economic opportunity is an influence.
Think: what information is this map missing that could help provide a more detailed answer?
Give an example of cultural landscape in your city; how does it reflect the values of its culture?
A cultural landscape (e.g., architecture, land use) reflects the values and beliefs of its culture.
Painted bison: shared history with animal, mascot for football team.
Using the political cartoon, discuss the implications of governance in China.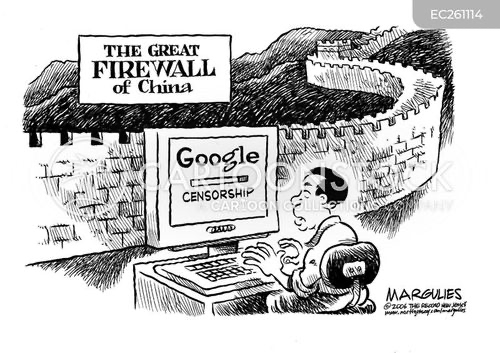
Censorship and government control due to China being a unitary communist state.
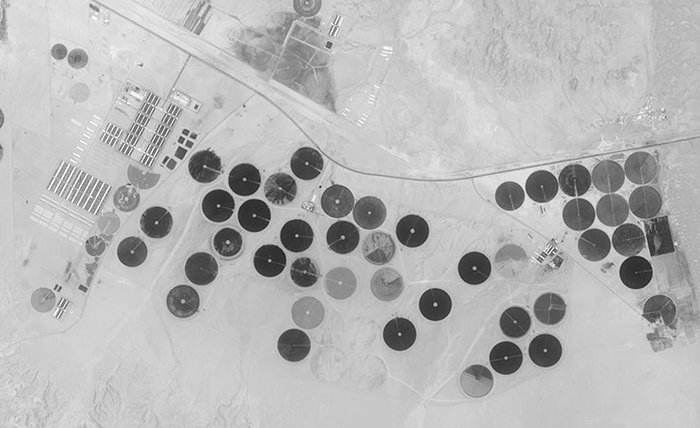
Explains why soil salinization is a concern in the arid landscape shown?
Irrigation increases the salt content of the soil, which disrupts the growth of crops and degrades soil fertility.
What challenges do cities face as they expand? Name at least 2.
Challenges may include overcrowding, infrastructure strain, pollution, and housing shortages.
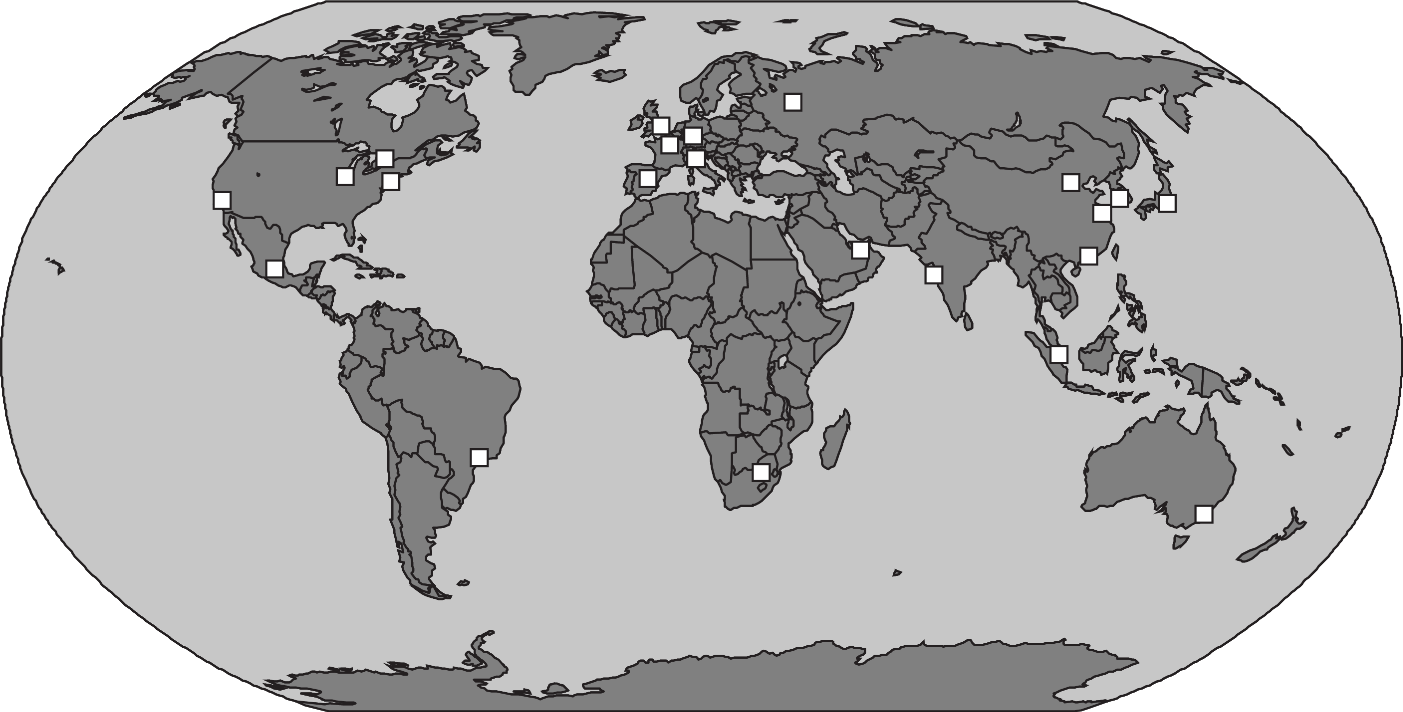
The map shows the locations of world financial, banking, and investment centers. What may be a limitation of the map’s representation of global economic patterns?
The map does not show the growth of investment in businesses in less developed countries.
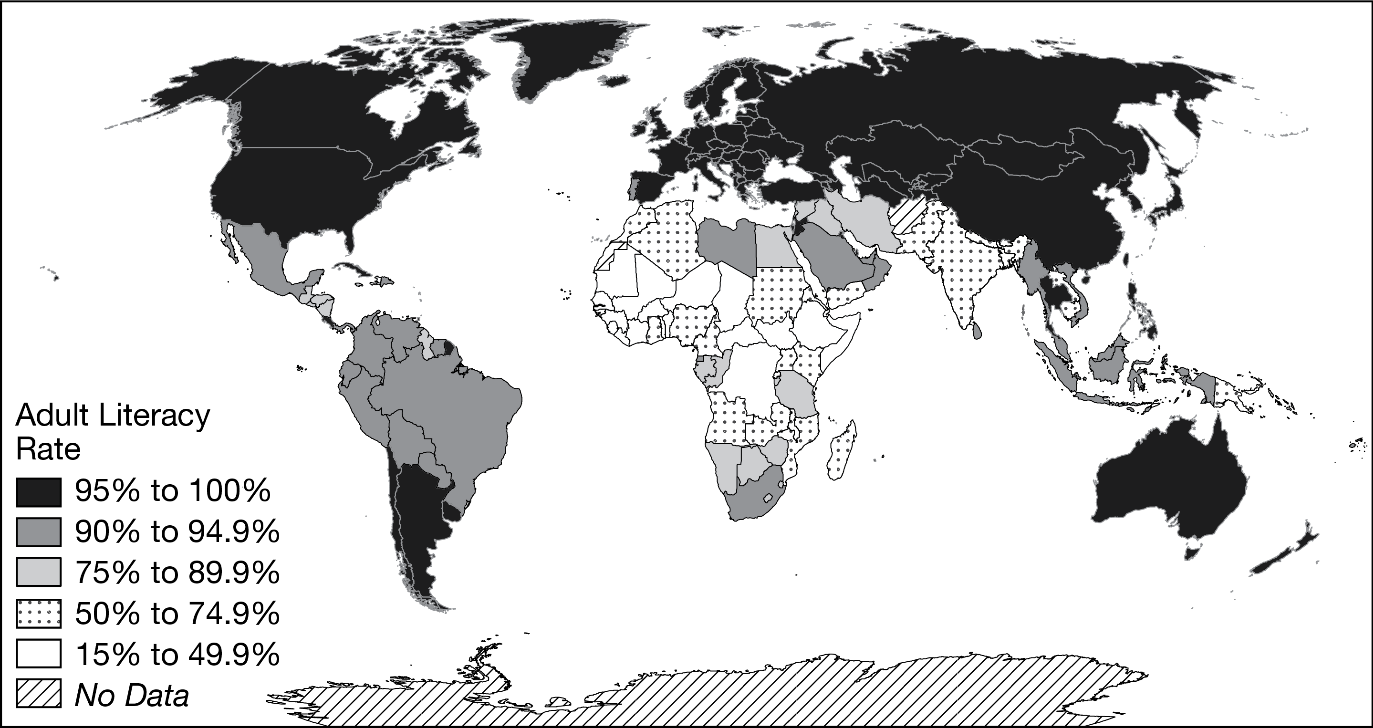 How can nongovernmental agencies use maps like the one above? Give a specific example!
How can nongovernmental agencies use maps like the one above? Give a specific example!
Deciding where to spend money on educational services.
Discuss the implications of migration on both the origin and destination regions.
What is the difference between acculturation and assimilation?
Migration brings cultural exchange and economic impacts to both origin and destination areas. Globalization.
Acculturation does not require the abandonment of home culture, which assimilation does.
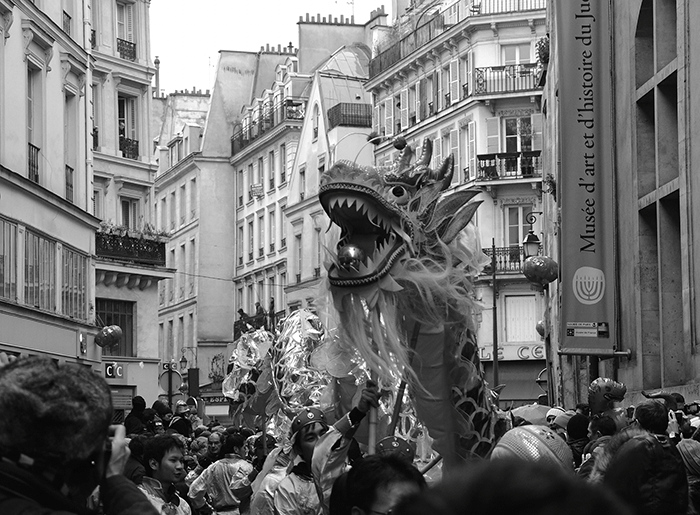

Discuss how globalization impacts cultural diversity.
Globalization can lead to the homogenization of cultures, threatening local traditions and languages.
OR
Globalization has increased cultural diversity through migration and increases exposure to diverse cultures.
Evaluate the impact of colonialism on contemporary political boundaries. Give a specific example outside of Africa.
Colonialism has led to borders that often ignore ethnic and cultural divisions, resulting in ongoing conflicts. I.e. Pakistan and India.
Using the following map showing production, discuss global trade implications.
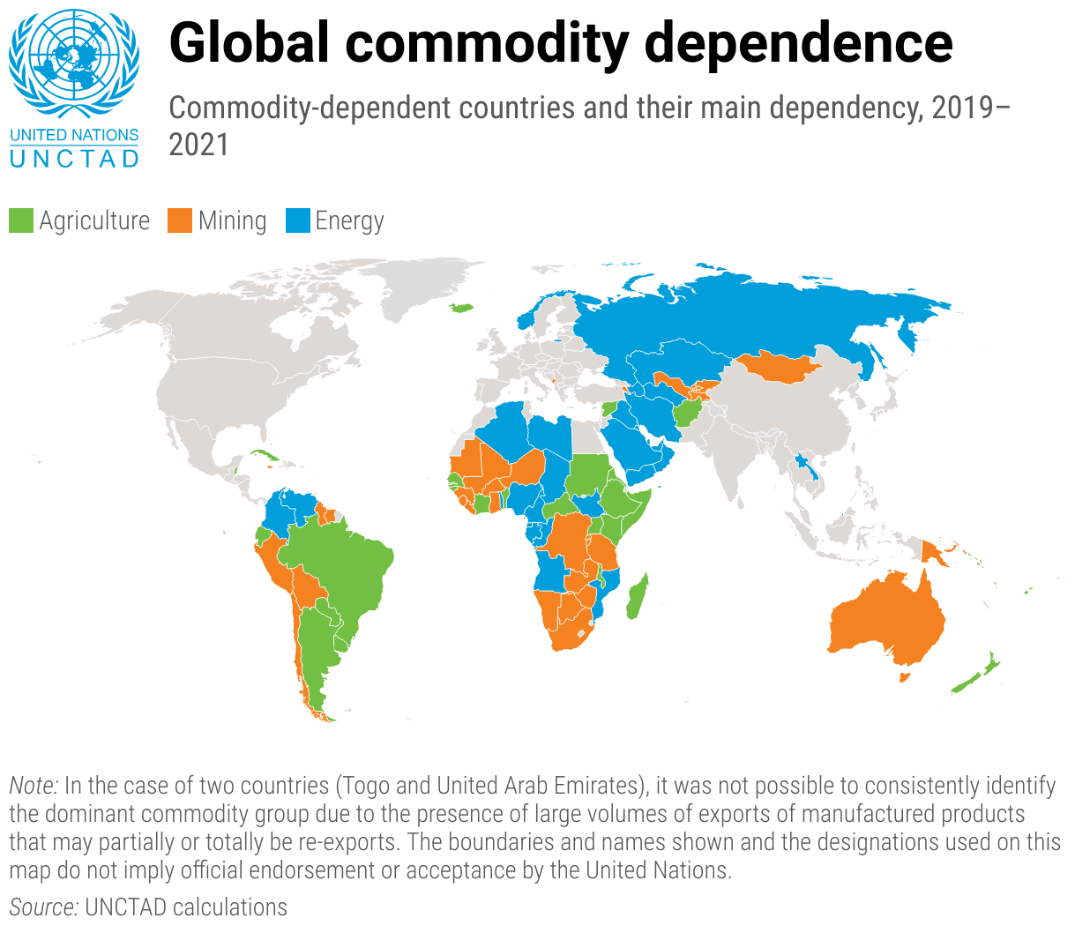
Global trade implications may include reliance on specific crops, economic dependencies, and food security issues.
Discuss the impact of gentrification on urban communities. Use the following image as an example:
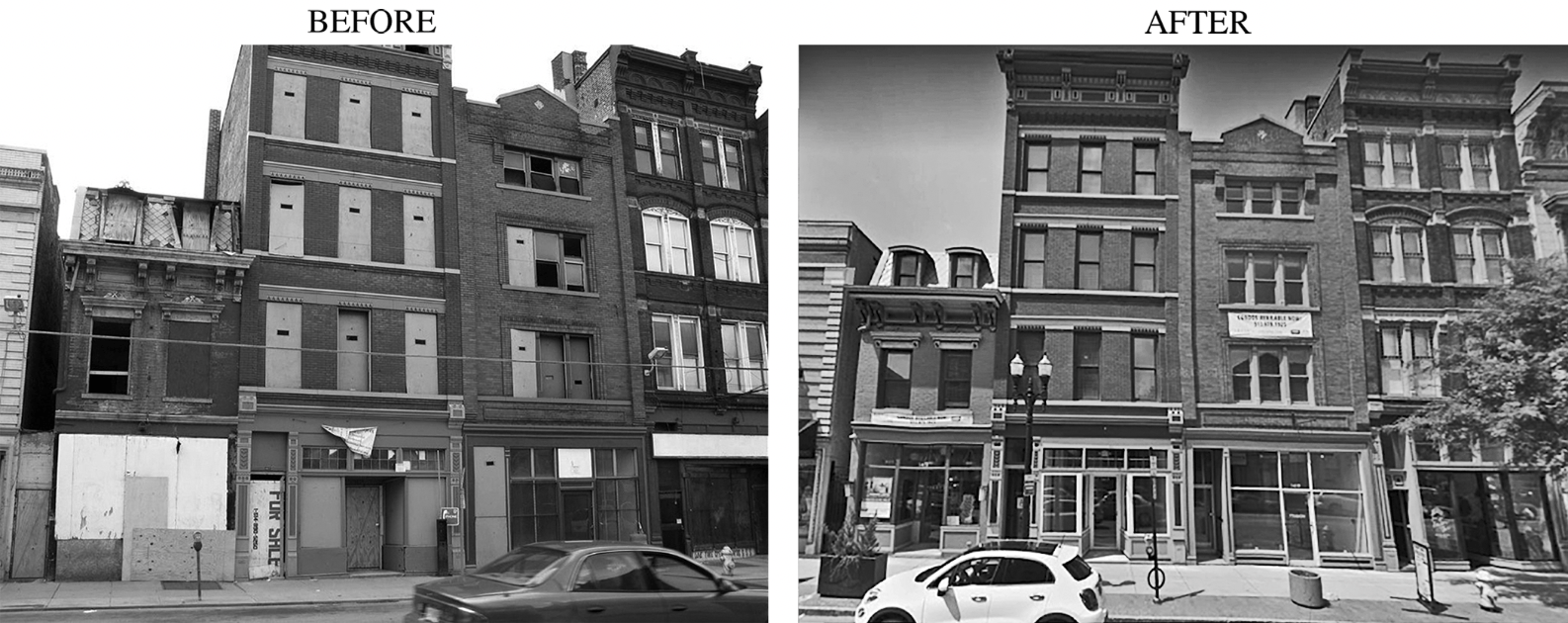

Gentrification can lead to displacement of lower-income residents and changes in neighborhood demographics.
What are some impacts of deindustrialization? I.e. the Rust Belt.
Economic and social: job loss, community decline, etc.