The scientific study of the statistics of a population.
Demography
The three things (data) that the demographic transition model shows.
Birth Rates, Death Rates, and Population or NIR
The three "groups" of people that a population pyramid shows.
Pre-Reproductive Years, Reproductive Years, Post-Reproductive Years (Kids, Adults, Old People)
The average number of children a woman will have in her lifetime is called:
Total Fertility Rate
China instituted this policy in hopes of controlling an out of control population.
One Child Policy
The largest number of people that the environment of a particular area can support.
Carrying Capacity
The dependency ratio seen in countries who are in Stage 2 of the DTM.
Youth Dependency Ratio
A population pyramid that is even through each age group with a long average life expectancy
Stage 4
Formula for calculating NIR
Crude Birth Rate- Crude Death Rate
In the Epidemiological Transition, this is the stage of "degenerative and human created diseases."
Stage 3
The term for a migrant who is leaving a country.
Emigrant
The Rate of Natural Increase in a country within stage 2 and 3 of the DTM.
High Natural Increase Rate
What stage of the demographic transition model is this country in?
Stage 3, (Low birth rates, low death rates, lower natural increase)
The population patterns seen in more developed countries include these traits
Lower fertility and death rates, aging population, elderly dependency ratio increases
The ratio comparing those who are too young or too old to work compared to the economically active.
Dependency Ratio
This English economist that argued that population will increase geometrically rather than arithmetically.
Thomas Malthus
Two main factors that lead to reduced birth rates in countries, and lead them to Stage 3.
Better Education and Contraception
A sudden dip in a population pyramid can be caused by:
war, disease, emigration, short term anti-natalist policies, etc.
Two physical traits and or characteristics that influence where population is distributed
Arable land, access to water (river, lake, ocean), climate, vegetation, natural resources
Migration that occurs because of a connection, either familial or to an ethnic community
Chain Migration
Internally Displaced Person
Two countries that are currently in stage 4 of the DTM (Zero population growth or very low growth)
Argentina, Australia, Canada, China, Brazil, most of Europe, Singapore, South Korea, and the U.S.
This population pyramid of a Colorado Community shows an anomaly, the reason for this strange structure is:
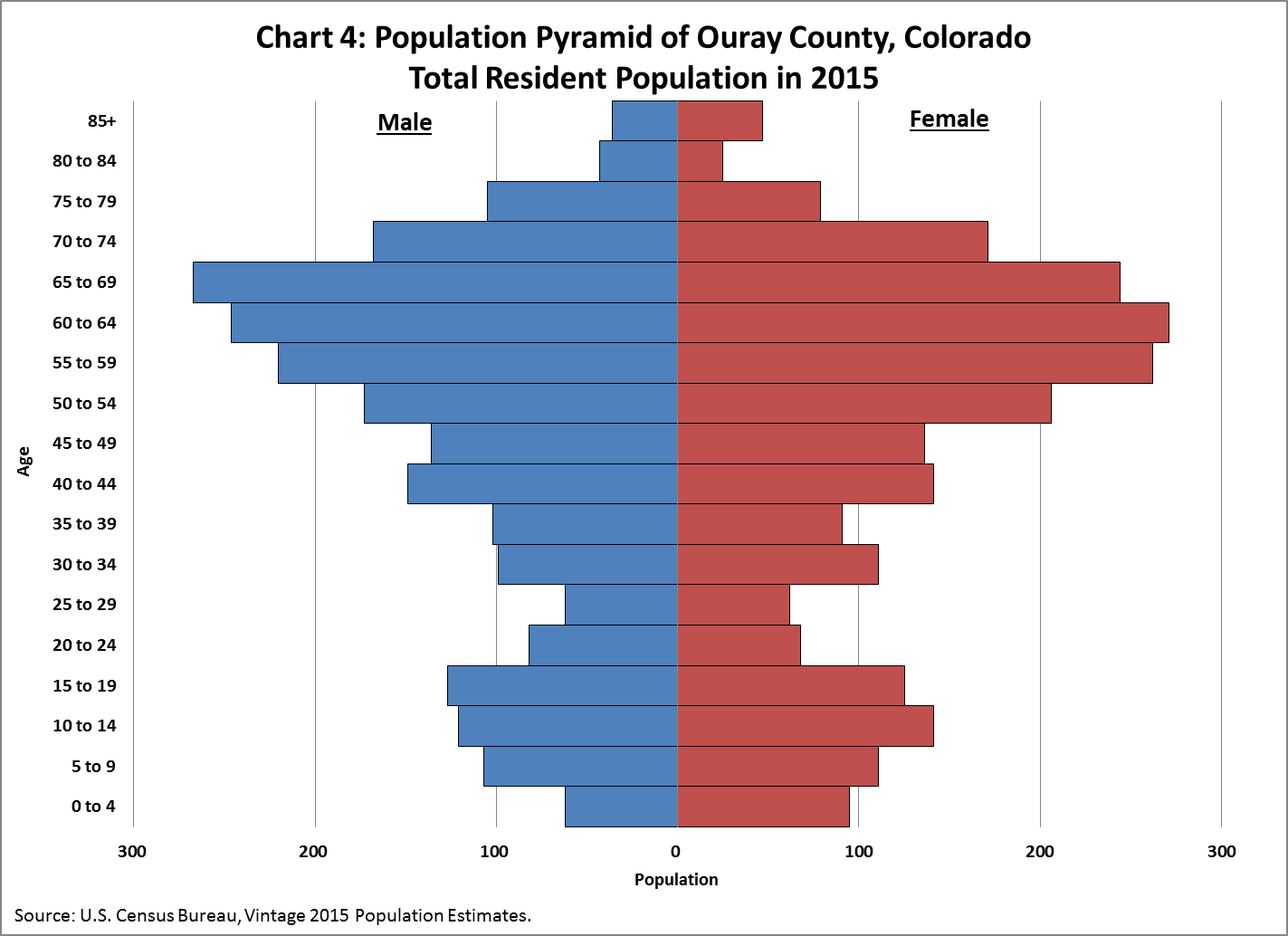
Large portions of people retire in this region of Colorado.
The term used to describe the population distribution seen below

Clustered Population Distribution
The main cause for the decrease in death rates seen as countries transition from Stage 1 to Stage 2 of the DTM.
Better hygiene, better sanitation, better access to healthcare.
