The scientific study of the statistics of a population.
Demography
The three things (data) that the demographic transition model shows.
Birth Rates, Death Rates, and Population or NIR
The three "groups" of people that a population pyramid shows.
Pre-Reproductive Years, Reproductive Years, Post-Reproductive Years (Kids, Adults, Old People)
The average number of children a woman will have in her lifetime is called:
Total Fertility Rate
China instituted this policy in hopes of controlling an out of control population.
One Child Policy
The largest number of people that the environment of a particular area can support.
Carrying Capacity
The main characteristics of the third stage of the DTM. (There should be 3)
Declining Birth Rates, Declining Death Rates, Slowing Population Growth.
Concave sides on a population pyramid means the country has:
A high death rate
Formula for calculating NIR
Crude Birth Rate- Crude Death Rate
In the Epidemiological Transition, this is the stage of "degenerative and human created diseases."
Stage 3
A portion of earth's surface occupied permanently by human settlement.
Ecumene
The revolution that allowed for rapidly declining death rates in the 2nd stage of the DTM.
The Industrial Revolution.
What stage of the demographic transition model is this country in?

Stage 3, (Low birth rates, low death rates, lower natural increase)
Formula for calculating physiological density
number of people divided by a unit (km) of arable land
The ratio comparing those who are too young or too old to work compared to the economically active.
Dependency Ratio
This English economist that argued that population will increase geometrically rather than arithmetically.
Thomas Malthus
Two main factors that lead to reduced birth rates in countries, and lead them to Stage 3.
Better Education and Contraception
A sudden dip in a population pyramid can be caused by:
war, disease, emigration, short term anti-natalist policies, etc.
Formula calculating agricultural density
The area of arable (farmable land) divided by the number of farmers in that region.
Term that best fits this scenario: Kathy wants to migrate to Canada, but there are laws that prevent it.
Intervening Obstacle
Someone who has been forced from their home because of unsafety, but is still within the borders of their country.
Internally Displaced Person
Two countries that are currently in stage 4 of the DTM (Zero population growth or very low growth)
Argentina, Australia, Canada, China, Brazil, most of Europe, Singapore, South Korea, and the U.S.
This population pyramid of Florida shows an anomaly, the reason for this strange structure is: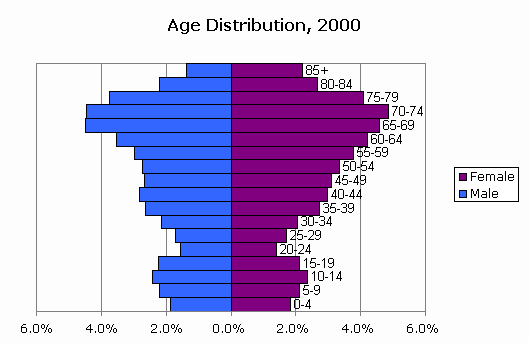
Large portions of people retire in this region of Florida.
The formula for the demographic equation (to determine total population)
Births-deaths+immigration-emigration=total population
The four most populated regions in the world where nearly 2/3 of the worlds population is located.
East Asia, South Asia, Europe, Southeast Asia