The variable of part of an experiment to which all others will be compared
What is the control?
Dendrochronology is the process of counting ______ to determine the _____ of a tree.
What are tree rings and age?
A force of attraction existing between any 2 masses
What is gravity?
The process of wearing or grinding something down by wind, water, or other natural agents
What is erosion?
The study of weather
What is meteorology?
The smallest chemical unit of matter
What is an atom?
A device that either multiplies or redirects a force
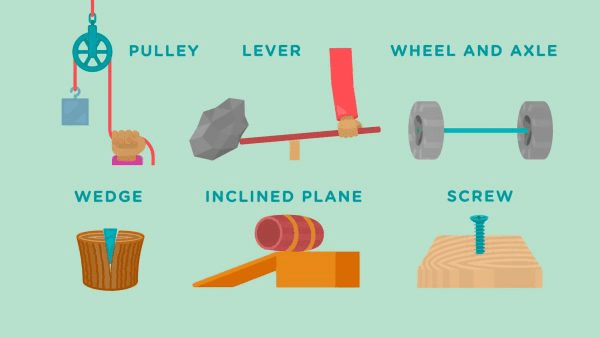
What is a simple machine?
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use the energy of sunlight and simple chemicals to produce their own food.
What is photosynthesis?
One of the main sources of food energy for most animals and are made up of simple sugars.
What are carbohydrates?
Organs for taking oxygen from water
What are gills?
An organism that makes its own food using energy from the sun or other sources.
What is a producer?
Experiments in which information about the test is kept from the participants to reduce bias
What are blind experiments?
The type of test that determines whether a document contradicts other known historical facts from other reliable documents or known archaeological
-internal
-external
-bibliographic
What is an external test?
A natural or artificial body orbiting a planet or star (i.e. the moon or the International Space Station)
What is a satellite?
Most of Earth's sediments are laid down by this material
What is water?
Moisture falling from the atmosphere as rain, snow, or hail
What is precipitation?
The 2 subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
What are protons and neutrons?
A closed path through which electric current flows
What is an electric circuit?
A method of sorting things according to shared qualities or characteristics
What is classification?
Animals with a supportive backbone.
What are vertebrates?
A community of organisms that interact with each other and their physical environment.
What is an ecosystem?
This biome is a treeless plain with a cold and dry climate
What is a tundra?
These are types of graphs used to visually represent data (list three)
What are bar graphs, line graphs, circle graphs, and double bar graphs?
The study of Earth's history as revealed in rocks that make up the Earth
What is Geology?
When the moon perfectly shields the sun's light so that only its atmosphere is visible.
What is a total solar eclipse?
The type of rock found in small amounts at the very top of the Grand Canyon as a result of volcanic activity.
What are igneous rocks?
The type of cloud that is white, puffy, and flat-bottomed
What is cumulus?
The temperature at which a solid material is heated so that it becomes a liquid.
An object in motion (or at rest) will tend to stay in motion (or at rest) until is is acted upon by an outside force.
What is Newton's First Law?
The material that exists in every cell that holds your genetic code, makes up your body's instruction manual, and is formed into a double helix.
What is DNA?
Complex molecules that are involved in nearly every reaction that supports life and primarily make up muscle and other organs of the body. They are made up of amino acids.
What are proteins?
A special gas-filled sac in most bony fishes that allows it to sink or rise in the water column depending on how much gas is inside.
What is an air bladder?
A symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit.
What is mutualism?
Experiments in which neither the experimenters nor the participants know the objects' identities in the setup
What are double-blind experiments?
Objects made by people, such as tools, weapons, containers, etc.
The wavelengths of visible light
What are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet? (ROY G BIV)
The layers of the Earth. 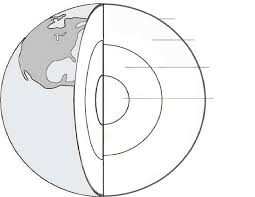
What are crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
The barrier at the upper edge of the mesosphere
What is the mesopause?
The type of bonding when 2 atoms share a pair of electrons.
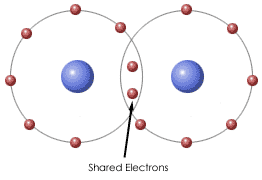
What is covalent bonding?
Allowing some light, but not detailed shapes, to pass through
A single-celled organism that does not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
What is a prokaryote (ex. bacteria)?
Tissue that rapidly multiplies to replace cells and also forms protective barriers within the body.
What is epithelial tissue?
A close living situation between 2 species where at least one of the species benefits.
What is symbiosis?
A model that shows feeding relationships in an ecosystem
What is a food web?
An aspect of an experiment that changes during the course of the experiment
What is an experimental variable?
What is the principle of superposition?
The amount of light or radiation reflected by a surface, typically that of a planet or moon.
What is an albedo?
The theory that much of the geology we see today is the result of sudden, violent, worldwide events that occurred once in Earth's past and will not be repeated
What is catastrophism?
Three of the air properties that are taken into consideration that meteorologists use to help predict the weather.
What are temperature, humidity, pressure and wind direction, wind speed?
The 3 main properties of a base
What is tasting chalky or bitter, feeling slippery to the touch, and receiving hydrogen ions?
This item is the load in an electrical circuit of a large flashlight powered by a 9-volt battery.
What is the light bulb?
List, in order from broadest to most specific, the 7 taxonomic classification divisions of living organisms (starting after Domain)
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Organisms that obtain their nourishment from dead organisms.
What are saprophytes?
The side of the jellyfish that is opposite the mouth.
What is the aboral side?
A symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits while the other is neither harmed nor helped.
What is commensalism?