What does it mean for two variables to be directly proportional?
1. The variables change by the same factor (if one doubles, the other also doubles).
2. A graph of the two variables is a straight line through the origin
3. The two variables have a constant ratio
What is the acceleration of the object represented in the graph below?
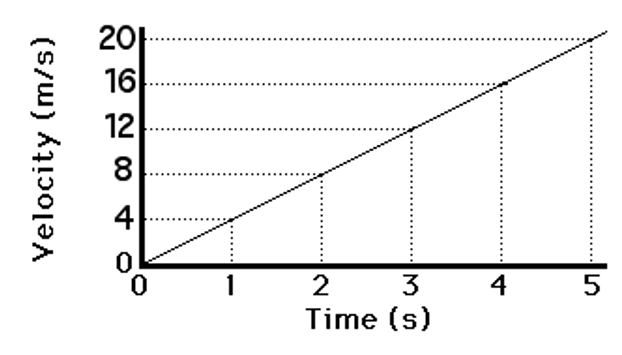
a = 4 m/s2
(acceleration is slope on a velocity-time graph)
How do you calculate the weight of an object?
F_g=mg
What must be true for an object to be slowing down?
Acceleration and Velocity must be in opposite directions (one negative and one positive)
Explain what must be true for an object in equilibrium? (hint: there are three key points)
An object in equilibrium must...
1. have zero acceleration
2. have zero net force
3. have a constant velocity (but not necessarily at rest)
A remote controlled car drives off a 100 m high cliff with a speed of 20 m/s. After falling for two seconds it has a speed of 28 m/s. What is the acceleration of the car as it falls?
a = g = -10 m/s2
Trick question: since the car is a projectile in free-fall after it leaves the cliff, it experiences the acceleration due to gravity as no other forces are acting on it. The numbers are there to confuse you
What are the two equations for work?
1.
W=Fd
2.
W=DeltaE=E_f-E_0
An elevator is moving downwards and undergoing a positive acceleration. What must be true about the normal force and force of gravity on a man in the elevator? (hint: draw a free-body diagram)
F_N>F_g
What types of energy does a bird flying above the ground have?
Only Kinetic Energy (for us to consider Gravitational Potential Energy, we'd need to look at the bird-Earth system)
A ball of mass M is launched straight up at a velocity of v and reaches a maximum height of h. A second ball of mass 2M is launched up with the same velocity v and a third ball of mass M/2 is launched up with a speed of 2v. What maximum heights will the second and third ball reach?
ball 2: h
ball 3: 4h
(remember that mass doesn't affect height for ball 2 and that doubling the velocity will change the initial energy by 4 since v is squared in the kinetic energy equation)
List the four pieces of lab equipment we've learned and what we can use them to measure.
1. Force sensor - measures (applied) force
2. Mass scale - measures mass
3. Ruler/Meter-stick - measures distance
4. Stopwatch/timer - measures time
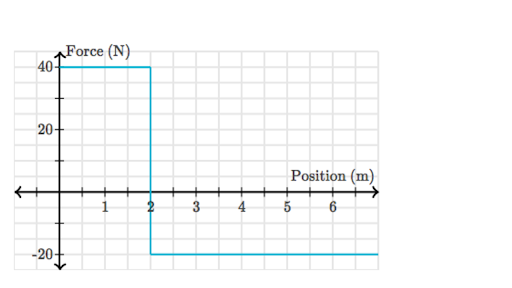
A cart undergoes the force shown in the graph below. Does the total energy of the cart increase, decrease, or remain the same?
The total energy decreases (since the total area) is negative.