Asia & Africa
Asia & Africa
Which continent was the birthplace of all the founding religions?
Asia
This trade network connected Europe, Asia, and North Africa, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies.
The Silk Roads
This deadly disease spread across Afro-Eurasia along trade routes in the 14th century.
the Black Death (will also accept bubonic plague)
This technological innovation transformed warfare and helped rulers consolidate power in land-based empires.
Gunpowder
This exchange transferred plants, animals, people, and diseases between the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
The Columbian Exchange
This dynasty expanded China’s territory, restored the civil service exam system, and promoted Confucian ideals.
The Song Dynasty
This luxury good from China was one of the most sought-after products traded across Afro-Eurasia.
Silk
This political system in medieval Europe was based on land ownership, mutual obligations, and decentralized authority.
This term describes the practice of rulers using religion to legitimize their authority.
Devine Right
(will also accept Mandate of Heaven)
This innovation improved maritime trade in the Indian Ocean by allowing sailors to navigate more accurately.
the Magnetic Compass
This belief system spread to China, Korea, and Japan along trade routes and emphasized the Four Noble Truths.
Buddhism
This animal revolutionized long-distance trade across the Sahara by carrying heavy loads over long distances.
The camel
This Church practice involved the sale of forgiveness for sins.
Indulgences
This empire, centered in Anatolia, captured Constantinople in 1453.
The Ottoman Empire
This deadly disease from Europe devastated Indigenous populations in the Americas.
Smallpox
This empire controlled large portions of Afro-Eurasia and facilitated trade and cultural exchange during the 13th and 14th centuries.
This religion spread widely along trade routes, especially throughout the Indian Ocean basin.
Islam
This pope called for the First Crusade in 1095 at the Council of Clermont.
Pope Urban II
This empire ruled much of Persia and made Shi’a Islam the official religion of the state.
The Safavid Empire
This Portuguese explorer was the first to sail around the southern tip of Africa to reach the Indian Ocean.
Vasco da Gama
This West African ruler famously demonstrated his empire’s wealth during a pilgrimage to Mecca in the 14th century.
Mansa Musa
This Abbasid capital became a center of commerce, learning (think House of Wisdom), and cultural exchange.
Baghdad
This invention helped spread Reformation ideas quickly across Europe.
the Printing Press
This land-based empire relied on a merit-based bureaucracy selected through civil service examinations.
The Qing Dynasty
(will also accept the Ming Dynasty)
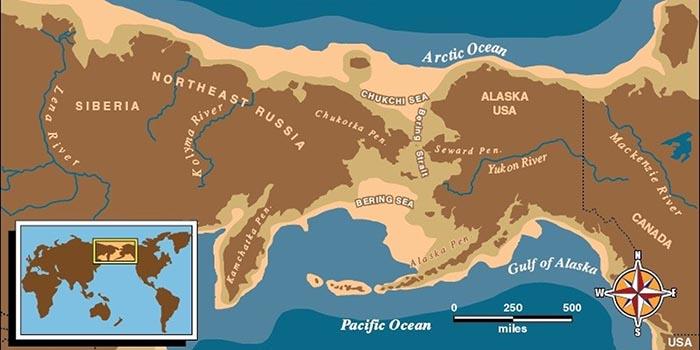
This narrow land bridge allowed early human migration into the Americas.
The Bering Land Bridge
(will also accept the Bering Strait)