A client is prescribed an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor for treatment of hypertension. What expected outcome does the nurse expect this medication will have?
A. Will prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II
B. Will have a direct vasoconstrictive effect on vessels of splanchnic circulation
C. Will increase extracellular fluid and decrease venous pressure
D. Will increase oxygen consumption of the heart
A. Will prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II
Rationale: Among the drugs used in the treatment of hypertension are ACE inhibitors. The ACE inhibitors act by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, thus decreasing angiotensin II levels and reducing its effect on vasoconstriction, aldosterone levels, intrarenal blood flow, and glomerular filtration rate. ACE inhibitors are increasingly used as the initial medication in mild to moderate hypertension.
The nurse will monitor a patient for signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia if the patient is taking which of these diuretics?
A. HCTZ
B. Furosemide
C. Acetazolamide
D. Spironolactone
D. Spironolactone
Rationale: Spironolactone is the only diuretic from these choices that is potassium sparing. Since it spares the potassium, persons taking this medications are more prone to developing hyperkalemia
The nurse is explaining to a patient the way that hydralazine lowers blood pressure. Which nursing statement is appropriate?
A. “Hydralazine helps arterial smooth muscle to contract.”
B. “Oral hydralazine is given to lower the blood pressure very quickly.”
C. “Hydralazine lowers peripheral vascular resistance, which lowers blood pressure.”
D. “Hydralazine is really for heart failure, but it can also lower blood pressure.”
B. “Oral hydralazine is given to lower the blood pressure very quickly.”
It often takes 1.5 to 3 months for a full therapeutic effect of oral hydralazine. Hydralazine or sodium nitroprusside can be administered intravenously to lower blood pressure quickly.
A client should be instructed to take sublingual NTG how often if they experience chest pain?
A. q 1 minute x3
B. q 2 minute X 5
C. q 5 minute x3
D. q 10 minute x 5
C. q 5 minute x3
A nurse is teaching a 54-year-old client how to take sublingual nitroglycerin. What statement by the client indicates an understanding of the nurse’s instructions?
A) “A headache means a toxic level has been reached.”
B) “I can take up to three tablets at 5-minute intervals.”
C) “I can take the drug as needed because it is not habit forming.”
D) “If I become dizzy after taking the medication, I should stop taking it.”
B) “I can take up to three tablets at 5-minute intervals.”
Identify this complex and what it does:
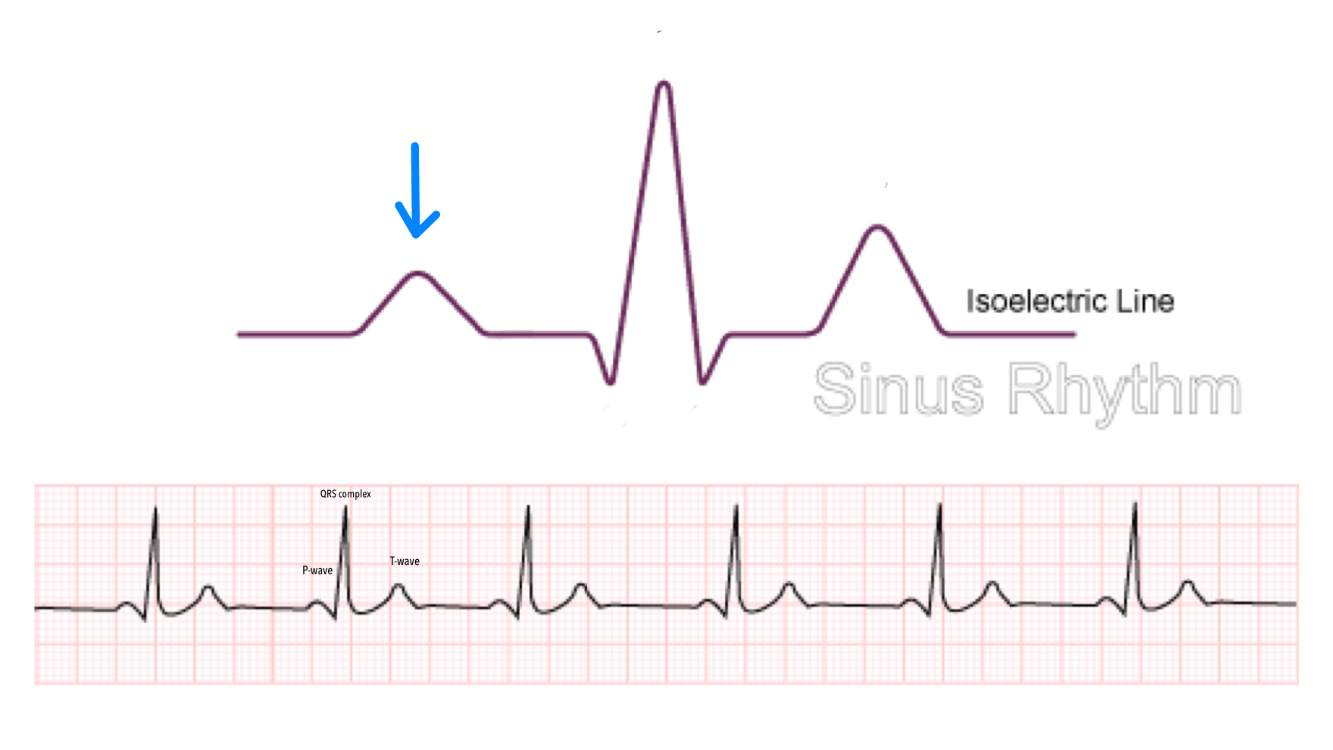
P wave
Atrial depolarization
An older adult client newly diagnosed with systolic hypertension asks their health care provider why this happens. Which response is most accurate?
A. “Everyone over the age of 50 tends to have their blood pressure creep up over the years.”
B. “With age, your arteries lose their elasticity and are replaced with collagen, which makes your arteries stiffer.”
C. “Your heart has to work harder to pump blood through your vessels as you get older.”
D. “If you slow down and rest more, your blood pressure will more than likely return to its normal level.”
B. “With age, your arteries lose their elasticity and are replaced with collagen, which makes your arteries stiffer.”
Rationale:
Systolic blood pressure rises almost linearly between 30 and 84 years of age, whereas diastolic pressure rises until 50 years of age and then levels off or decreases. This rise in systolic pressure is thought to be related to increased stiffness of the large arteries. With aging, the elastin fibers in the walls of the arteries are gradually replaced by collagen fibers that render the vessels stiffer and less compliant.
A client taking an antihypertensive drug for several months comes to the health care provider’s office with a dry, persistent cough. The nurse knows that this cough is an adverse effect of which class of antihypertensive drugs?
A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
B. Beta Blockers
C. Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
D. Calcium Channel Blockers
A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Rationale: ACE inhibitors inhibit bradykinin degradation in the lungs, which can cause a common side effect of a dry, nonproductive cough.
Furosemide is prescribed for a patient who is about to be discharged, and the nurse provides instructions to the patient about the medication. Which statement by the nurse is correct?
- A: “Take this medication in the evening.”
- B: “Avoid foods high in potassium, such as bananas, oranges, fresh vegetables, and dates.”
- C: “If you experience weight gain, such as 5 pounds or more per week, be sure to tell your physician during your next routine visit.”
- D. “Be sure to change positions slowly and rise slowly after sitting or lying so as to prevent dizziness and possible fainting because of blood pressure changes.”
- D. “Be sure to change positions slowly and rise slowly after sitting or lying so as to prevent dizziness and possible fainting because of blood pressure changes.”
Rationale:
Persons taking furosemide, a loop diuretic, are prone to developing orthostatic hypotension.
A patient who has been admitted for a hypertensive crisis is prescribed hydralazine. Which nursing intervention is the priority?
Orient the patient to the unit.
Place a fall-risk armband on the patient.
Place an order for appropriate diet.
Complete the history and physical.
Place a fall-risk armband on the patient.
A client who experienced an ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) received fibrinolytic therapy with streptokinase. Which manifestation alerts the nurse to a developing complication?
A. Decreased level of consciousness
B. Hypoglycemia
C. Symmetrical joint pain
D. Diarrhea
A. Decreased level of consciousness
Fibrinolytic therapy is most effective in treating STEMI when administered within 30 minutes after the onset of symptoms. It can still be beneficial up to 12 hours after the onset of ischemic pain. Clients who should not receive fibrinolytic therapy are those with a history of intracranial hemorrhage or significant trauma within the preceding 3 months. The primary complication of fibrinolytic treatment is intracranial bleeding that usually occurs within the first 24 hours following treatment. This would be evident with a change in mental status or level of consciousness (LOC).
When the nurse administers a beta-adrenergic blocker to a client with angina, the nurse expects the drug will help to control angina. What other effect does a beta-adrenergic blocker have?
A) increased heart rate
B) increased oxygen consumption
C) decreased strength of heart muscle contraction
D) decreased urinary output
C) decreased strength of heart muscle contraction
Identify this complex and its action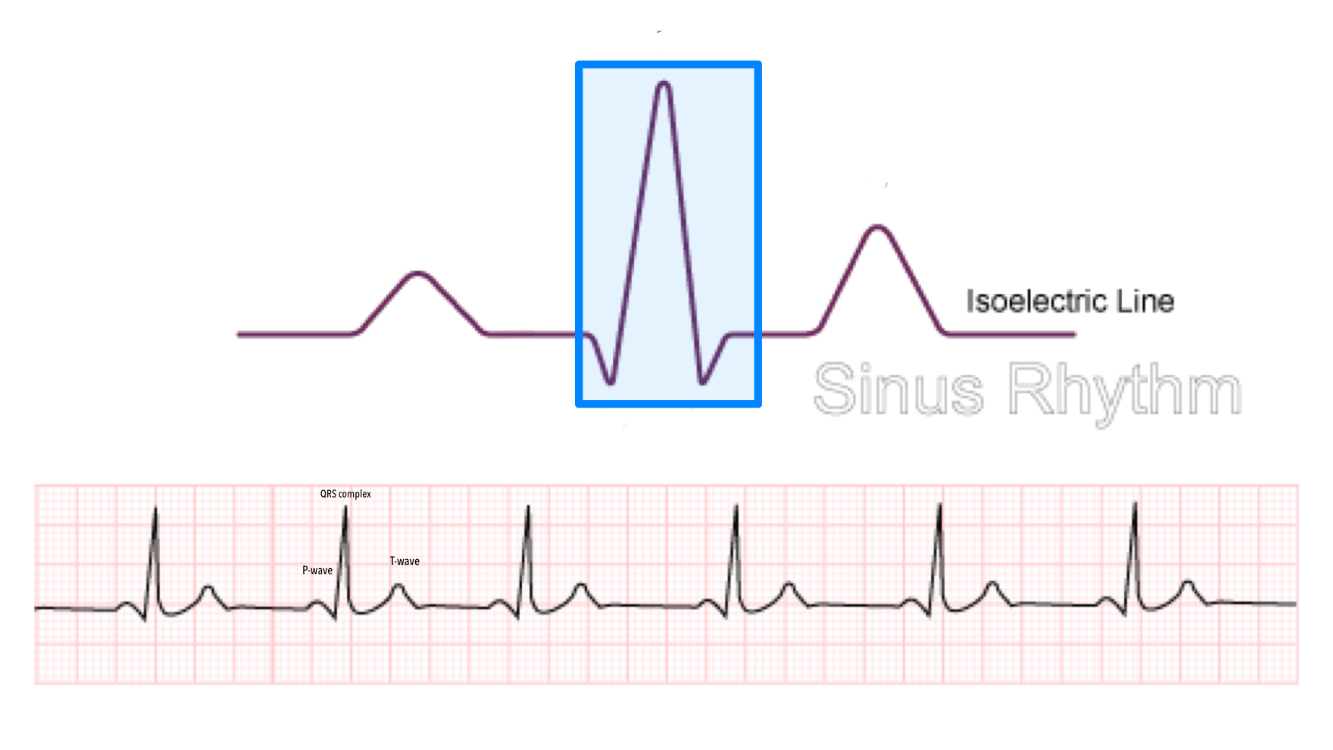
QRS
Ventricular depolarization
DAILY DOUBLE!!!
When reviewing diagnostic test results and physical assessment data for a client with a history of stage II hypertension, which of the following would be of most concern to the nurse?
A. an ejection fraction of 40%
B. Blood pressure of 146/80
C. Point of maximum impulse is located midclavicular at the 5th intercostal space
D. A heart rate of 62 bpm
A. an ejection fraction of 40%
Rationale: This ejection fraction is below normal (normal is about 55% to 75%) and indicates a poor prognosis. This low ejection fraction is a result of the complications of long-standing hypertension.
A patient taking an ACE inhibitor is scheduled for surgery. Because this medication may be dangerous in the setting of general anesthesia, the nurse should
A. stop the drug without discussing with the providers.
B. alert the provider caring for the patient and mark the patient’s chart prominently.
C. cancel the surgery and consult with the prescriber.
D. monitor fluid levels and make sure the fluids are restricted before surgery.
B. alert the provider caring for the patient and mark the patient’s chart prominently.
When reviewing the mechanisms of action of diuretics, the nurse knows that which statement is true about loop diuretics?
A. They work by inhibiting aldosterone.
B. They are very potent, having a diuretic effect that lasts at least 6 hours.
C. They have a rapid onset of action and cause rapid diuresis.
D. They are not effective when the creatinine clearance decreases below 25 mL/min.
C. They have a rapid onset of action and cause rapid diuresis.
A patient with hypertension is prescribed amlodipine. The patient asks the nurse, “Why do I only take it once a day?” Which nursing response is appropriate?
A.
“It’s easier to take medications that are dosed once daily.”
B.
“By just taking it once a day, there is a cost savings.”
C.
“Amlodipine has a long half-life so it is only needed once a day.”
D.
“Taking the drug once a day allows for peak effect at the right time.”
“Amlodipine has a long half-life so it is only needed once a day.”
A client is prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin for treatment of angina. The nurse instructs the client to do what if chest pain occurs?
A. “Use the nitroglycerin if your chest pain doesn’t subside on its own in 3 minutes.”
B. “If the medication burns or causes a headache, get a new prescription.”
C. “If the chest pain doesn’t go away after three tablets are given 5 minutes apart, call 911.”
D. “The pills are usually good for 12 to 18 months after the prescription is filled.”
C. “If the chest pain doesn’t go away after three tablets are given 5 minutes apart, call 911.”
Which statement by the client would lead the nurse to believe that the client has understood the teaching provided regarding angina?
A) “I will not exercise because it precipitates angina.”
B) “As long as I take the medicine, I can maintain my current lifestyle.”
C) “There is no correlation between my hypertension and angina.”
D) “Heavy meals and cigarette smoking can precipitate an angina attack.”
D) “Heavy meals and cigarette smoking can precipitate an angina attack.”
A nurse is preparing to administer a prescribed cardiac glycoside to a patient based on the understanding that this group of drugs acts in which way?
A. They work in the kidneys to increase fluid excretion.
B. They affect renin release in the renin–angiotensin system.
C. They block the parasympathetic influence on the heart muscle.
D. They affect intracellular calcium levels in the heart muscle.
D. They affect intracellular calcium levels in the heart muscle.
A 60-year-old female has survived a myocardial infarction. The nurse is providing care for impaired ventricular function because:
A. the cells become hypertrophic
B. the resulting ischemia leads to hypoxic injury and myocardial cell death
C. there is a temporary alteration in electrolyte balance
D. there is too much stress on the heart
B. the resulting ischemia leads to hypoxic injury and myocardial cell death
Rationale:The patient has impaired ventricular functioning because a portion of the myocardium has died due to ischemia. Impaired ventricular function is due to damage to the myocardium; it is not due to electrolyte imbalance. There was stress on the heart, but the impaired functioning is due to myocardial damage secondary to ischemia. The impaired ventricular dysfunction is due to myocardial cell death, not hypertrophy.
At a follow-up appointment, a patient who is taking hydralazine for hypertension reports feeling lightheaded and dizzy when standing up. What teaching will the nurse provide?
“Be sure to rise quickly when you stand up.”
“Sit on the edge of the chair and stand up slowly.”
“Consuming less alcohol will help with this. “
“If you exercise more, the dizziness will subside.”
“Sit on the edge of the chair and stand up slowly.”
When a patient is receiving diuretic therapy, which of these assessment measures would best reflect the patient’s fluid volume status?
A. Blood pressure and pule
B. Serum potassium and sodium levels
C. Intake, output, and daily weight
D. Measurements of abdominal girth and circumference
C. Intake, output, and daily weight
3. Diltiazem has been prescribed for a client who has been taking cyclosporine to prevent rejection of a kidney transplant. What is the nurse’s best action?
A) Ensure that the client is frequently assessed for signs and symptoms of diltiazem toxicity.
B) Notify the primary health care provider about the potential for elevated or toxic cyclosporine levels.
C) Monitor the client’s renal function closely for signs or symptoms of kidney rejection.
D) Ensure that the client’s cyclosporine is administered at least 2 hours before or after diltiazem.
B) Notify the primary health care provider about the potential for elevated or toxic cyclosporine levels.
A client with a long-standing diagnosis of angina has been prescribed nitroglycerin and diltiazem. In addition to monitoring the client’s heart rate, the nurse should prioritize what assessment?
A) blood pressure
B) level of consciousness
C) daily weights
D) respiratory status
A) blood pressure
As part of their orientation to a cardiac care unit, a group of recent nursing graduates is receiving a refresher in cardiac physiology from the unit educator. Which teaching point captures a component of cardiac function?
A. “Efficient heart function requires that the ventricles not retain any blood at the end of the cardiac cycle.
B. “The heart sounds that we listen to as part of our assessments are the sounds of myocardium contracting.”
C. “The diastolic phase is characterized by relaxation of ventricles and their filling with blood.”
D. “Aortic pressure will exceed ventricular pressure during systole.”
C. “The diastolic phase is characterized by relaxation of ventricles and their filling with blood.”
Rationale: Diastole is associated with ventricular filling and relaxation. Cardiac output is not 100% or near to it with each cardiac cycle. Heart sounds are associated with valve closing. Ventricular pressure exceeds that of the aorta during systole.
1. A nurse is providing education to a client who has been experiencing unstable angina. What is the nurse’s best explanation of this condition?
A) “A coronary vessel has become completely plugged and is unable to deliver blood to your heart.”
B) “The pain is caused by a spasm of a blood vessel, not just from the vessel narrowing.”
C) “There is serious narrowing of a coronary artery causing a reduction in oxygen to the heart.”
D) “Your body’s response to a lack of oxygen in the heart muscle is causing the pain you are feeling.”
C) “There is serious narrowing of a coronary artery causing a reduction in oxygen to the heart.”
Which is the cause of peripheral edema in an individual with heart failure?
A. The backup effect of left-sided heart failure
B. The forward effect of left-sided heart failure
C. The backup effect of right-sided heart failure
D. The forward effect of right-sided heart failure
A. The backup effect of left-sided heart failure
Pulmonary congestion is experienced by the patient with the backup effects of left-sided heart failure.
B. The forward effect of left-sided heart failure
Fatigue and mild acidosis are experienced by the patient with the forward effect of left-sided heart failure.
C. The backup effect of right-sided heart failure
The backup effect results in systematic congestion and peripheral edema.
D. The forward effect of right-sided heart failure
Less blood is pumped into the systemic circulation as a result of the forward effect of right-sided heart failure.
A patient with primary hypertension is prescribed drug therapy for the first time. The patient asks how long drug therapy will be needed. Which answer by the nurse is the correct response?
A. “Therapy for high blood pressure is usually lifelong.”
B. “This therapy will go on until your symptoms disappear.”
C. “This therapy will take about 3 months.”
D. “This therapy will take about a year.”
A. “Therapy for high blood pressure is usually lifelong.”
The nurse would anticipate an order for a loop diuretic as the drug of choice for a patient with
A. hypertension.
B. septic shock.
C. pulmonary edema.
D. fluid retention of pregnancy.
C. pulmonary edema.
5. A nurse is caring for a client taking a beta-blocker and a nitrate to treat angina. The nurse recognizes the need for careful monitoring because of what comorbidity?
A) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
B) rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
C) irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
D) chronic urinary tract infection (UTI)
A) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
An older adult client who is taking metformin has just been seen in the clinic. The primary health care provider prescribes metoprolol for angina. What assessment data should the nurse prioritize due to this drug combination?
A) white cell differential
B) blood glucose
C) urine specific gravity
D) intake and output
B) blood glucose
The nurse knows that the primary long-term regulation of blood pressure is exerted by which body system?
A. Hormonal activity
B. Humoral influence
C. The kidneys
D. Neural Mechanisms
C. The kidneys
Rationale:
The kidneys exert long-term control of blood pressure by modulating sodium content and extracellular fluid volume. An increase in extracellular fluid will yield an increase in blood volume and an increase in cardiac output. If this results in too great an increase in blood pressure, the kidneys will excrete sodium and water. Neural (autonomic nervous system) and humoral mechanisms (renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and vasopressin) exert short-term control of blood pressure. Hormonal influence involves release of epinephrine (which works through the sympathetic nervous system) from the adrenal glands.
Increased cardiac workload with left-sided heart failure can result in which change to the myocardial cells?
A. Hyperplasia
B. Atrophy
C. Hypertrophy
D. Dysplasia
C. Hypertrophy
Myocardial hypertrophy is a compensatory mechanism in heart failure as the heart attempts to maintain adequate pumping ability. Paradoxically, hypertrophy can gradually decrease cardiac efficiency.
A client with heart failure tells the nurse that they are frustrated and are unable to get “a good night’s rest.” The client relates that they fall asleep and are suddenly awakened and feel as though they are having a hard time breathing and are suffocating. The nurse recognizes this assessment as:
A. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
B. Orthopnea
C. Cardiac asthma
D. Sleep apnea
A. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea is a sudden attack of dyspnea that occurs during sleep. It disrupts sleep, and the person awakens with a feeling of extreme suffocation that resolves when they sit up. Orthopnea is shortness of breath that occurs when a person is supine. Cardiac asthma is a bronchospasm due to congestion of the bronchial mucosa that may cause wheezing and difficulty in breathing. In obstructive sleep apnea, the upper airway collapses, which leads to the complete cessation of airflow (apnea) or partial cessation of air flow (hypopnea) during sleep.