ARRHYTHMIAS
- When the frequency of the atrial and ventricular beats are different it’s call an arrhythmia
- When cardiac cells lack oxygen, they become depolarized which leads to altered impulse formation and/or altered impulse conduction.
Class Ia
procainamide, disopyramide, quinidine
Name 2 meds
Esmolol (Brevibloc)
Propranolol (Inderal)
Name 5
Amiodarone (Cordarone)
Afib: 600 to 800 mg daily in divided doses for a total load of up to 10 g, then a maintenance dose of 200 mg once daily
VT: 400 mg every 8 to 12 hours for 1 to 2 weeks, followed by 200 to 400 mg once daily
Dofetilide (Tikosyn) initiate inpatient
500mg twice daily if QTc is >500 msec reduce to 240mg twice daily
Sotalol (Betapace)
80 mg twice daily if after 3 days QTc is <500mcg increase to 160mg twice daily
Ibutilide (Covert)
<60 kg: 0.01 mg/kg over 10 minutes or ≥60 kg: 1 mg over 10 minutes
Dronaderone (Multaq)
400mg twice daily with meals
Names top 2
Diltiazem (Cardizem, Cartia, Tiazac)
Acute ventricular rate control:
IV: Bolus dose: 0.25 mg/kg (actual body weight) over 2 min; if rate control is insufficient after 15 min, a repeat bolus dose of 0.35 mg/kg over 2 minutes may be given (average dose: 25 mg). Start continuous infusion if patient responds after 1 or 2 bolus doses
Continuous infusion): Initial: 5 to 10 mg/hour; infusion rate may be increased in 5 mg/hour increments according to ventricular response, up to a maximum of 15 mg/hour.
Chronic ventricular rate control (off-label use):
Oral:
IR: 30 mg 4 times daily; ↑to achieve rate control; max: 480 mg/day
ER: 120 mg once daily or in 2 divided doses depending on formulation; max: 480mg/day
Verapamil (Veralan, Calan)
Acute ventricular rate control:
IV:
Bolus: Initial: 5 to 10 mg over ≥2 minutes; if there is inadequate response, dose may be repeated after 15 to 30 min; if there is adequate response after 1 to 2 bolus doses, then may begin a continuous infusion
Continuous infusion: Initial: 5 mg/hour; titrate to goal heart rate up to a maximum of 20 mg/hour
Chronic ventricular rate control:
Oral:
IR: 40 mg 3-4 times daily; ↑to achieve rate control; max: 480 mg/day
ER: 120 or 180 mg once daily; ↑to achieve rate control; max: 480 mg/day
Name the top 3 mentioned
Adenosin (Adenocard) slows conduction time through the AV node, interrupting the re-entry pathways through the AV node, restoring normal sinus rhythm
Digoxin (Lanoxin) When changing from oral (tablets or liquid) to IV therapy, dosage may need to be reduced by 20% to 25%
Magnesium sulfate off label IV for torsades de pointes
frequent cause of arrhythmia is
coronary artery disease
Class Ib
lidocaine, mexiletine
CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL - non-pacemaker cardiac myocytes
Summit, Plummet, Continue, Plummet
Class IC
flecainide, propafenone
Summit
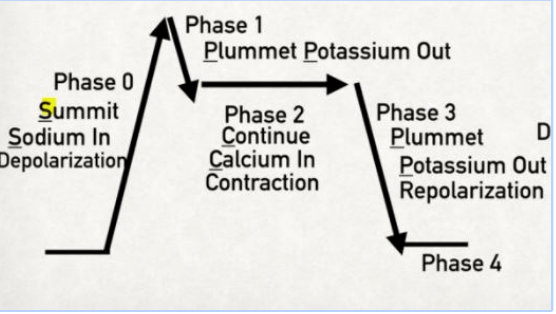 Sodium = Phase 0 (influx of sodium)
Sodium = Phase 0 (influx of sodium)
Plummet
Potassium = Phase 1 (slight potassium efflux)
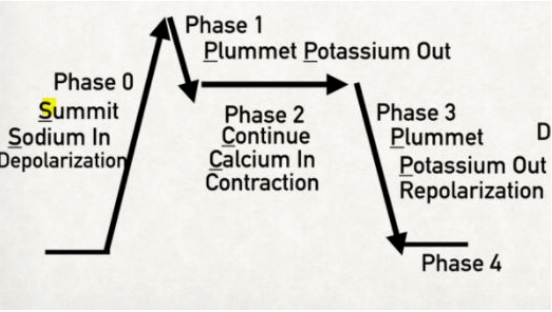
Continue
Calcium = Phase 2 (calcium influx in exchange for potassium efflux)
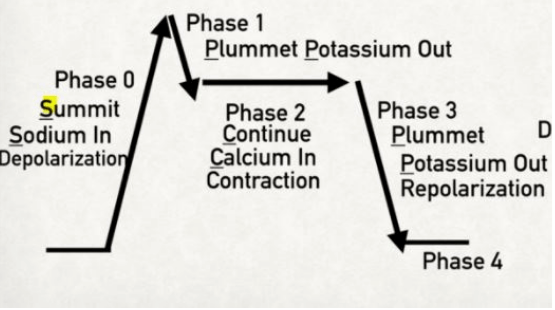
Plummet
Potassium = Phase 3 (major potassium efflux)
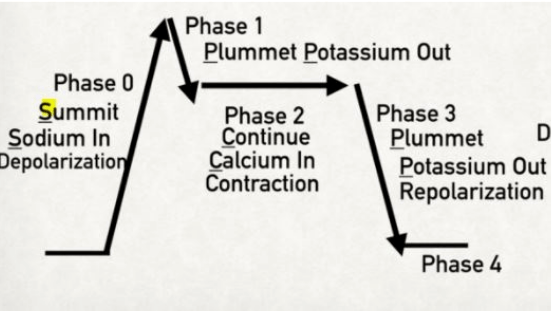
Resting Phase
Phase 4