Voluntary opening of the upper eyelid is produced by the motor innervation of what nerve?
Trochlear nerve
Oculomotor nerve
Abducens nerve
Facial nerve
Trigeminal nerve
B. Oculomotor Nerve
Motor, movement of eye
Foramen: superior orbital fissure (sphenoid bone)
Muscles:
Levator Palpebrae superioris
Superior rectus
Medial rectus
Inferior rectus
Inferior oblique
What nerve supplies sensation to the skin of the cheek, upper lip, and lower eyelid.
Infraorbital Nerve
The subclavian artery and subclavian vein are usually separated in the posterior triangle of the neck by what structure?
The first rib
One belly of the omohyoid muscle
Anterior scalene muscle
Clavicle
Vagus Nerve
C. Anterior scalene muscle
You are removing the brain from your cadaver to help prepare for neuroanatomy next block. As Dr. Solounias takes the bone saw, he asks you which layer of the scalp connects the occipitalis muscle with the frontalis muscle. You respond with…
“The skin”
“The aponeurosis”
“The pericranium”
“The occipitalis muscle”
“The loose connective tissue”
“The connective tissue”
“The frontalis muscle"
B! The aponeurosis
Recall the mnemonic: SCALP
Lists the levels of the scalp from superficial to deep:
Skin
Connective tissue (contains nerves and vessels)
Aponeurosis (connects frontalis to occipitalis)
Loose connective tissue (lets scalp move over skull)
Pericranium (periosteum of cranial bones
The subclavian artery and subclavian vein are usually separated in the posterior triangle of the neck by what structure?
The first rib
One belly of the omohyoid muscle
Anterior scalene muscle
Clavicle
Vagus Nerve
3. Anterior Scalene Muscle
A 23-year-old male is hospitalized and undergoing treatment to resolve a clot and infection in the cavernous sinus. You are evaluating the patient and discover he is unable to abduct his right eye. What structure is most likely affected?
Abducens nerve
Lateral rectus muscle
Trochlear nerve
Superior oblique muscle
Medial rectus muscle
A. Abducens Nerve
What nerve carries taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. (Hint: It is a branch of the facial nerve)
Chorda Typmani
Muscles innervated by the hypoglossal nerve receive a larger portion of their arterial blood supply from the branches of the:
Internal carotid artery
Facial artery
Maxillary Artery
Superior Thyroid Artery
Lingual Artery
E. Lingual Artery
Think about what muscles the hypoglossal nerve innervates: tongue muscles!!
Think about what is the likely artery in the mouth: Lingual! ”lingual” means tongue
The roots of the brachial plexus pass through which triangle with which part of the subclavian artery?
Carotid triangle; 1st part
Interscalene triangle; 2nd part
Posterior triangle; 2nd part
Interscalene triangle; 3rd part
Carotid triangle; 2nd part
Anterior muscular triangle; 2nd part
D! Interscalene triangle; 3rd part
This is an important clinical correlate for thoracic outlet syndrome (though not super important for you now)
All other triangles are not really associated with the subclavian artery
Which of the following can be found in the posterior triangle of the neck?
Omohyoid muscle
Posterior belly of the digastric muscle
CN XII
CN XI
Anterior jugular vein
D. CN XI
The maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2) exits the skull through this foramen.
Foramen Rotundum
Branches:
Infraorbital
zygomaticotemporal
zygomaticofacial
What nerve provides sensory innervation to the temporal region and helps carry parasympathetic fibers to the parotid gland.
Auriculotemporal Nerve
What spinal level does the common carotid artery bifurcate?
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
4. C4
Does the internal carotid artery have any extra-cranial branching?
NO!! Look at which artery has a ton of the branches coming off of it and you found the external carotid artery. The internal carotid artery doesn’t branch until its inside the cranium
What vein does the retromandibular vein receive blood from and where does it directly drain into?
Maxillary vein; internal jugular vein
Superficial temporal vein; anterior jugular vein
Superficial temporal vein; internal jugular vein
Maxillary vein; external jugular vein
Infraorbital vein, anterior jugular vein
Supraorbital vein, external jugular vein
D! Maxillary vein; External jugular vein
The maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein both drain into the maxillary vein
The maxillary vein and the posterior auricular vein then drain into the external jugular vein
The facial nerve innervates which 2 muscles? (choose 2)
Digastric (anterior belly)
Stylopharyngeus
Stapedius
Digastric (posterior belly)
Stylohyoid
D. Digastric (posterior belly)
E. Stylohyoid
Facial Nerve (CNVII) exits the stylomastoid foramen. It makes sense that the stylohyoid and posterior belly of digastric are innervated by it.
A small growth or tumor in the jugular foramen may affect which nerves?
Hypoglossal and vagus
Vagus, glossopharyngeal, hypoglossal
Facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
Vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus
Glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory
5. Glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory
You have stumbled into a dental rotation and are required to place a nerve block to operate on a patient’s lower teeth. The nerve enters the mandible at which point?
Mental foramen
Mandibular foramen
Temporal fossa
Infraorbital foramen
Stylomastoid foramen
Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum
B! Mandibular foramen
The nerve in question is the inferior alveolar nerve, which innervates the lower teeth
Any manipulation of the superior thyroid artery must be undertaken with care to not damage what small companion nerve?
Cervical sympathetic trunk
External branch of superior laryngeal nerve
Inferior root of ansa cervicalis
Internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
2. External branch of superior laryngeal nerve
Question 6: You have stumbled into a dental rotation and are required to place a nerve block to operate on a patient’s lower teeth. The nerve enters the mandible at which point?
Mental foramen
Mandibular foramen
Temporal fossa
Infraorbital foramen
Stylomastoid foramen
Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum
B! Mandibular foramen
- The nerve in question is the inferior alveolar nerve, which innervates the lower teeth
The mental foramen is where the mental nerve exits the mandible
The temporal fossa is a groove where the temporalis muscle resides
The infraorbital foramen is where the infraorbital nerve exits
The stylomastoid foramen is where CN VII exits the skull
Foramen ovale is where CN V3 exits the skull
Foramen spinosum is where the middle meningeal artery enters the skull
During a carotid endarterectomy, a mistake occurs which causes a blockage in the external carotid artery. However, the thyroid can still receive blood from which artery?
Superior thyroid artery via thyrocervical trunk
Inferior thyroid artery via thyrocervical trunk
Inferior thyroid artery via costocervical trunk
Superior thyroid artery via costocervical trunk
Middle thyroid artery via costocervical trunk
Middle thyroid artery via thyrocervical trunk
B! Inferior thyroid artery via thyrocervical trunk
- The thyrocervial trunk branches off of the subclavian artery, and one of the branches, the inferior thyroid artery, will supply the thyroid
Other branches of the thyrocervical include the transverse cervical artery and the suprascapular artery
The superior thyroid artery branches off of the external carotid artery
The costocervical trunk branches off of the 2nd part of the subclavian
- There is no middle thyroid artery, only a middle thyroid vein
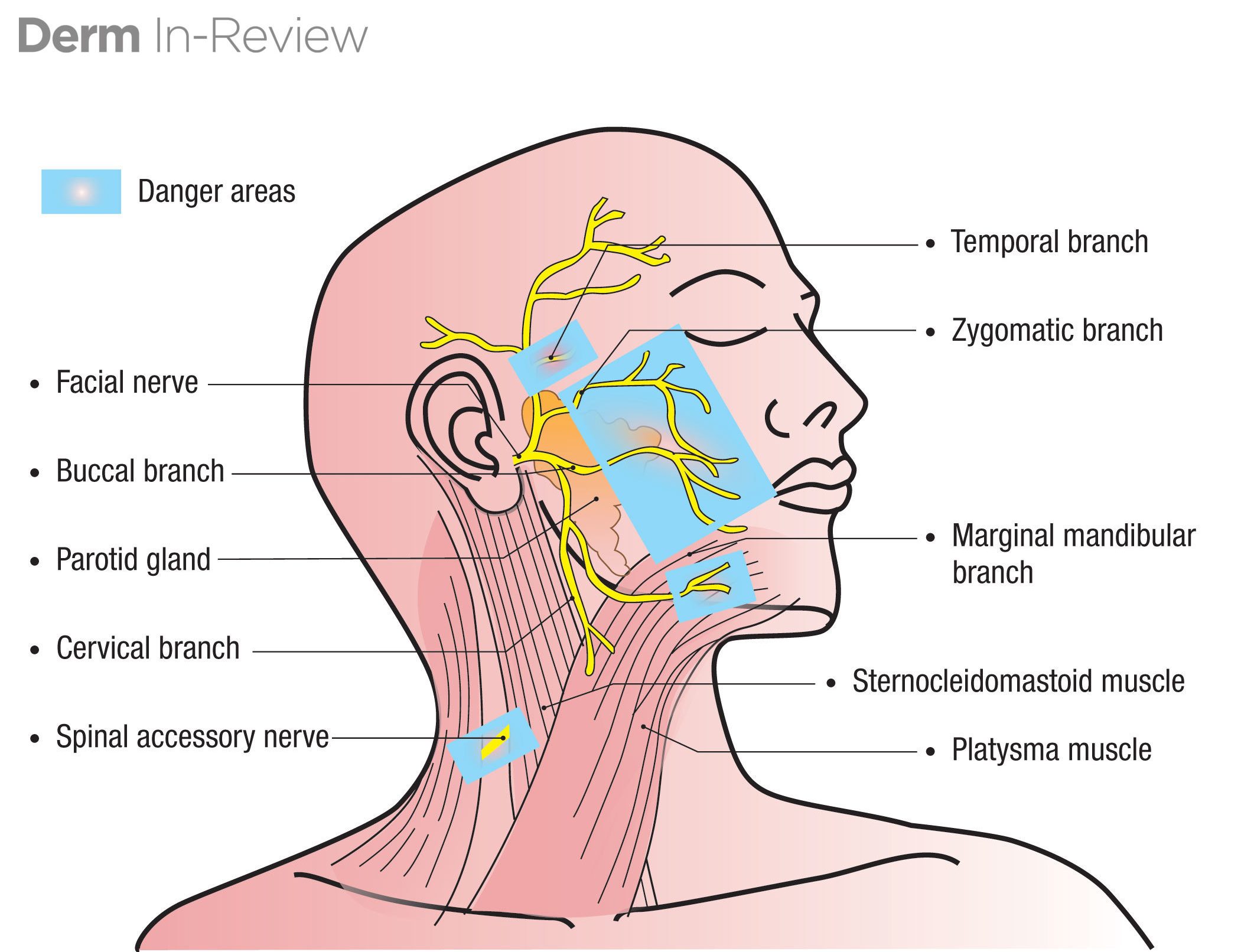
Name the terminal branches of the facial nerve (CN VII)
Temporal/Zygomatic/Buccal/Marginal Mandibular/Cervical
mnemonic: To Zanzibar By Motor Car
Which of these structures are part of the sphenoid bone? Select all that apply:
Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum
Supraorbital notch
Lateral pterygoid plate
Infraorbital foramen
Mental foramen
Foramen ovale, foramen spinosum, and the lateral pterygoid plate
Foramen ovale: where CN V3 exits
Foramen spinosum: where the middle meningeal artery enters the skull
Lateral pterygoid plate: where the lateral pterygoid attaches
A 16-year-old male is brought in by emergency medical services to the emergency department after being involved in a head-on collision. He is currently awake and alert, and responds to questions and commands. However, a CT scan of the head shows a collection of blood in the epidural space. The most likely source of this blood is a(n):
Rupture of the bridging veins
Tear of the middle meningeal artery
Rupture of a berry aneurysm
Embolus to the left posterior cerebral artery
Rupture of a Charcot-Bouchard microaneurysm
B. Tear of the middle meningeal artery
You are having a bad day and hear a friend say “It takes more muscles to frown than to smile.” Rightfully irritated by this cliché, you challenge them to name the muscles for frowning and smiling. Which muscles are not involved with smiling or frowning?
Orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oris
Levator labii superioris
Depressor anguli oris
Buccinator
Zygomaticus major
Depressor labii inferioris
Levator anguli oris
A, B, and E! Orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris, and buccinator
Orbicularis oculis is the sphincter of the eye
Orbicularis oris is the sphincter of the mouth
Buccinator assists in eating
Levator labii superioris, levator anguli oris, and zygomaticus major all assist in lifting the lips superiorly
Depressor labii inferioris and depressor anguli oris pull the lips down
All listed muscles are innervated by CN VII
What are the muscles of the anterior triangle?
Thyrohyoid, Omohyoid, Sternohyoid, and Sternothyroid
mnemonic: TOSS