These control breath, the fundamental element of most speech sounds.
What are the lungs?
The ligaments on either end of the glottis.
What are the vocal folds?
Parts of the anatomy that are employed to produce (articulate) speech sounds.
What are articulators?
In the source-filter model, how the sound source is powered.
What is the power? - In speech, usually the lungs.
Airflow is completely blocked in the vocal tract for a moment, and then completely released
What is a stop or plosive?
a phonological process whereby a sound or sequence of sounds changes in order to make neighboring sounds more alike.
What is assimilation?
This type of speech sound is produced using air controlled by the lungs.
What are pulmonic sounds?
The vocal folds and all the space between them.
What is the glottis?

The articulator labeled as (d) on the diagram.
What are the lips?
In the source-filter model, where the sound is produced.
What is the source? - In speech, usually the vocal folds.
Articulators come near each other, but not enough to cause turbulence in airflow
What is an approximant?
a phonological process whereby a sound or sequence of sounds changes in order to make neighboring sounds less alike.
What is dissimilation?
This organ contains the vocal folds.
What is the larynx?
The term referring to the opening of the vocal folds.
What is abduction?

The articulator labeled as (c) on the diagram.
What are the teeth?
In the source-filter model, what changes the properties of the sound from the source.
What is the filter? - In speech, the pharynx along with the oral and sometimes the nasal cavity.
Airstream is stopped from exiting the oral cavity and instead redirected through the nasal cavity
What is a nasal?
a phonological process in which a sound is inserted into a word.
What is epenthesis?
These vibrate to give voice to the air from the lungs, and control pitch.
What are the vocal folds?
The term referring to the closing of the vocal folds.
What is adduction?
 The articulator labeled as (i) on the diagram.
The articulator labeled as (i) on the diagram.
What is the velum?
A very brief contact of one articulator against another
What is a tap or flap?
a sound change that occurs because of neighboring words or morphemes.
This term refers to the space of the throat above the larynx, behind the tongue.
What is the pharynx?
The flag of cartilage that opens and closes the opening to the glottis, allowing airflow or blocking passage by food or drink.
What is the epiglottis?
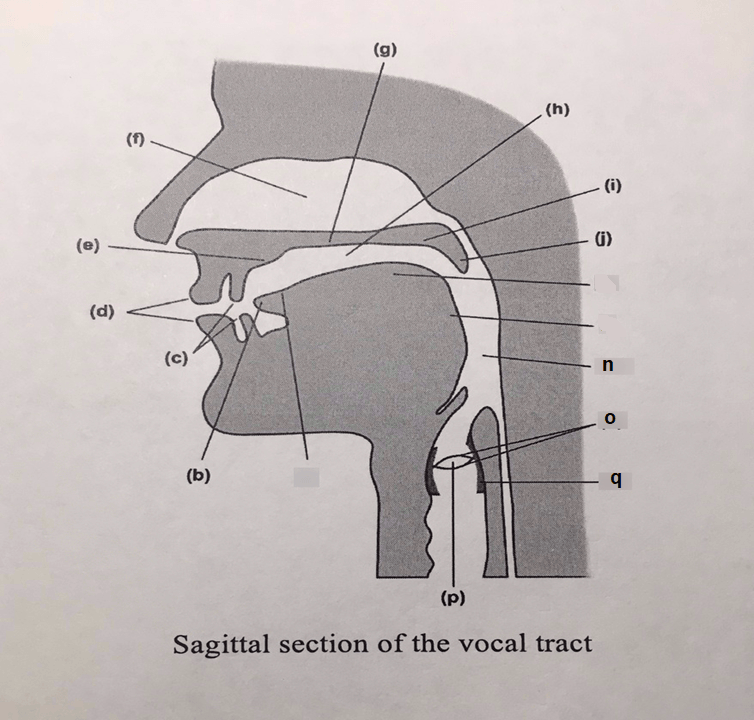 The articulator whose tip is labeled (b) on the diagram.
The articulator whose tip is labeled (b) on the diagram.
What is the tongue?
A consonant produced by rapidly vibrating one articulator against another.
What is a trill?
the phonological phenomenon in French in which word-final consonant sounds which would otherwise be silent are pronounced due to the next word beginning with a vowel.
What is liaison?
This term refers to the space inside of the mouth.
What is the oral cavity?
The vocal folds are in this state when they are loose (relatively drawn apart), vibrating at lower pitches during phonation.
What is abducted? (opened)
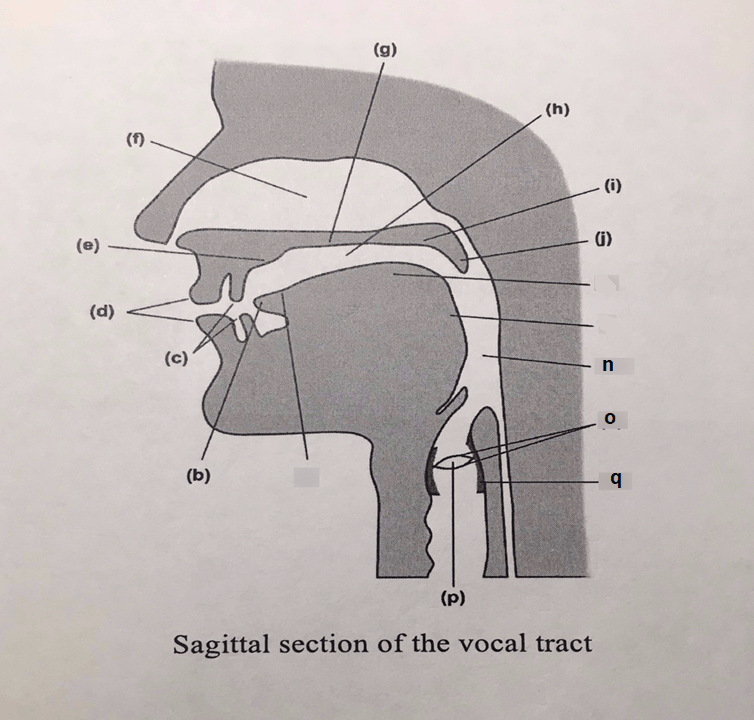 The articulator labeled (e) on the diagram.
The articulator labeled (e) on the diagram.
What is the alveolar ridge?
An approximant or fricative in which airflow is directed around the sides of the tongue rather than over the top.
What is a lateral?
the phonological phenomenon in Mandarin in which when several words with the same tone occur in sequence, some of the tones change so as to avoid a sequence of several of the same tone in a row.
What is tone sandhi?
This term refers to the large cavity of the sinuses that air passes through on its way into and out of the nose.
What is the nasal cavity?
The vocal folds are in this state when they are stretched tight, resulting in higher pitches of phonation when they are vibrated.
What is adducted? (closed)
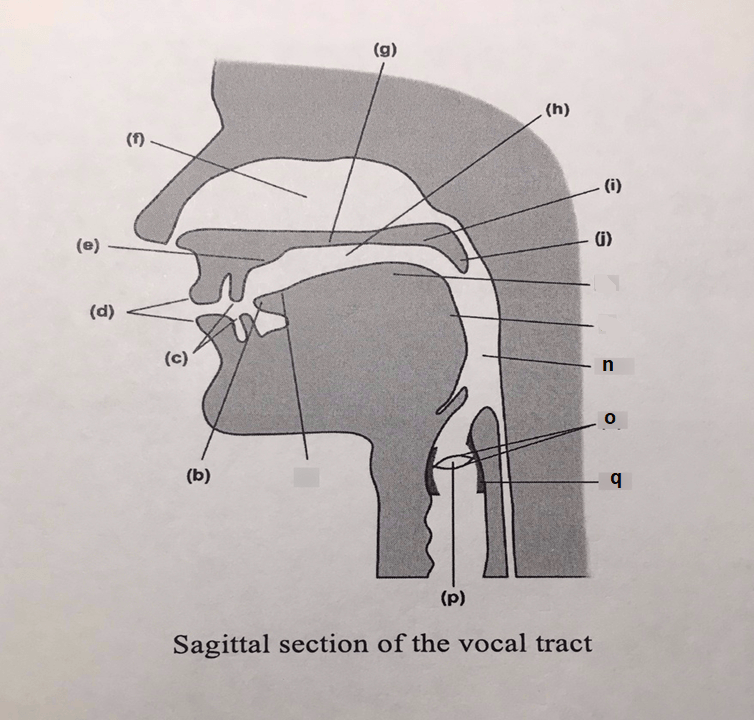 The articulator labeled (p) on the diagram.
The articulator labeled (p) on the diagram.
What is the glottis?
A complex consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative.
What is an affricate?
Articulators come close enough to nearly touch; airflow is limited to a thin, hiss-like, turbulent stream.
What is a fricative?