This is a requirement for quality monitoring to maintain CLIA certificate compliance that involves blind sample testing evaluated against results from peer laboratories.
What is Proficiency Testing?
Packed Red Cell Volume
What is the Hematocrit?
This structure is the only part of the nephron which is located in the renal cortex
What is the Loop of Henle?
Name 2 widely abused drugs in the USA
What is alcohol, marijuana?
This parasite was found in the blood smear of a patient who had a recent summer vacation in New England and reported many insect and tick bites
What is Babesia spp.?
These are the two components of the major crossmatch
What are donor red cells and recipient plasma (or serum)?
These cells are the major component in Natural Non-Specific Immunity
What are neutrophils?
This anticoagulant is used for most routine coagulation studies
What is sodium citrate
These are errors caused by uncontrollable factors that occur in an unpredictable manner during analytical laboratory testing.
What is random error?
This is the layer between the Red Blood Cells and Plasma after centrifugation of a blood sample
What is the buffy coat?
This chemical urinalysis test shows abnormal levels when there is an increase of fatty acid metabolism
What is/are ketones?
Name an analytical method to screen for substances of abuse
What is immunoassay?
This organism can be found in the feces of a patient complaining of abdominal distress and diarrhea
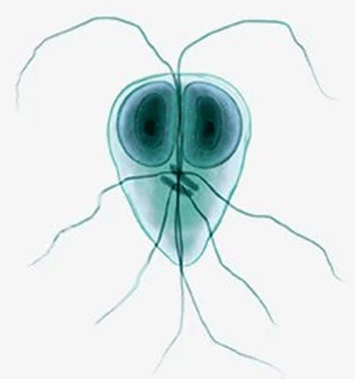
What is Giardia lamblia?
This gene codes for production of the same basic antigen as the gene known as H
What is the Se gene?
This immunoglobulin has five individual heavy chains making its structure a pentamer
What is IgM?
This test is used to monitor patients on unfractionated heparin therapy
What is the Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)?
This statistical measure is used to compare the variability of different measurements.
What is the coefficient of variation?
This hemoglobin is the major hemoglobin during fetal life and has a higher oxygen affinity than adult hemoglobin
What is Hb F?
This chemical urinalysis test is increased when there is damage to the glomerular filtration barrier and substances with higher molecular weight are passing into the urine
What is protein?
Name the next test performed when a pediatric patient’s PB smear shows microcytic RBCs and marked basophilic stippling
What is lead level?
This gram-positive, catalase-negative coccus formed alpha-hemolytic colonies on blood agar. Follow-up testing revealed gas production from glucose, acid production from mannose, sucrose and sorbitol, PYR positive, motility and growth in the presence of 6·5% NaCl
What is Enterococcus faecalis?
The agglutination reaction of red cells from a Bombay phenotype with anti-H lectin
What is a negative reaction?
This titer indicates immunity in a pregnant woman exposed to Rubella
What is a titer greater than 1:8?
This abnormality should be suspected when a 1:1 mixing of patient plasma with normal plasma is not corrected
What is an immediate acting inhibitor
These are regulations that include federal standards applicable to all U.S. facilities or sites that test human specimens for health assessment or to diagnose, prevent, or treat disease.
What is CLIA'88?
RBC= 2.0 x 1012/L
Hb= 7.6 g/dL
HCT= 22%
RDW= 19.0
This is the morphologic appearance of the red cells given the results above
What is macrocytic with anisocytosis?
The significance of an ascitic fluid exudate with a positive CA 125 and a negative CEA.
What is ovarian malignancy?
Name an antibiotic monitored by therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)
What is Aminoglycosides?
A sputum culture from an alcoholic seen in the ER grows gray, mucoid, stringy colonies on sheep blood agar. The isolate grows readily on MacConkey agar and forms mucoid, dark pink colonies. This organism had the following biochemical reactions: negative for both indole and oxidase, and positive for ONPG, glucose, citrate and Voges-Proskauer.
What is Klebsiella pneumoniae?
At the blood donor laboratory, this forward typing reagent is used to confirm group O units before placing them into inventory
What is Anti-A,B reagent?
A pregnant woman positive with this DNA virus requires that a baby be born via C-section to prevent dissemination to the skin, conjunctiva, and visceral organs
What is Herpes Simplex Virus Type II?
This coagulopathy develops after a patient has received unfractionated heparin for more than 5 days resulting in a moderate thrombocytopenia
What is Heparin Induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
These documents address physical characteristics, safe handling and storage, and specific health hazards of hazardous chemicals.
What are SDS's?
During this process, RBC production is defective and many are destroyed before leaving the bone marrow.
What is ineffective erythropoiesis?
This would diagnosed based on the below CSF results:
WBC count: 1,000/µL Glucose: 15 mg/dL
Lymphocytes: 10% Blood glucose: 90 mg/dL
Neutrophils: 90% Lactate: 40 mg/dL
Protein: 150 mg/dL
What is bacterial meningitis?
State the purpose of measuring serum pseudocholinesterase (SChE) activity
What is screening for organophosphate poisoning?
A 29-year-old man is seen for recurrence of a purulent urethral discharge 10 days after the successful treatment of culture proven gonorrhea. The most likely cause of urethritis
What is Chlamydia trachomatis?
Anti-M reacted with red cells that are M+N+, how would this compare when tested with red cells that are M+N–?
What is the reaction will be weaker?
The blood has a high level of this antigen/protein after becoming infected with HIV
What is p24?
This coagulopathy is associated with E.coli O157:H7 and presents with thrombocytopenia, anemia, and renal failure
What is Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)?