These subatomic particles change to form a positively-charged cation.
What are electrons? (Protons do not change during normal chemical reactions. Only the outer electrons move).
What is hydrogen bromide?
This is the number of electrons in the compound shown below.

What is 8?
This is the formal charge of the atom ICl4-.
What is -1?
I: 7-8 = -1
Cl: 7-7 = 0
-1 + 0 = -1
This theory enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure.
This type of bond results from the mutual attraction of atoms for a shared pair of electrons.
What is a covalent bond?
This is the chemical formula for sodium oxide.
What is Na2O?
The element Li+ has this many electorns.
What is zero?
This is the most likely molecular structure for the (NO2-) ion.
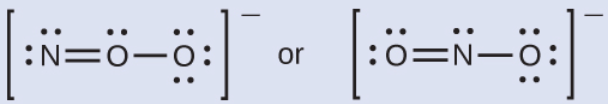
What is ONO-?
Two regions of electron density around a central atom in a molecule form this type of geometry.
What is linear?
This is the chemical formula for titanium(IV) oxide.
What is TiO2?
The Lewis symbol for this ionic compound is shown here.

What is K2O?
What is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms? (AKA the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure)?
This is the electron-pair geometry of BCl3.
What is trigonal planar?
This factor causes increasing polarity in covalent bonds.
The absolute value of the difference in electronegativity increases.
This is the name for the compound (NH4)2SO4
A triple bond shares this many electrons.
What is six?
If two or more Lewis structures with the same arrangement of atoms can be written for a molecule or ion, this is the actual distribution.
What is the average of that shown by the Lewis structures? (a resonance hybrid)
This is the electron-pair geometry of PF5.
What is trigonal bipyrimidal?
This element in the periodic table is the most electronegative.
What is F (flourine)? (electronegativity increases as you go to the right and up in the periodic table, but noble gases are excluded).
This is the name of the compound MoS2.
What is molybdenum(IV) sulfide?
This electron configuration corresponds with this atom.
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4
What is selenium?
This is the formal charge of Cl in the molecule ClF5.
What is 0?
This is the bond angle in a linear molecular structure.
What is 180 degrees?