A high pitched inspiratory noise.
What is stridor?
Structure within the respiratory system responsible for gas exchage
What is alveoli
Systolic BP of < 90 or MAP <65
What is hypotension
Prior to administration of Warfarin, this laboratory value must be reviewed.
What is INR
A nebulized medication used commonly to treat stridor.
What is racemic epinephrine
On assessment, your patient has a “gurgling or rattling” noise with each breath, what is your priority intervention?
What is encourage the patient to cough if able and suction the airway
Normal adult respiratory rate
What is 12-20 breaths/minute
A _______ mls/hr indicates adequate renal perfusion
What is UOP of 30?
What laboratory value must be reviewed prior to Enoxaparin or Heparin administration
What is platelet count
First line medication used to treat fluid overload in patients with normal renal function
What is Furosemide
Sound heard on assessment with the presence of bronchoconstriction
What is wheezing
A non invasive high flow oxygen delivery device that can deliver 100 FiO2
What is a non-rebreather
On assessment, your patient is diaphoretic, cool, clammy and is not as responsive as they have been. What are some immediate interventions that should be done.
Finger stick, vital signs, assess capillary refill.
What laboratory abnormalities could you see in a patient with septic shock
What are
Platelet < 100
INR> 1.5 not on therapy
APTT> 60 sec not on therapyCreatinine > 2
Bilirubin > 2
Lactic > 2
What is Albuterol or bronchodilator
A tube that is inserted into the trachea that is connected to a ventilator
What is an endotracheal tube
Absent breath sounds on affected side, tracheal deviation to unaffected side, JVD, tachycardia, hypotension
What is a tension pneumothorax
The bodies initial compensatory mechanism to maintain cardiac output when in a state of shock
What is tachycardia
In a patient with known renal failure, this electrolyte abnormality is most concerning.
What is hyperkalemia?
What is 30ml/kg
You patient does not have a gag reflex and does not cough when deep suctioned-what could these findings mean
What is does not have the ability to protect their airway
Tachypnea, accessory muscle use, retractions, decreased oxygen saturation
What are signs of respiratory distress
A patterned discoloration typically seen first in the extremities of patients that have diminished cardiac output and decreased peripheral perfusion
What is mottling
A patient who has received numerous albuterol treatments in the past 24 hours is at risk for what electrolyte abnormality?
What is hypokalemia
2 medications that are ordered on almost every patient in the hospital to prevent development of DVT
What are heparin and Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Your post op patient’s monitor alarms for low oxygen saturation, when you enter the room you hear a “snoring” noise with each breath. What is your first intervention.
After performing bed bath, your patient with a chest tube now has new a finding of bubbling in water seal chamber. What could this mean?
What is dislodgement of chest tube
You see this on your patient’s monitor, what is the first thing you do
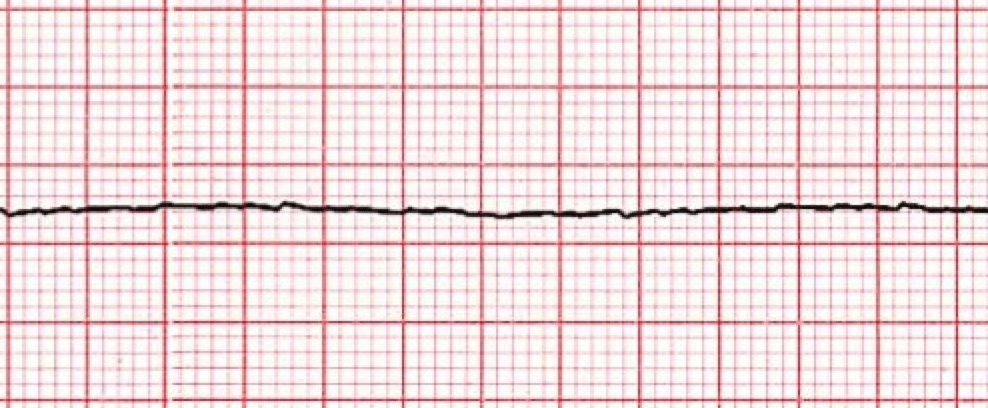
Check for a pulse-start CPR
You notice on your patient’s AM labs that the BUN is 98 and Creatinine is 3.7, what assessment value will you closely monitor throughout your shift
What is urine output
Class of medication ordered for almost every hospitalized patient to prevent development of stress ulcers
What are PPI or proton pump inhibitors