The moon blocks light to the Earth during the day during this type of eclipse.
Solar
What letter represents our sun?
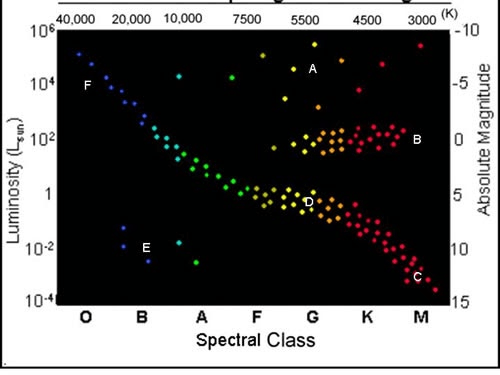
D
The moon has no ________ so erosion cannot occur on its surface.
Atmosphere
What causes seasons on Earth?
The tilt of the Earth
The ______________ theory models the formation of the universe.
Big Bang Theory
The Earth cast its shadow on the moon during the night during this type of eclipse.
Lunar
What letter(s) represents the white dwarfs?
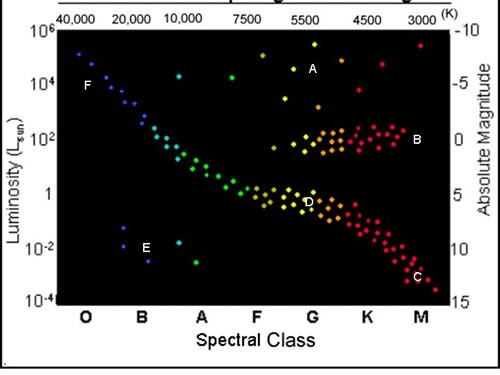
E
The sun gives off light because of its constant _______ type nuclear explosions.
Fusion
The longest and shortest days of the year are called ____________.
Solstices
Most asteroids are located between what two planets?
Mars & Jupiter
The alignment during a lunar eclipse.
Sun, Earth, moon
What does this graph compare? (2 variables)
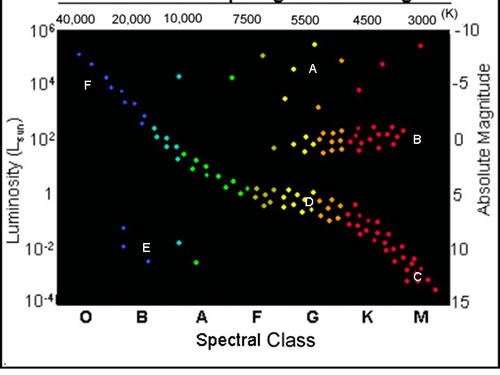
Brightness & Temperature
The Earth’s ______ gives us day and night.
Rotation
When day length equals night length it is called a(n) _______ .
Equinox
The Earth’s ________ is equal to one year on Earth.
Revolution
The alignment during a solar eclipse.
Sun, moon, Earth
What letter(s) represent a giant type star?
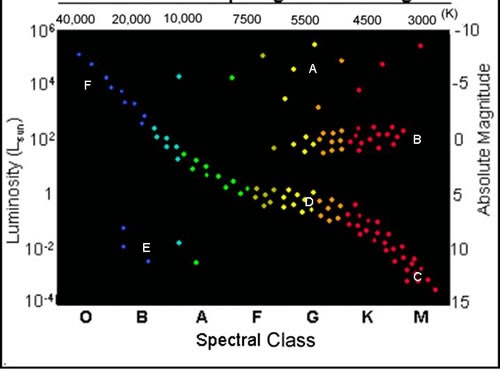
A or B
A neap tide occurs during the ____ moon phase(s).
First & Last (half) quarters
Every ______ months there is a change in the season.
3
The Milky Way is a ________ type of galaxy.
Spiral
Explain what happens during tides
Oceans bulge on Earth on the farthest and closest sides to the moon
What type of star will our sun become next?
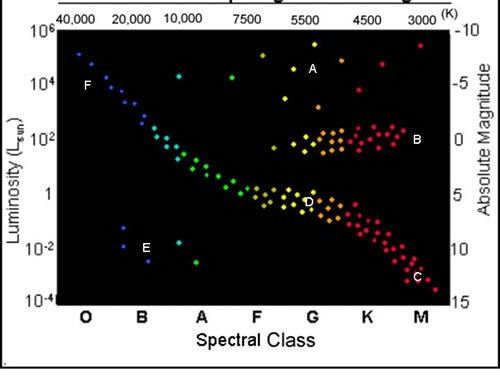
Giant
List the planets in order beginning with the planet closest to the sun.
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto (dwarf)
How many solstices are there per year?
How many equinoxes are there per year?
2 and 2
A light year measures ________ .
Distance