What is the formula for the doppler effect?
v = c(∆lambda)/lambda_0
What happens to the energy of light as it changes from radio wave to gamma rays?
The energy increases
Your eye has a diameter of 0.8 cm. Your telescope has a diameter of 20 cm. How much more light does your telescope collect than your eye?
625 times more light
How do stars generate light and energy?
Nuclear fusion in their core
What type of galaxy is this?
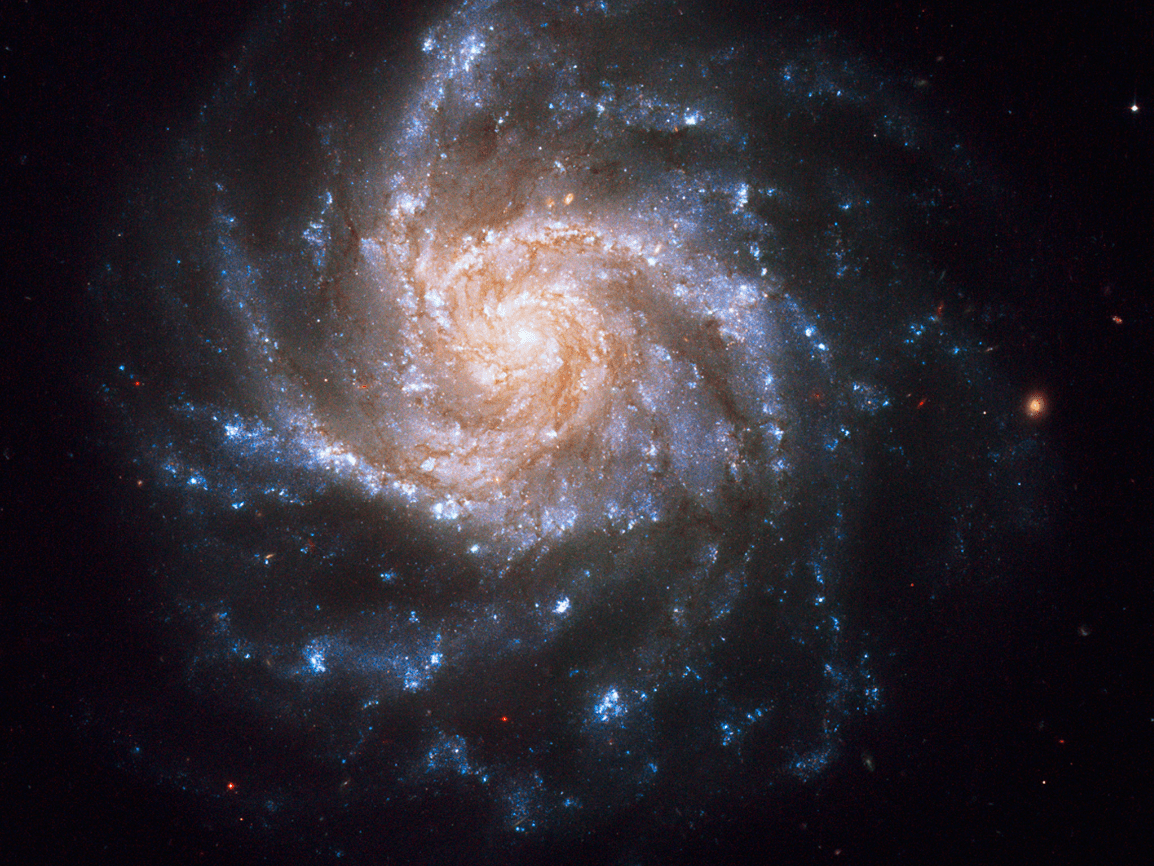

Spiral
What is the formula for light gathering power and what does it tell us?
((D_1)/(D_2))^2
It tells us how many times more light one telescope can collect compared to another telescope.
What happens to the wavelength of visible light as it changes from violet to red?
The wavelength increases (gets longer).
You want to build a refracting telescope and not a reflecting telescope. This means you'll have to buy a __________.
Lens
What happens to the lifespan of a star as the mass of the star decreases?
The lifespan increases
What type of galaxy is this?
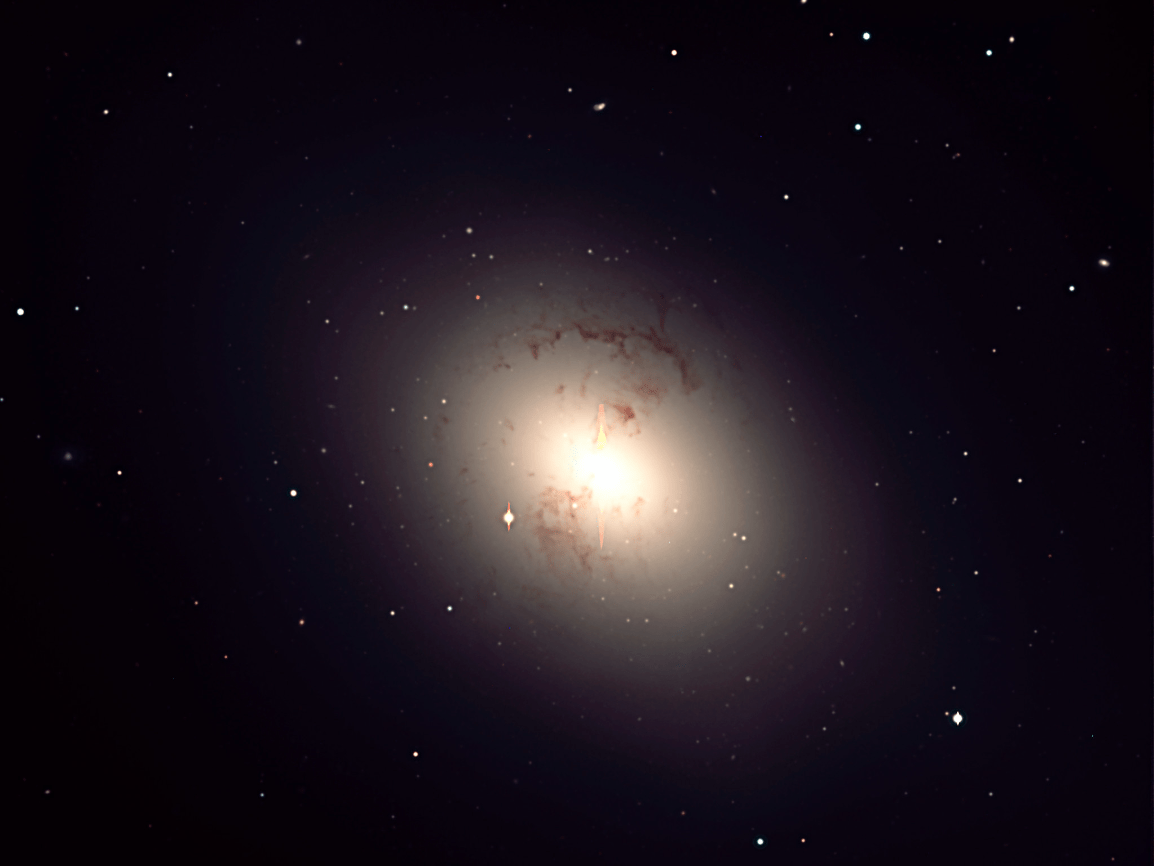
Elliptical
What is the speed of light in m/s?
c = 3 x 10^8
What color of visible light has a wavelength of 600 nm?
Orange
What is an atmospheric window?
The range of light wavelengths that can pass through the atmosphere and reach the ground.
How do we use an H-R diagram to tell whether a star cluster is young or old?
Younger star clusters have more spectral classes present and older star clusters have fewer spectral classes present.
In which kind(s) of galaxy would we expect to see a supernova?
Spirals and Irregular galaxies since they have high-mass stars.
What is the formula for resolution?
R = (252,000* lambda)/D
Which spectrum is continuous?

Spectrum C
If we want to build a telescope that detects infrared light, where should this telescope be placed?
In space
Is the Sun going to explode at the end of its life?
No, the Sun is a lower-mass star and will end its life as a planetary nebula and white dwarf.
What does it mean that the light from galaxies is redshifted?
They are moving away from us and the universe is expanding.
What is the formula for telescope magnification?
M = (F_O)/(F_e)
Which star is the dimmest?
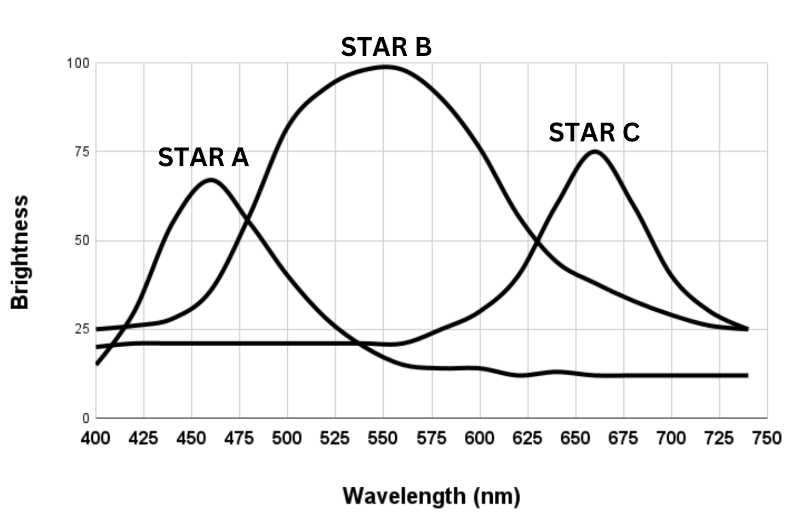
Star A
Which telescope can see smaller details:
Telescope 1 with a resolving power of 0.70"
Telescope 2 with a resolving power of 1.80"
Telescope 1
When a star goes supernova, why do its outer layers explode outward if the core collapses inward?
The outer layers of the star rebound (bounce) off the core when the core suddenly stops collapsing. This causes the outward explosion.
How would the age of the universe be impacted if the Hubble Constant was larger than 70 km/s/Mpc?
It would mean that the universe is expanding faster than we thought and that the universe is younger than we thought.
What is the formula for the Schwarzschild Radius of a black hole?
R = (2GM)/(c^2)
A star's light is shifted from 656 nm to 657.1 nm. Is this a redshift or blueshift, and how fast is this star moving?
This is a redshift and the star is moving at a velocity of 503,048.78 m/s away from us.
Calculate the magnification achieved by this combination of lenses:
Objective Lens focal length = 30 cm
Eyepiece Lens focal length = 5 cm
This combination of lenses will make the image appear 6 times bigger.
Calculate the Schwarzschild Radius of a black hole for an object with the same mass as Earth.
M_(Earth) = 5.97*10^24kg
R = 0.0088 m
Are we at the center of the universe?
Yes and No! We are at the center of our observable universe, but there is no center to the actual whole universe.