
What is cord compression
What is a Variable
A nurse is caring for a client who is pregnant and states that her last menstrual period was July 4th. Which of the following is the client's estimated date of delivery?
A. April 18
B. April 11
C. March 18
D. March 11
What is April 11th?
A nurse is caring for a client who is in active labor and becomes nauseous and vomits. The client is very irritable and feels the urge to have a bowel movement. She states "I've had enough. I can't do this anymore. I want to go home!" Which of the following stages of labor is the client experiencing?
What is C.
The transition phase of labor occurs when the client becomes irritable, feels rectal pressure similar to a bowel movement, and can experience N/V.
A nurse is caring for a client who is 1 hour postpartum following a vaginal birth and experiencing uncontrollable shaking. The nurse should understand that the shaking is due to which of the following factors? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY)
A. Change in body fluids
B. Metabolic effort of labor
C. Diaphoresis
D. Decrease in body temperature
E. Decrease in prolactin levels
What are A and B.
A shift in body fluids the first 2 hours of puerperium can cause a pp chill.
The work of labor can cause a PP chill with in the first 2 hours puerperium.
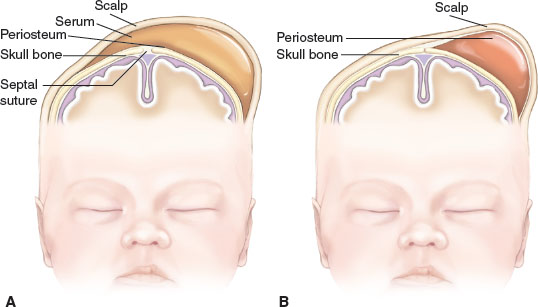
A--What is Caput succedaneum (localized swelling of the soft tissues caused by pressure on the head during labor) it is an expected finding that can be palpated as a soft edematous mass and can cross of the suture line. Using resolves within 3-4 days without treatment.
B- Cephalohematoma is a collection of blood between the periosteum and the skull bone that it covers. It does not cross the suture line. It results from trauma during birth such as pressure of the fetal head against the maternal pelvis in a prolonged difficult labor or forceps delivery. It appears in the first 1-2 hours after birth and usually resolves in 2-3 weeks.
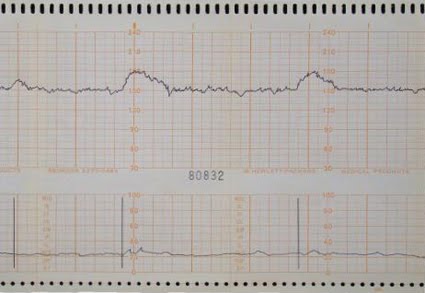
What is an acceleration/everything is OKAY
32+ weeks 15x15
<32 weeks 10 x 10
A nurse is providing care for a client who is 28 weeks gestation who has a placenta previa. The nurse notes that the client is actively bleeding. Which one of the medications should the nurse anticipate the provider will prescribe?
A. Nifedipine
B. Betamethasone
C. Indomethacin
D. Methergine
What is B. Betamethasone is given to promote lung maturity of delivery is anticipated.
A nurse is caring for a client who is at 40 weeks gestation and experiencing contractions every 3-5 minutes and becoming stronger. A vaginal exam reveals 3cm dilated, 80% effaced, -1 station. The client asks for pain medication. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
A. Encourage the use of patterned breathing
B. Insert an indwelling urinary catheter.
C. Administer opioid analgesic medication.
D. Suggest application of cold
E. Provide ice ships
What are A, C, D
B-there is no indication for an indwelling catheter at this time
E-This action does not address the client's request for assistance with pain management
A client is in the early postpartum period is very excited and talkative. She repeatedly telling the nurse every detail of her labor and birth. Because the client will not stop talking, the nurse is having difficulty completing the pp assessments. Which of the following action should the nurse take?
A. Come back later when the client is more cooperative.
B. Give the client time to express her feelings.
C. Tell the client she needs to be quiet so the assessment can be completed.
D. Redirect the client's focus so that she will become quiet.
What is B.
The nurse should recognize that the client is in the "taking in" phase, which begins immediately following birth and lasts a few hours to a couple of days.
A nurse completing a newborn assessment and observes small white nodules on the roof of the newborns mouth. This finding is a characteristic of which of the following conditions?
A. Mongolian spots
B. Milia Spots
C. Erythema Toxicum
D. Epstein's pearls
What is D (Epstein's Pearls)
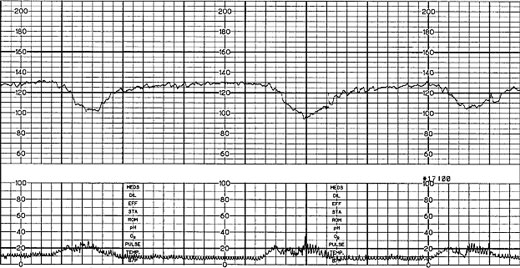
What is placental insufficiency
What is a late deceleration
A nurse is reviewing ways to prevent TORCH infection during pregnancy with a group of newly licensed nurses. Which of the following statements by a nurse indicates understanding of the teaching?
A "Obtain an immunization against rubella early in pregnancy."
B. Seek prophylactic treatment if cytomegalovirus is detected during pregnancy."
C. " A woman should avoid crowded places during pregnancy."
D. "A woman should avoid consuming undercooked meat while pregnant."
What is D- Toxoplasmosis, a TORCH infection, is contracted by consuming undercooked meat.
(p. 54-55)
A nurse reviewing EFM tracing of a client who is in active labor. The nurse should know that a fetus receives more O2 when which of the following appears on the tracing?
A. Peak of uterine contraction
B. Moderate variability
C. FHR accelerations
D. Relaxation between uterine contractions
What is D
A fetus is most oxygenated during the relaxation period between contractions. During contractions , the arteries to the uteroplacental intervillous spaces are compressed resulting in a decrease in fetal circulation and oxygenation.
A nurse is caring for a client who has disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Which of the following antepartum complications should the nurse understand is a risk factor for this condition?
A. Preeclampsia
B. Thrombophlebitis
C. Placenta Previa
D. Hyperemesis gravidarum
What is A
Preeclampsia is a risk factor for DIC.
A nurse is caring for a newborn immediately following birth. Which of the following nursing interventions is the highest priority?
A. Initiating breastfeeding
B. Performing initial bath
C. Giving Vitamin K injection
D. Covering the newborn's head with a cap
What is D
the greatest risk to the newborn is cold stress. Therefore the highest priority intervention is to prevent heat loss. Covering the newborn's head with a cap prevents cold stress due to excessive evaporative heat loss.

What is an Early deceleration?
What is head compression?
A nurse is caring for a woman in labor. The nurse should identify that which of the following infections can be treated during labor or immediately following birth? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
A. Gonorrhea
B. Chlamydia
C. HIV
D. Group B Strep
E. TORCH infection
What is ....ALL EXCEPT E.
A&B Erythromycin is administered immediately after birth to prevent Gonorrhea and Chlamydia.
C. Retrovir is prescribed to a client in labor who is HIV positive
D. Penicillin G or Ampicillin is administered during labor to treat clients who are GBS+
E. TORCH infection can be treated during pregnancy depending upon infection.
A nurse is caring for a client who has had no prenatal care, is RH-, and will undergo an external version at 37 weeks gestation. Which of the following medication should the nurse plan to administer prior to the version?
A. Prostaglandin gel
B. Magnesium Sulfate
C. Rho(D) immune globulin
D. Oxytocin
What is C
Rho(D) immune globulin is administered to an RH- client at 28 weeks gestation. Because this client had no prenatal care, it should be given prior to the version to prevent isoimmunization.
A nurse is caring for a client with mastitis. Which of the following is the typical causative agent of mastitis?
A. Staphylococcus aureus
B. Chlamydia trachomatis
C. Klebsiella pneumonia
D. Clostridium perfringens
What is A Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and streptococcus are usually the infecting agents that enter the breast due to sore or cracked nipples, which results in mastitis.
A nurse is reviewing contraindications for circumcision with a newly hired nurse. Which of the following conditions are contraindications? (Select all that apply)
A. Hypospadias
B. Hydrocele
C. Family history of hemophilia
D. Hyperbilirubinemia
E. Epispadias
What are C, D, and E
Hypospadias and Epispadias are defects in the location of the meatus and are contraindicated in circumcisions.
Family history of hemophilia is also contraindicated
Interventions for variable, late, and prolonged decelerations
Position change
Oxygen
IVF Bolus
Sterile vaginal exam
Oxytocin OFF
Notify Provider
A nurse is administering magnesium sulfate IV to a client who has pre-eclampsia with severe features for seizure prophylaxis. Which of the following indicates magnesium sulfate toxicity? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
A. Respirations <12/min
B. Urinary output <30 ml/hr
C. Hyperreflexic deep tendon reflexes
D. Decreased level of consciousness
E. Flushing and sweating
What are A, B, D
C-ABSENCE of DTR's is a sign of magnesium toxicity not hyperreflexia
D. Flushing and sweating are adverse effects of magnesium but not a sign of toxicity
A nurse is caring for a client who is at 42 weeks of gestation and in active labor. Which of the following findings is the fetus at risk of developing?
A. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
B. Hyperglycemia
C. Meconium aspiration
D. Polyhydramnios
What is meconium aspiration?
Post-term neonates are at risk for meconium aspiration.
IUGR occurs earlier in pregnancy
Post-term at risk for hypoglycemia and oligohydramnios
A nurse is caring for a postpartum client who delivered her third infant 2 days ago. the nurse recognizes that which of the following findings are suggestive of PPD? Select all that apply
A. Fatigue
B. Insomnia
C. Euphoria
D. Flat affect
E. Delusions
What are A, B, and D
Fatigue, Insomnia, and Flat Affect are findings suggestive of PPD
A nurse is called to the birthing room to assist with the assessment of a newborn who was born at 32 weeks gestation. The newborn's birth weight is 1100grams. Which of the following are expected findings in this newborn? (Select all that apply)
A. Lanugo
B. Long nails
C. Weak grasp reflex
D. Translucent skin
E. Plump face
What are A, C, and D